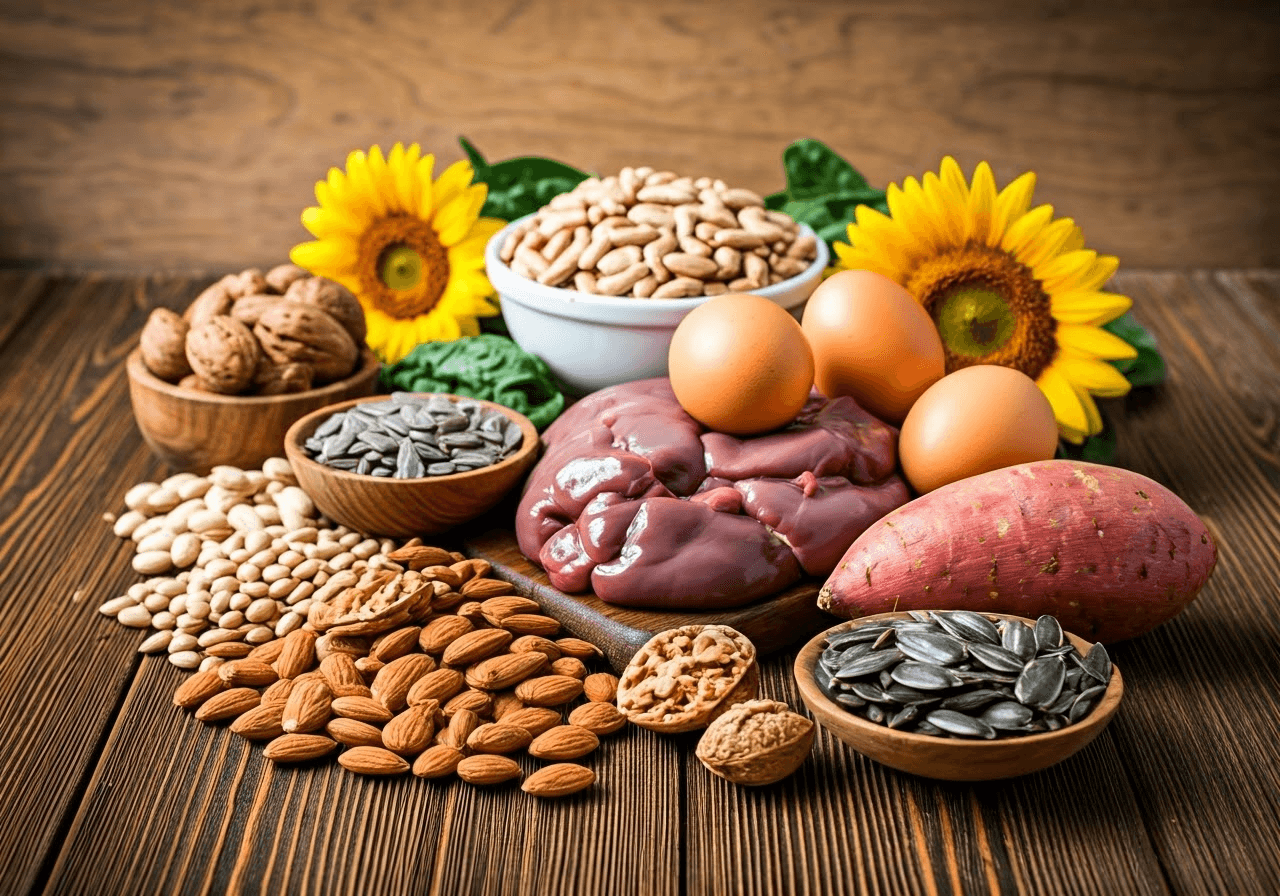

Introduction to Vitamin B7 (Biotin)
Vitamin B7, also known as biotin, is an important B vitamin. It helps with many body functions. Biotin is needed to keep hair, skin, and nails healthy, which is why many people take it as a dietary supplement. It also helps the body break down fats, carbohydrates, and amino acids, which is good for overall health. You need enough vitamin B7 to support your nervous system and keep your energy levels high. Its role in helping hair growth and keeping nails healthy makes it a key nutrient for beauty and wellness.
What Is Biotin and Why Is It Important?
Biotin is a key nutrient known as a B vitamin, specifically vitamin B7. This vital nutrient is important for many body functions and is necessary for staying healthy. One of its main roles is to work as a coenzyme. It helps our bodies turn food into energy that we can use.
Vitamin B7 also plays a big part in healthy cell growth and development. It keeps our hair, skin, and nails healthy. During pregnancy, it helps with the growth of a healthy fetus. If we do not get enough biotin, our bodies can struggle to use carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. This can lead to lower energy levels and affect how our cells work.
Biotin is important because it impacts many body processes. From turning food into energy to helping hair and nails grow, this nutrient is essential for our overall health.
Discovery and Historical Significance
The discovery of biotin started with research on a condition called “egg white injury” in animals. Scientists found that a protein in raw egg whites, called avidin, blocked the absorption of vitamin B7. This caused deficiency symptoms. This important finding led to more vitamin studies. It resulted in the isolation and identification of biotin as a separate vitamin in 1940.
At first, biotin was called “vitamin H.” The name “biotin” comes from the Greek word “bios,” which means “life.” This shows how important it is for many biological processes. Biotin’s discovery was a key moment in understanding how vitamins help maintain health.
Biotin is recognized as an important part of metabolism and growth, playing a crucial role in biotin metabolism. Because of this discovery, doctors could create treatments for biotin deficiency and research its potential to help with different health issues.
Biotin’s Role in the Human Body
Biotin is very important for our health. It works as a coenzyme in many metabolic processes. It helps enzymes break down macronutrients like carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into energy our body can use. When we don’t get enough vitamin B7, our metabolism can slow down. This may cause fatigue, weakness, and other health issues.
Biotin also helps in processing fatty acids and amino acids, which are important parts of proteins. It assists in using these components to produce energy and create hormones and other essential molecules. This support is key for growth, development, and keeping our bodies functioning well.
In addition, biotin plays a role in gene regulation and cell signaling pathways. It helps cells function, grow, and communicate properly. By being part of these processes, vitamin B7 is necessary for our overall health and well-being.
