
Resveratrol is a powerful natural antioxidant found in foods like grapes, red wine, and berries. Known for its potential to support heart health, fight aging, and protect the body from oxidative stress, resveratrol has become one of the most popular wellness supplements worldwide. In this comprehensive guide, discover what resveratrol is, its key health benefits, best food sources, supplement options, dosage tips, side effects, and how to use it safely for maximum results.
How Resveratrol Works: Antioxidant Mechanisms & Health Effects
Resveratrol has caught the eye of many scientists and health fans. It is known as a strong antioxidant that may offer various health benefits. But what makes it stand out?
Resveratrol works mainly as an antioxidant. It helps fight against the harmful effects of oxidative stress and cellular DNA damage in our bodies caused by reactive oxygen species (ROS). Oxidative stress occurs when there is an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants. This imbalance can lead to aging and many diseases. Resveratrol fights back by neutralizing free radicals, which are unstable molecules that harm cells and can lead to chronic health issues.
How Antioxidants Like Resveratrol Protect Your Health
To understand how important resveratrol is, we need to know what antioxidants do for our health.
Imagine this: our cells face attacks from free radicals. These are harmful molecules that come from normal body activities and things like pollution and UV rays. They can harm our cells by damaging DNA, proteins, and fats, which speeds up aging and leads to many health problems.
This is where antioxidants step in to help. They protect our cells by neutralizing these damaging free radicals, which helps to prevent or slow down cell damage. Resveratrol is a strong antioxidant that fights against oxidative stress, helping to keep our cells safe from harm.
Why Resveratrol Stands Out: Unique Mechanisms & Health Advantages
Many antioxidants are available, but resveratrol is special due to its unique features and possible health benefits. What makes it different?
In addition to being a strong antioxidant, resveratrol shows interesting interactions with different processes in the body. It has a special attraction to the estrogen receptor, which is a protein that helps control things like cell growth, inflammation, and metabolism. This relationship is important, especially for health issues related to estrogen levels.
Resveratrol also impacts how genes work. It can turn specific genes on or off that are important for things like inflammation, cell survival, and energy use. This ability helps explain the many ways resveratrol can be good for health.
Resveratrol Benefits for Heart, Brain, Skin & Longevity