Health Benefits of Vitamin B7
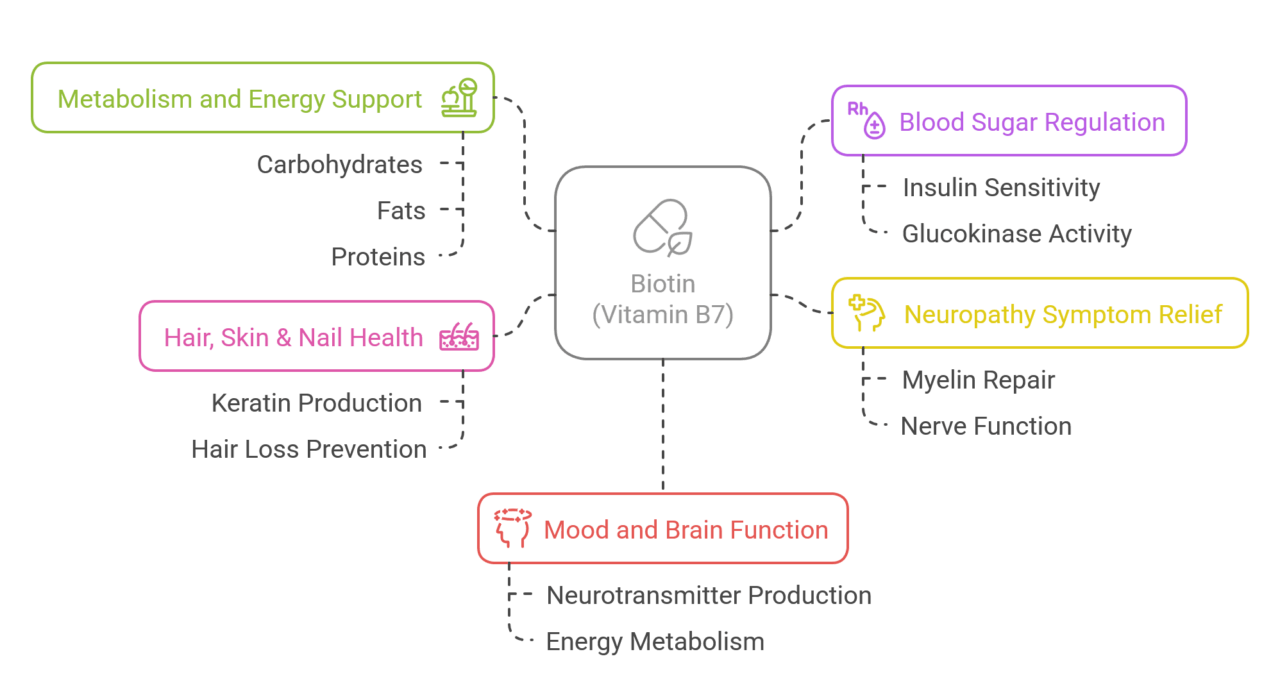
Biotin is important for our overall health because it helps many functions in our bodies. It aids in breaking down food to create energy. This process keeps us feeling energized and helps avoid tiredness. Biotin also helps keep blood sugar levels healthy by playing a part in glucose metabolism.
Furthermore, biotin is vital for the health of our hair, skin, and nails by helping with cell growth and repair. Studies show it may help reduce symptoms of neuropathy and support brain health. These benefits show why it is important to get enough biotin for our overall well-being.
Metabolism and Energy Support
Biotin is an important part of how our body makes energy. It helps our metabolism work well. Vitamin B7 acts like a helper, changing the food we eat into energy we can use. If we don’t get enough vitamin B7, we might feel tired and have low energy.
Biotin is crucial for metabolism because it activates special enzymes that break down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. These are part of the main energy sources for our body. Furthermore, biotin catabolism helps change these nutrients into glucose, which is what our body uses for energy.
By being part of these important processes, biotin helps give our body a steady supply of energy for everyday activities. Its role in making energy shows how important it is for our overall health and well-being.
Blood Sugar Regulation
Research shows that biotin might help control blood sugar by affecting how our body processes glucose. More studies are needed to be sure it works, but some evidence suggests that vitamin B7 could improve insulin sensitivity. This means our cells may use glucose better.
Biotin could help manage blood sugar by increasing the activity of glucokinase. This enzyme is important for glucose processing in the liver and pancreas. By helping this enzyme work well, biotin supports healthy glucose levels.
However, biotin is not a replacement for standard diabetes treatment. Its possible role in blood sugar control shows that it can be a helpful nutrient for good metabolic health. Still, people with diabetes should always check with their healthcare providers before changing their diet or adding supplements.
Neuropathy Symptom Relief
Neuropathy is when nerves get damaged, often causing pain, tingling, or numbness. Some people may find help with biotin therapy as an additional treatment. Studies show that vitamin B7 can help repair nerve damage and improve their function, which may reduce the symptoms of neuropathy.
Biotin is important for making myelin. Myelin is a protective layer around nerve fibers that helps signals travel properly. When myelin is damaged in neuropathy, it messes up these signals, leading to different problems with feeling and movement. Using vitamin B7 therapy might support the repair and growth of this myelin layer, which can lead to fewer symptoms.
Even though more studies are needed to confirm how well biotin therapy works for neuropathy in cases like progressive multiple sclerosis, early results show it might be helpful. It’s very important to talk to a healthcare professional for the right diagnosis and treatment.
Hair, Skin & Nail Health
Biotin is commonly known for helping with healthy hair, skin, and nails, and the use of biotin supplements is gaining attention. More studies are needed to prove its effects, but some research shows that vitamin B7 may help with hair loss, weak nails, and skin health.
When you lack biotin, it can lead to hair loss and brittle nails, which shows how important it is for their health. Biotin helps make keratin, a protein that gives strength to hair, skin, and nails.
Many people buy vitamin B7 supplements for beauty reasons. But eating enough biotin-rich foods or consulting a healthcare professional about the right supplements can be good for the health of your hair, skin, and nails.
Mood and Brain Function
New research hints that having enough biotin may improve our mood. More studies need to be done to confirm this link. However, some evidence shows that vitamin B7 can help support a good mood and brain health.
Biotin may help with mood by being involved in making neurotransmitters. These are important for regulating mood, like serotonin and dopamine. Having enough vitamin B7 might help these neurotransmitters work well, which could help keep our mood balanced.
Also, biotin is important for energy metabolism, which affects how our brain functions. Our brain needs a lot of energy, and biotin helps produce it efficiently. Keeping vitamin B7 levels healthy supports good brain functions like memory, focus, and attention.
How to Get More Vitamin B7 in Your Diet
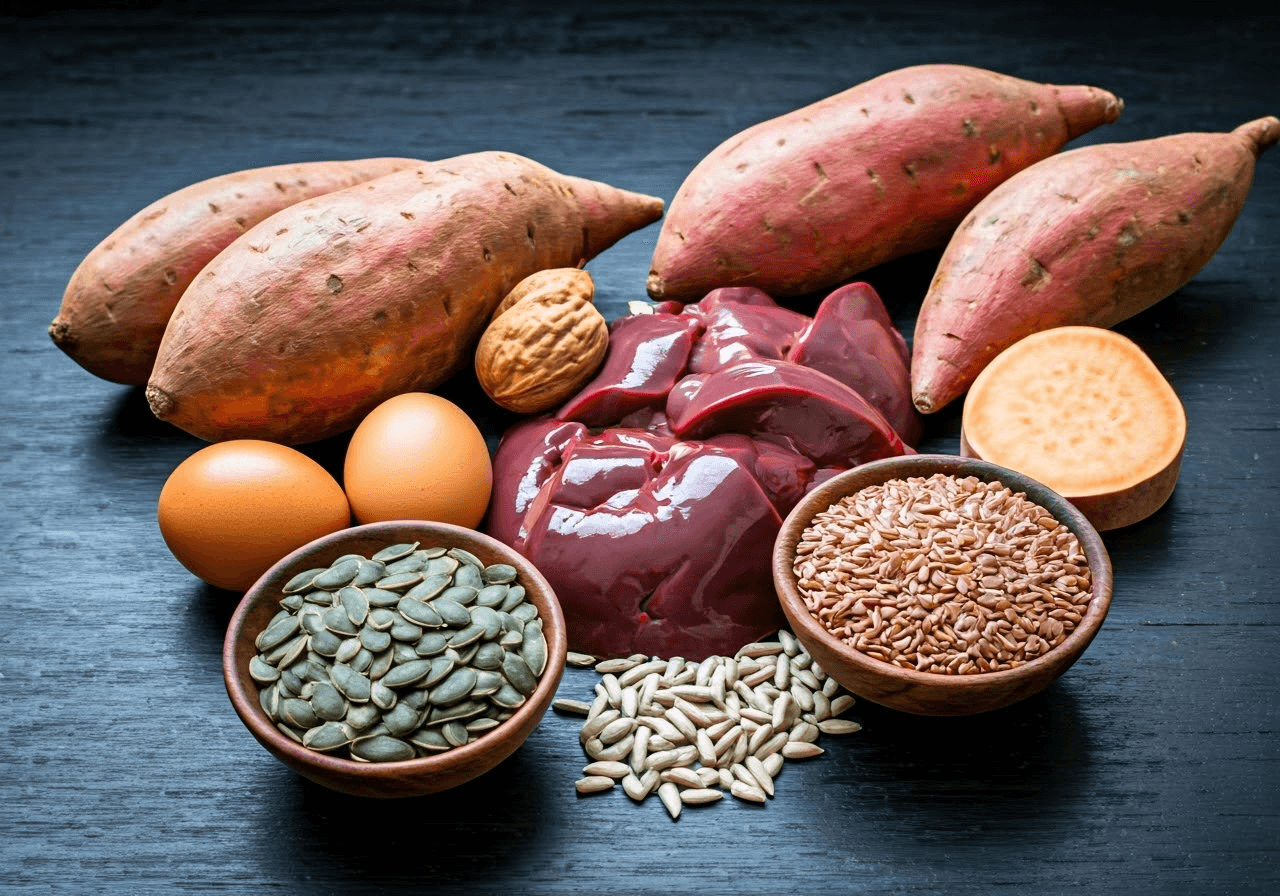

A good diet with biotin-rich foods can meet your daily vitamin B7 needs. Eating different foods with biotin, along with those that provide vitamin D, in your meals helps you get enough of this important nutrient, which supports your overall health.
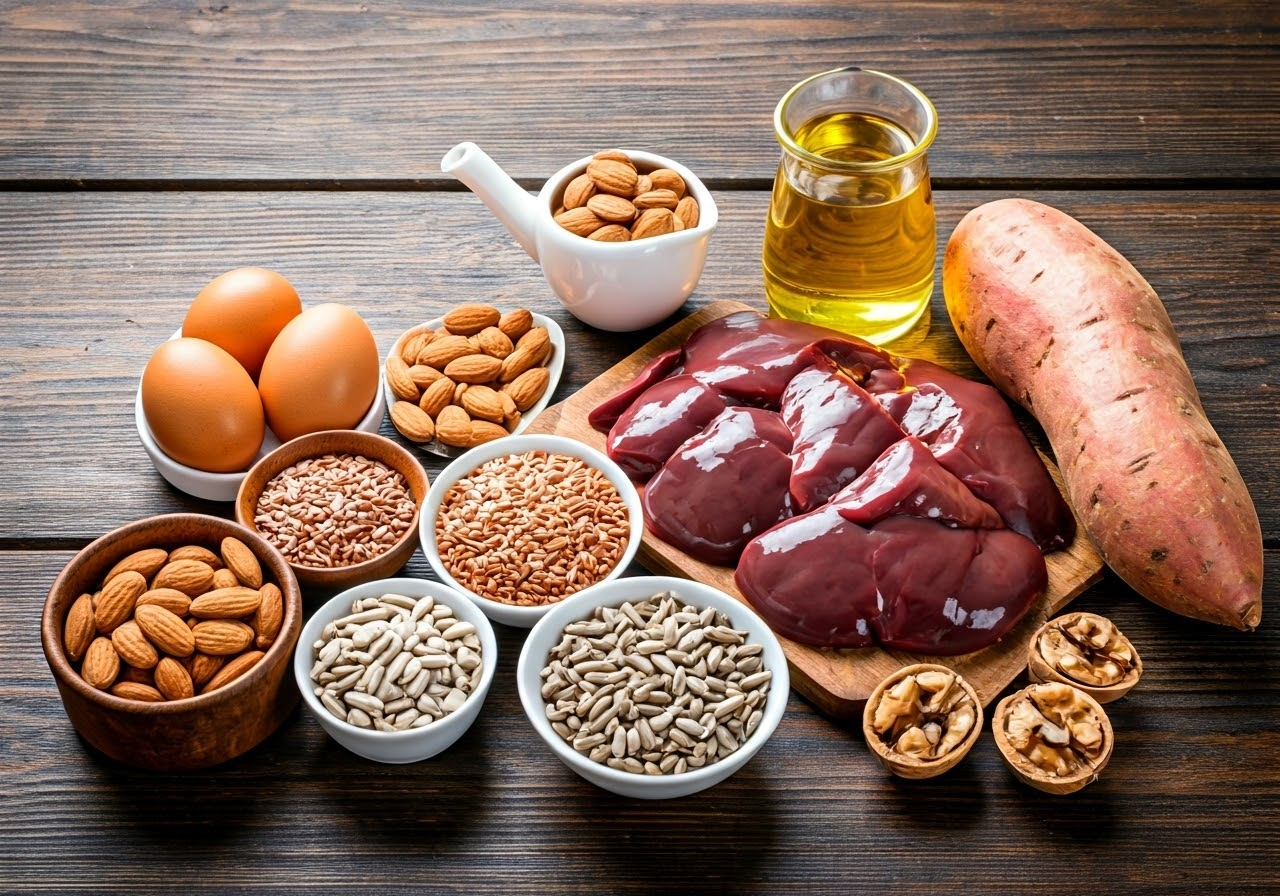
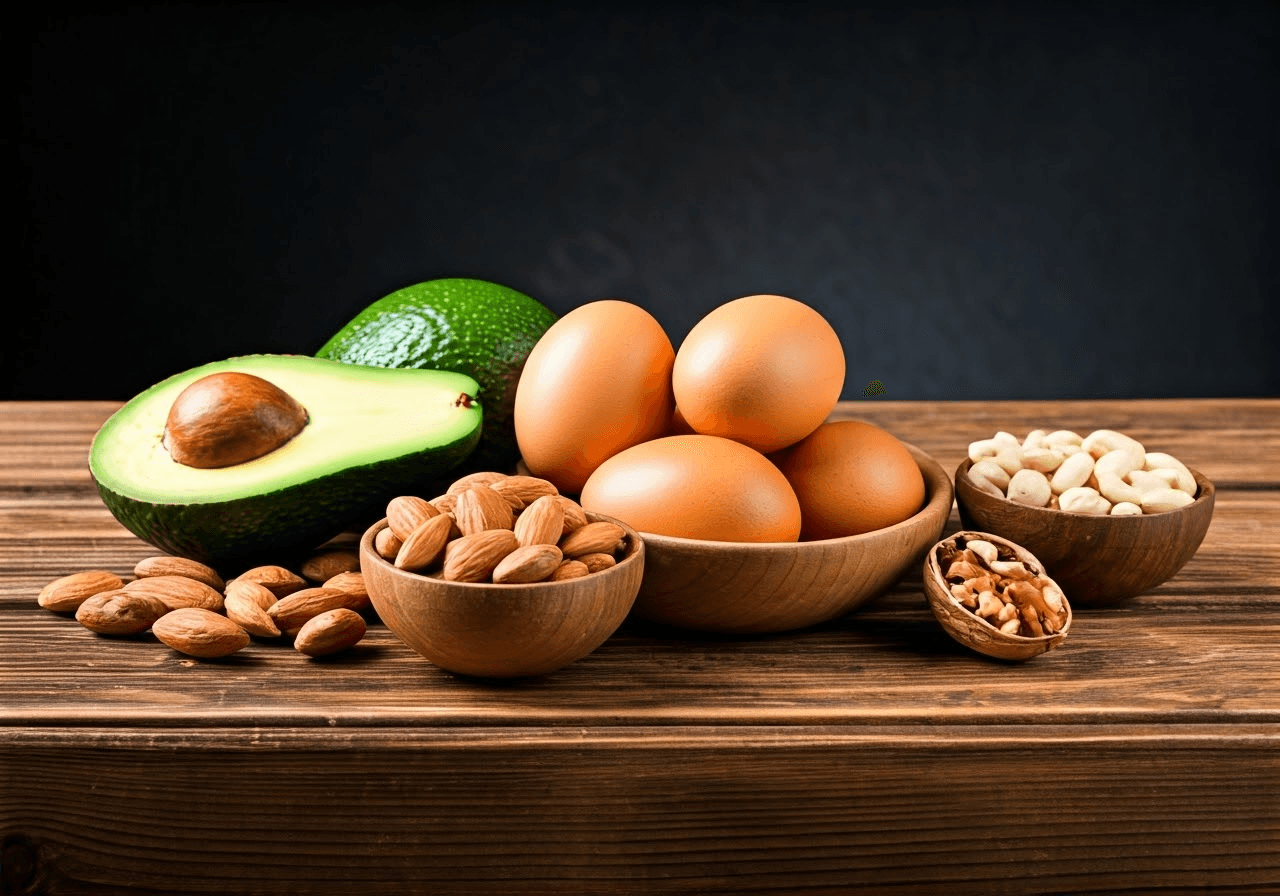
Adding foods like eggs, nuts, seeds, sweet potatoes, and whole grains to your diet can naturally increase your biotin intake. Liver, salmon, and avocado are also great sources of biotin and other essential nutrients.
Top Biotin-Rich Foods to Eat
Getting enough biotin is easy with a balanced diet that includes foods rich in this nutrient. Eating these foods regularly helps you take in the right amount of vitamin B7 to support your body’s metabolism and overall health.
Here are some excellent sources of vitamin B7:
- Eggs: Whole eggs, especially the yolks, are a great source of vitamin B7 and other necessary nutrients.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, sunflower seeds, and flaxseeds have a good amount of vitamin B7 along with healthy fats and fiber.
- Organ Meats: Liver is very high in biotin. Other organ meats like kidney and heart also contain this nutrient.
- Sweet Potatoes: These colorful root vegetables give you a good dose of vitamin B7, along with fiber and other vitamins and minerals.
By including a mix of these biotin-rich foods in your daily meals, you can easily achieve nutritional adequacy for vitamin B7 and promote your health and well-being.
Comparison Table: Biotin-Rich Foods
| Food | Biotin Content (µg per serving) | Other Nutrients | Ease of Use in Diet |
|---|---|---|---|
| Egg Yolks | 10–25 µg (per yolk) | Protein, Vitamin D, B12, Iron | Very easy — boiled, scrambled |
| Almonds | 1.5–2.5 µg (¼ cup) | Healthy fats, Vitamin E, Magnesium | Easy — snacks, smoothies |
| Sunflower Seeds | 2.5 µg (¼ cup) | Vitamin E, Selenium, Fiber | Easy — salads, trail mixes |
| Liver (Beef) | 30–35 µg (3 oz cooked) | Iron, Zinc, Vitamin A, Protein | Moderate — cooked or pâté style |
| Sweet Potatoes | 2.4 µg (½ cup cooked) | Fiber, Vitamin A, C, Potassium | Easy — roasted, mashed |
| Flaxseeds | 0.6 µg (1 tbsp) | Omega-3s, Fiber, Lignans | Easy — oatmeal, yogurt, baking |
| Walnuts | 1.3 µg (¼ cup) | Omega-3s, Antioxidants | Easy — snacking, baking |
| Kidney (Lamb/Beef) | ~3–5 µg (3 oz cooked) | Iron, Protein, B-vitamins | Moderate — stews, sautéed |
When and How to Use Vitamin B7 Supplements
Getting vitamin B7 from a healthy diet is usually enough for most people. However, some may need extra help from biotin supplements. It’s important to talk to Office of Dietary Supplements health professionals before starting any supplements. They can help figure out the right daily intake based on your personal needs and health history.
Biotin supplements are safe for most people if taken at the recommended amount. Still, taking too much can affect some lab tests, as highlighted in the FDA safety communication, so you should tell your doctor about any supplements you are using. Your doctor can guide you on any possible interactions or changes you need based on your health.
Biotin supplements can help people who have trouble absorbing biotin due to digestive issues or those with strict diets. Working with healthcare providers is key. They can make sure you use vitamin B7 supplements safely to meet your specific needs.
Popular Forms of Vitamin B7 Supplements (Capsules, Gummies, Powders)
Biotin supplements are available as capsules, gummies, and powders. These choices help meet different likes, making it easy for people to add biotin to their daily habits. Capsules are a simple way to take vitamin B7. Gummies are a fun option for those who want a tasty supplement. Powders can be mixed into various recipes, allowing users to include vitamin B7 in flexible ways.
Choosing a High-Quality Supplement
Choosing a good biotin supplement can be tough because there are many options out there. It’s important to look for high-quality products. This way, you can be sure that what you take is both safe and effective. Find supplements from trusted brands that follow good manufacturing practices (GMP) to ensure their quality.
You should also check for third-party certifications from organizations like USP or NSF. These certifications help show that the product is pure and strong. Remember, the FDA does not regulate supplements like it does with medicines, but they do provide advice and information on safety.
To focus on quality, make sure you research and pick brands that are open about their ingredients and how they make their products. Talking with your healthcare provider can help you get supplement recommendations that fit your needs. This way, you can make smart choices.
Natural vs. Synthetic Biotin: Pros and Cons
Choosing between natural and synthetic biotin can be confusing for many people. Natural vitamin B7 comes from food, while synthetic biotin is made in labs. Knowing the good and bad points of each option can help you decide what you prefer.
Supporters of natural biotin often argue that it has a more holistic approach. They believe that the body absorbs and uses it better because it comes with other helpful nutrients in whole foods. But, the amount of natural vitamin B7 in food can change a lot, making it hard to know exactly how much you’re getting.
On the other hand, synthetic biotin offers a set dose, so it is easier to track how much you consume. Both types work similarly because the body can absorb and use biotin no matter where it comes from.
Comparing Natural and Synthetic Biotin: Pros and Cons:
| Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Natural Biotin | – Sourced from real foods and whole-food-based supplements – May contain synergistic nutrients (e.g., enzymes, fiber) – Perceived as more “holistic” or “clean” by some users | – Biotin content may vary – May be less concentrated – Not always vegan-friendly |
| Synthetic Biotin | – Stable and consistent dosage – Widely available and affordable – Often vegan and allergen-free | – Lacks other nutrients present in food-based sources – Some users prefer more “natural” products |
Easy Recipes with Biotin-Rich Ingredients
Adding foods rich in biotin to your meals is not hard. Many healthy recipes use these nutritious ingredients, making vitamin B7 cooking both tasty and healthy.
Here are some simple recipe ideas to increase your biotin intake:
- Breakfast: Begin your day with scrambled eggs mixed with spinach and mushrooms. You can also try a biotin smoothie made with almond butter and berries.
- Lunch: Have a salad with grilled chicken or salmon. Top it with avocado and sunflower seeds for a biotin-rich dish.
- Dinner: Use sweet potatoes at dinner with roasted chicken and veggies or enjoy a lentil soup with some whole-grain bread.
- Snacks: Choose snacks like a handful of almonds, a hard-boiled egg, or a bit of Greek yogurt with berries for a healthy biotin boost.
By adding biotin-rich foods into your daily meals and snacks, you can easily get enough of this important nutrient for your overall health.
Tips to Maximize Vitamin B7 Absorption
Ensuring good absorption of biotin is very important to enjoy its health benefits. Biotin is easy to absorb, but some factors can affect how well your body uses it. Taking care of your digestive health is key. A healthy gut helps you absorb nutrients better.
Eating foods rich in probiotics, like yogurt, kefir, or sauerkraut, or taking a probiotic supplement can help your gut stay healthy and improve vitamin B7 absorption. On the other hand, some foods can slow down biotin absorption. For example, raw egg whites contain a protein called avidin that binds to biotin and blocks its absorption.
Cooking egg whites breaks down avidin, so this issue is no longer a concern. When taking vitamin B7 supplements, use the recommended doses and talk to your healthcare provider. They can help you find the best way to meet your needs.
Biotin Dosage and Needs by Life Stage
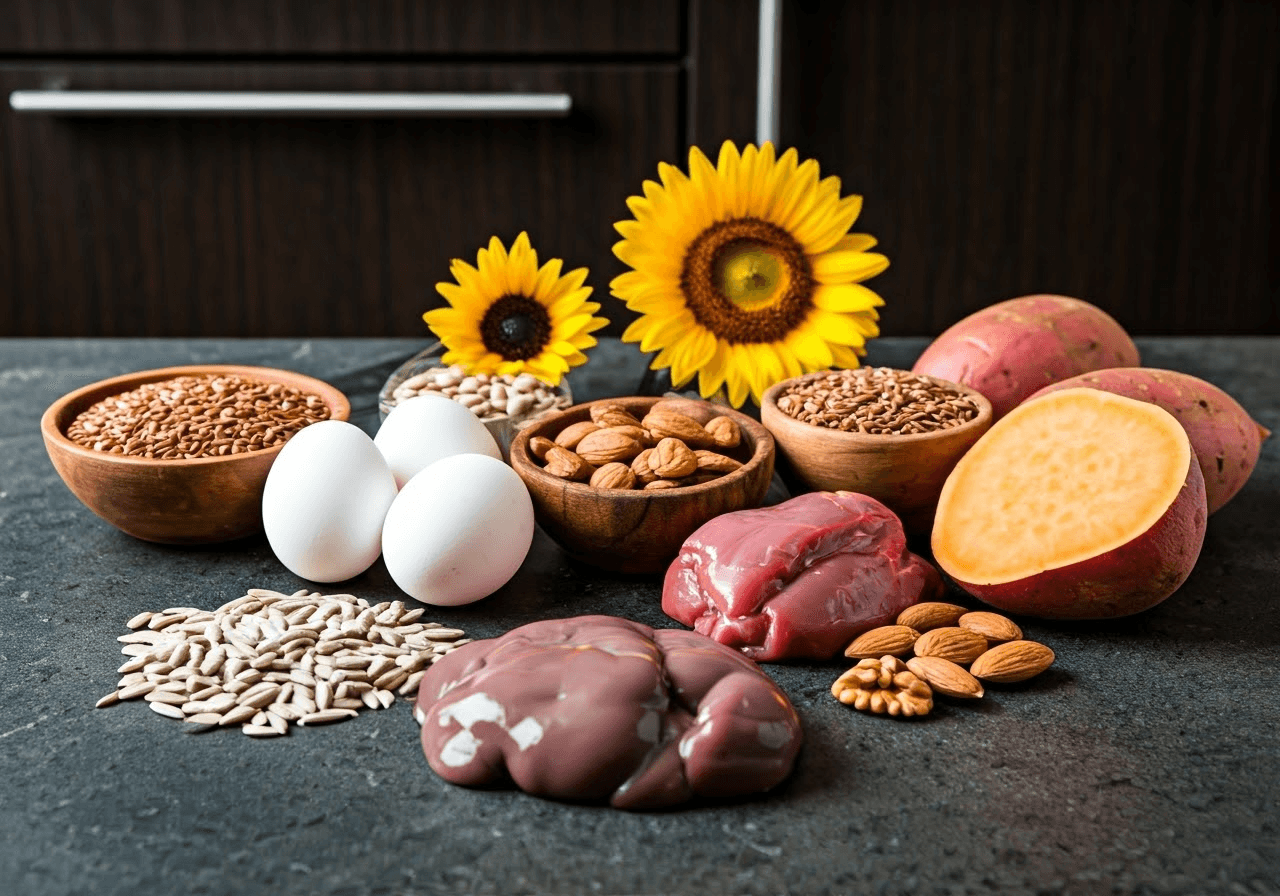

Biotin dosage depends on your age, life stage, and health. In general, adults need about 30 mcg each day. Pregnant and breastfeeding women may need a bit more. It’s a good idea to check with a healthcare provider to find out the right biotin dose for you.
Getting enough biotin is important for everyone. This nutrient helps with growth, development, and overall health. Sticking to the recommended doses and adding biotin-rich foods to your diet can help meet your body’s needs for good health.
How Much Biotin Do You Need Per Day?
Finding the right daily amount of biotin, according to the National Institutes of Health, depends on your age, life stage, and overall health. Health experts usually suggest an intake of about 30 mcg for adults. This amount helps your body work well.
However, if you are pregnant, breastfeeding, or have certain medical conditions, you may need to change your daily vitamin B7 amount. For example, pregnant women often require more biotin to help their baby develop properly.
It’s important to talk to your healthcare provider. They can help you figure out the best daily value of vitamin B7 for your specific needs. They will give you advice based on your health history and eating habits. This way, you can make sure you get enough biotin for your health.
Vitamin B7 Needs in Childhood and Adolescence
Growing bodies need enough nutrients, especially biotin, to help them grow quickly during childhood and adolescence. Getting enough biotin is important for energy, cell growth, and a healthy brain, all of which are very important during these years.
As children get older, their need for biotin increases. This change is linked to their growth and higher energy needs. A healthy diet that includes a lot of biotin-rich foods usually meets these needs. However, in some cases, like when someone has dietary restrictions or medical conditions that affect how they absorb nutrients, supplements might be needed.
Pediatricians and registered dietitians can help parents understand how to meet the nutritional needs of children and teenagers according to dietary reference intakes. They ensure that kids get enough biotin along with other important nutrients to help them grow and develop well.
Adult and Senior Vitamin B7 Requirements
Maintaining enough vitamin B7 is very important for adult health and for dealing with aging issues. The general recommendation for adults is about 30 mcg each day. However, needs may vary based on lifestyle, diet, and health.
As we get older, our metabolism slows down, and absorbing nutrients may not work as well. In these situations, changing our diet to include more foods rich in vitamin B7 or thinking about taking supplements with the help of a doctor can be helpful.
Adults and older people should focus on a well-balanced diet that includes biotin-rich foods along with other key nutrients. This can help maintain energy levels, brain health, and overall well-being. Regular check-ups with a doctor or dietitian can help find any possible deficiencies and make sure we get enough nutrients as we grow older.
Importance of Vitamin B7 for Fetal Development
Biotin is very important for prenatal health. It helps with cell growth, DNA copying, and breaking down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. These are all key steps during fetus growth and development. Getting enough vitamin B7 while pregnant supports healthy cell division. It also helps the developing baby get the nutrients it needs to grow well.
Maternal nutrition is very important for having the right vitamin B7 levels during pregnancy. Eating different biotin-rich foods like eggs, nuts, and whole grains helps meet the extra needs during this time. Sometimes, prenatal vitamins with biotin are suggested to boost dietary intake and ensure both mother and baby have enough.
Keeping good biotin levels during pregnancy is crucial for a healthy pregnancy. It supports the best growth and development of the fetus. Prenatal care providers stress the need for a balanced diet and proper supplements to help ensure adequate biotin intake for a healthy start to life.
Risks of Deficiency During Pregnancy
Biotin deficiency during pregnancy is not common, but it can still lead to health problems for about a third of pregnant women. It is important to take in enough vitamin B7 during this important time. This is vital for both mothers and babies since a lack of biotin can cause health complications.
For the growing baby, not having enough vitamin B7 can increase the chance of birth defects, especially those that affect the brain and nervous system. Low vitamin B7 levels might also lead to premature birth or low birth weight. For pregnant women, signs of deficiency can include hair loss, skin rashes, or problems with the nervous system.
To lower these risks, it is important to keep good biotin levels along with adequate folic acid. This can be done through a balanced diet and, if needed, supplements with help from healthcare professionals. Prenatal care focuses on the need for adequate biotin and folic acid intake to help with a healthy pregnancy and proper fetal development.
Safe Upper Limits for Vitamin B7 Intake
Biotin is mostly safe, but you should follow safety standards and guidelines for the best dosage. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) does not set a specific limit on how much vitamin B7 you can take. However, taking too much, especially from supplements, can cause health issues or affect some medical tests.
If you take more than the daily intake of biotin, especially from high-dose supplements, it might cause faulty results in lab tests. This includes tests for thyroid function or heart health. That is why it is important to tell your healthcare provider about any supplements you use.
Always stick to the recommended dosage on vitamin B7 supplement labels. It is a good idea to see your doctor or a registered dietitian to find out the right amount based on your health and needs. A balanced diet with biotin-rich foods, along with careful use of supplements when needed, helps you take vitamin B7 safely and effectively.
Special Needs During Illness or Recovery
Illness and recovery can put extra strain on the body. This might mean you need more of some nutrients, like biotin. During this time, getting enough vitamin B7 is very important. It helps support your body’s healing and improves your overall health.
Recovery nutrition is all about giving your body the key nutrients it needs. These nutrients help rebuild tissues, boost the immune system, and bring back your overall health. Biotin is important for cell growth, energy use, and how the nervous system works, making it a key nutrient during recovery.
Even though a balanced diet should provide biotin, those recovering from illness or surgery may need more of it. It’s good to talk with your healthcare provider or a registered dietitian to see if you should take vitamin B7 supplements. They can help you based on your needs and diet.
Biotin Deficiency: Symptoms, Risks, and Treatment

Biotin deficiency is rare but can cause several health problems. Symptoms can include hair loss, brittle nails, and even issues like depression and seizures. Some groups are more likely to have this deficiency. This includes pregnant women, people with digestive disorders, and those who take long-term medication.
To treat this, you usually need to eat more biotin-rich foods. In some cases, doctors may suggest vitamin B7 supplements to fix the deficiency and help with the symptoms. It’s important to see a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Early Signs of Biotin Deficiency
Early detection of biotin deficiency is very important to avoid serious health problems. Although biotin deficiency is not common, spotting the early signs can help to treat it quickly and stop it from getting worse.
Some early signs of biotin deficiency are hair thinning or hair loss, brittle nails that can break or split easily, and skin rashes, especially around the eyes, nose, and mouth. Other early symptoms may include feeling tired, depressed, or having numbness or tingling in your hands and feet.
If you notice any of these health signs, especially if you are in a high-risk group for vitamin B7 deficiency, talk to your doctor right away. They can check your symptoms, run tests, and suggest a good plan for you. This could include changing your diet or taking supplements to fix the deficiency and avoid more problems.
Who Is at Risk of Biotin Deficiency?
Biotin deficiency is not common for most people. However, some factors can make a person more likely to have it. Pregnant women need more vitamin B7 to support their baby’s growth. Also, people with digestive issues might not absorb nutrients well, increasing their risk.
Those with a rare genetic issue called biotinidase deficiency are also at risk for a profound deficiency. This problem makes it hard for the body to use vitamin B7 properly. Taking certain medicines, like anticonvulsants or antibiotics for a long time, can also block biotin absorption, which may lead to a deficiency.
Diet choices can matter too. Eating a lot of raw egg whites can raise the risk. This is because raw egg whites contain avidin, a protein that prevents biotin from being absorbed. It’s important to know your risk factors and talk to a doctor to get help when needed.
What Causes Biotin Deficiency?
Biotin deficiency is rare, in the United States, but it can happen due to several reasons, leading to not getting enough nutrients or problems with absorption. One main cause is not eating enough foods rich in biotin, especially for people with strict diets that lack variety.
Certain medical conditions, like Crohn’s disease or celiac disease, can greatly reduce the absorption of vitamin B7, raising the risk of being deficient. There are also genetic issues, such as biotinidase deficiency, which affect how the body uses and processes biotin.
Lifestyle habits, like drinking too much alcohol and using specific medicines, like anticonvulsants or antibiotics, can interfere with vitamin B7 absorption and use. To fix and prevent vitamin B7 deficiency, it’s important to tackle these causes. This can be done by changing diets, taking the right supplements, and treating any medical conditions.
How It’s Diagnosed and Treated
Diagnosing biotin deficiency usually involves checking a person’s medical history, doing a physical exam, and running lab tests. Doctors will ask about diet, symptoms, and any other medical conditions. Blood tests can measure biotin levels to find out if someone has a deficiency.
To treat biotin deficiency, the focus is on fixing the cause and raising vitamin B7 levels. If someone eats less biotin, doctors often suggest adding more biotin-rich foods like eggs, nuts, seeds, and whole grains to their meals. For those who can’t absorb vitamin B7 or need more than usual, biotin supplements may be given to make sure they get enough.
Getting medical help is very important for an accurate diagnosis and a treatment plan made just for you. Doctors and dietitians can offer special advice on diet changes or supplements based on individual needs. This supports better biotin levels, which is key for overall health and well-being.
Vitamin B7 Absorption, Side Effects, and Interactions
Biotin mainly gets absorbed in the small intestine, and this process usually works very well. However, some things can affect how well it is absorbed. For example, gut health problems or eating raw egg whites, which have avidin, can cause issues. Biotin doesn’t usually cause many side effects, but taking high doses from supplements may affect certain lab tests. This can lead to misdiagnosis.
It is very important to tell your healthcare provider about all the supplements you take. This important information helps avoid bad interactions with medications. Always stick to the suggested dosages and talk to your doctor if you have any worries. Being open about this will help you use vitamin B7 safely and effectively, allowing you to enjoy its benefits while reducing any risks.
How Vitamin B7 Is Absorbed in the Body
The absorption of biotin starts in the small intestine. Here, this water-soluble vitamin is quickly absorbed into the bloodstream. After it’s taken in, vitamin B7 moves through the portal vein to the liver, where the urinary excretion of biotin and other metabolites occurs. The liver plays a key role in processing and distributing nutrients.
Once in the liver, biotin goes to different tissues in the body. It performs important tasks in metabolism, cell growth, and other essential functions. The body absorbs vitamin B7 well. This means it can use both food sources and supplements easily.
However, some health problems in the gut, like inflammation or malabsorption issues, can slow down vitamin B7 absorption. It is important to fix these gut health issues to improve vitamin B7 uptake. This ensures that the body uses it effectively.
What Affects Vitamin B7 Absorption
Several things can affect how well the body absorbs vitamin B7. These include what we eat and health issues we might have. Knowing about these factors is important for making sure we get enough vitamin B7 in our bodies.
One food that can block vitamin B7 absorption is avidin. Avidin is a protein found in raw egg whites. It sticks to vitamin B7 and stops it from being absorbed in our intestines. Cooking eggs makes avidin inactive, which lets the body absorb vitamin B7. Drinking a lot of alcohol can also make it hard for the body to take in biotin, which may cause a deficiency.
Some medicines, like anti-seizure drugs and certain antibiotics, can affect how well vitamin B7 is absorbed, too. Also, digestive problems that harm the gut lining, such as Crohn’s disease or celiac disease, can greatly reduce nutrient absorption, including biotin.
Biotin Blood Tests: Are They Accurate?
While lab tests can check the levels of biotin in your blood, there are some concerns about how vitamin B7 might affect certain tests. High doses of biotin, especially from supplements, may change the results of tests that use biotin-streptavidin binding technology.
This interference can cause false high or low results for hormones and other substances. This can possibly lead to misdiagnosis or wrong treatment. For example, vitamin B7 can change the results of thyroid function tests, which might give an incorrect picture of your health.
It is very important to tell your doctor about any vitamin B7 supplements you take before having blood tests. They can recommend stopping the supplements for a while or help interpret your test results with the possibility of biotin interference in mind. Good communication between patients and doctors helps make sure diagnoses are accurate and treatment is right.
Side Effects and Safety Warnings
Biotin is mostly safe and people generally tolerate it well, even in high doses. Side effects from vitamin B7 supplementation are uncommon. Still, it’s important to know about possible safety issues and adverse effects, even if they don’t happen often.
Some people may feel mild digestive issues. This can include nausea, stomach cramps, or diarrhea, especially when taking high doses of biotin supplements. These side effects usually go away on their own or can improve with lower doses.
A bigger concern is that taking high doses of biotin can affect certain lab tests. This may lead to incorrect results for thyroid function, heart health markers, and hormone levels. It’s important to tell healthcare providers if you are using biotin supplementation. This helps them understand the test results correctly and avoid misdiagnosis.
Drug Interactions to Be Aware Of
Biotin is usually safe, but it can interact with some medications. This means it’s important to be careful and talk to your doctor. These interactions can change how well medicines work or increase the chance of side effects.
For example, vitamin B7 may reduce the effectiveness of some medications used for epilepsy. Patients may need to change their dosage to keep their seizures under control. Also, biotin supplements could affect lab tests that use biotin-streptavidin binding. This may lead to incorrect diagnoses.
Always tell your doctor if you are taking vitamin B7 supplements. They can check for interactions with your medicine, adjust doses if needed, and watch for any side effects. Good communication and being proactive can help reduce health risks from possible medication interactions.
Biotin and Athletic Performance

Biotin is not directly connected to better athletic performance, but it is important for energy metabolism. This is very important for athletes who engage in tough activities. Biotin helps turn food into energy that the muscles need during training and competitions.
Even though studies on its effects on endurance and muscle recovery are unclear, it is important to keep vitamin B7 levels healthy through a balanced diet. This helps improve overall health and supports the body’s metabolism, which is key for reaching the best athletic performance.
Does Biotin Help with Endurance?
The possible benefits of biotin for improving endurance in athletes have sparked interest, but clear evidence is still lacking. Biotin plays an important role in energy production. This raises the question of whether taking more vitamin B7 could enhance stamina and performance in endurance events.
Biotin works as a coenzyme. It helps break down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into energy that muscles need during long physical activities. However, research on whether vitamin B7 supplementation directly boosts endurance has mixed findings.
Getting enough vitamin B7 is important for good energy production, but taking too much may not lead to better endurance. Athletes should aim to get enough vitamin B7 from a balanced diet. They should also talk with sports nutritionists or healthcare providers to see if biotin supplementation is right for them.
Biotin’s Role in Muscle Recovery
Biotin is not usually seen as a top nutrient for fixing and building muscles. However, it plays a role in making proteins and helps with energy use, which can aid recovery after hard exercise. To support muscle recovery, it’s important to provide the body with enough materials and energy for these processes.
After a workout, nutrition should focus on restoring glycogen stores, fixing damaged muscle, and lowering inflammation. Protein often gets the most attention in recovery meals. But getting enough vitamin B7 helps the body use amino acids, which are the basic parts of protein.
Good biotin levels help the body fix and rebuild muscle fibers that get stressed during workouts. Even though more research is needed to grasp its exact role in muscle recovery, biotin is important for overall metabolic health. This health is necessary for improving recovery and adapting to exercise.
Use of Biotin in Sports Supplements
Biotin is found in many sports supplements. People often add it for its general health benefits, not just for improving performance. Biotin helps convert food into energy. This makes it important for athletes.
It’s important to be careful when using supplements. Taking too much of any nutrient can have bad effects. Athletes should try to get key nutrients, like vitamin B7, from a balanced diet that fits their training needs.
Sports nutritionists are helpful. They can check an athlete’s diet and see if they need vitamin B7 or other supplements. A complete plan for athlete health includes good nutrition, enough rest, hydration, and wise supplement use when needed.
Biotin and Its Relationship with Other Nutrients
Biotin interacts with many nutrients in the body, including its notable effect of biotin in how these nutrients are absorbed, used, and how well they work. Biotin especially works well with other B vitamins, like B6, B12, and folate. These vitamins are important for producing energy, cell growth, and forming red blood cells.
Keeping a good balance of these nutrients is important for health in healthy individuals. Some foods, like raw egg white protein called avidin, can reduce how well vitamin B7 is absorbed. Knowing about these interactions shows why a balanced diet and careful use of supplements are important for feeling good.
Nutrients That Enhance Biotin Function
Biotin needs other helpful nutrients to work well in the body. These biotin co-factors team up, improving how each one is absorbed, used, or helps with metabolism.
| Nutrient | How It Supports Biotin | Food Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Magnesium | Acts as a cofactor in enzymes that work with biotin | Leafy greens, nuts, whole grains |
| Zinc | Supports biotin-dependent enzyme activity | Pumpkin seeds, lentils, beef |
| Vitamin B6 | Helps in amino acid metabolism, complements biotin’s function | Bananas, chickpeas, potatoes |
| Vitamin B12 | Works with biotin in nerve health and red blood cell formation | Fish, dairy, fortified cereals |
| Folate (B9) | Supports DNA synthesis; complements biotin in cell growth | Leafy greens, beans, citrus fruits |
| Chromium | May improve biotin’s role in blood sugar regulation | Broccoli, whole grains, grape juice |
What Can Inhibit Biotin Absorption?
Some things can reduce how well our bodies take in biotin. Raw egg whites, using antibiotics for a long time, and drinking too much alcohol can all affect vitamin B7 absorption. These can stop our bodies from using biotin properly. This may result in not having enough biotin. It is important to know about these blockers to get the most benefits from vitamin B7.
| Inhibitor | How It Affects Biotin | Details / Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Avidin (Raw Egg Whites) | Binds to biotin and prevents absorption in the intestines | Cooking eggs destroys avidin |
| Alcohol | Interferes with absorption and storage of biotin in the liver | Heavy, chronic use increases deficiency risk |
| Certain Antibiotics | Disrupt gut bacteria that naturally produce biotin | Especially with long-term use |
| Anticonvulsant Medications | Increase biotin breakdown or reduce absorption | E.g., carbamazepine, phenytoin |
| Smoking | May accelerate biotin degradation in the body | Linked to faster B-vitamin depletion |
| Digestive Disorders | Conditions like Crohn’s or leaky gut may impair absorption | Inflammation affects nutrient uptake |
Debunking Biotin Myths
Biotin is often thought to be a quick fix for hair growth, but this isn’t true. While vitamin B7 is important for keeping hair healthy, it cannot alone bring your hair back. Taking too much vitamin B7 won’t give you fast results for better hair health. Many people believe that biotin can help hair grow very quickly. It is important to know that biotin is mainly useful for fixing specific deficiencies, not for promoting fast or large amounts of hair growth.
Truth About Hair Growth Claims
Biotin, known as Vitamin B7, is often said to help with hair growth. However, the reality is more complicated. If someone lacks vitamin B7, they may experience hair loss. In these cases, adding biotin may help. But for people who already have enough vitamin B7, taking extra may not lead to big improvements in hair growth. Research that shows vitamin B7 directly boosts hair growth is not strong, and there’s a lack of evidence suggesting how it affects healthy people with enough biotin. It is important to talk to health professionals before hoping for big changes in hair growth from biotin supplementation.
Misconceptions About Supplementing Biotin
Many people mistakenly believe that biotin can fix hair and nail health problems instantly. While vitamin B7 is important for our hair and nails, its effects can be different for everyone. Another common mistake is thinking that taking high doses will give faster results. However, it’s better to follow the recommended daily intake to avoid adverse effects and keep vitamin B7 levels balanced.
Conclusion
Vitamin B7, or biotin, is important for your overall health. It helps with your hair, nails, and skin. Many people think vitamin B7 can boost hair growth, but it isn’t the only answer. Biotin deficiency isn’t common, but some people may benefit from supplements. It’s better to get vitamin B7 from a balanced diet instead of only taking supplements. Always talk to a healthcare provider before starting any new dietary supplement. They can help you understand what is right for your needs.
The content on WellwayHub.com is intended for general informational purposes only and should not be taken as medical advice. Please consult your doctor or a qualified health professional before making any changes to your health routine.
Some links on WellwayHub.com may be affiliate links. This means we may earn a small commission if you make a purchase through these links, at no extra cost to you. This helps support our mission to provide trusted wellness content.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, vitamin B7 and biotin are the same thing. You can use these terms interchangeably. This vitamin is water-soluble. It is important for metabolism as well as for the health of your skin, hair, and nails.
Taking too much biotin is uncommon, but it can cause some side effects. These may include skin rashes and stomach problems. For adults, the safe limit for biotin at high intakes is 9,000 mcg each day. It is important to talk to a healthcare provider before using high doses of biotin supplements.
Biotin usually needs a few weeks to work. However, how quickly it works can be different for each person. You might see hair growth results after using it for 2-3 months. Improvements in nail health and skin fit may take a little longer.
Biotin supplements can affect lab test results. This includes tests for thyroid function and troponin levels. It is important to tell your healthcare provider if you are taking biotin. This way, they can avoid making mistakes with your test results. Knowing how biotin interacts with tests can help with getting the right diagnoses and treatments.
Biotin is safe for vegans because it is found naturally in plant-based foods. If vegans have a deficiency, they can benefit from taking biotin supplements. It is important to make sure the supplements are vegan-friendly to support overall health.
Biotin deficiency is found through blood tests that check biotin levels. Symptoms such as hair loss, skin rash, and brittle nails can lead to testing. Sometimes, people may be misdiagnosed because these symptoms can look like other problems. That’s why it is important to talk with a healthcare provider for the correct diagnosis.
If you do not get enough biotin, it might lead to hair loss, brittle nails, and skin rash. Biotin deficiency is uncommon, but it can happen to people with specific health problems or bad eating habits.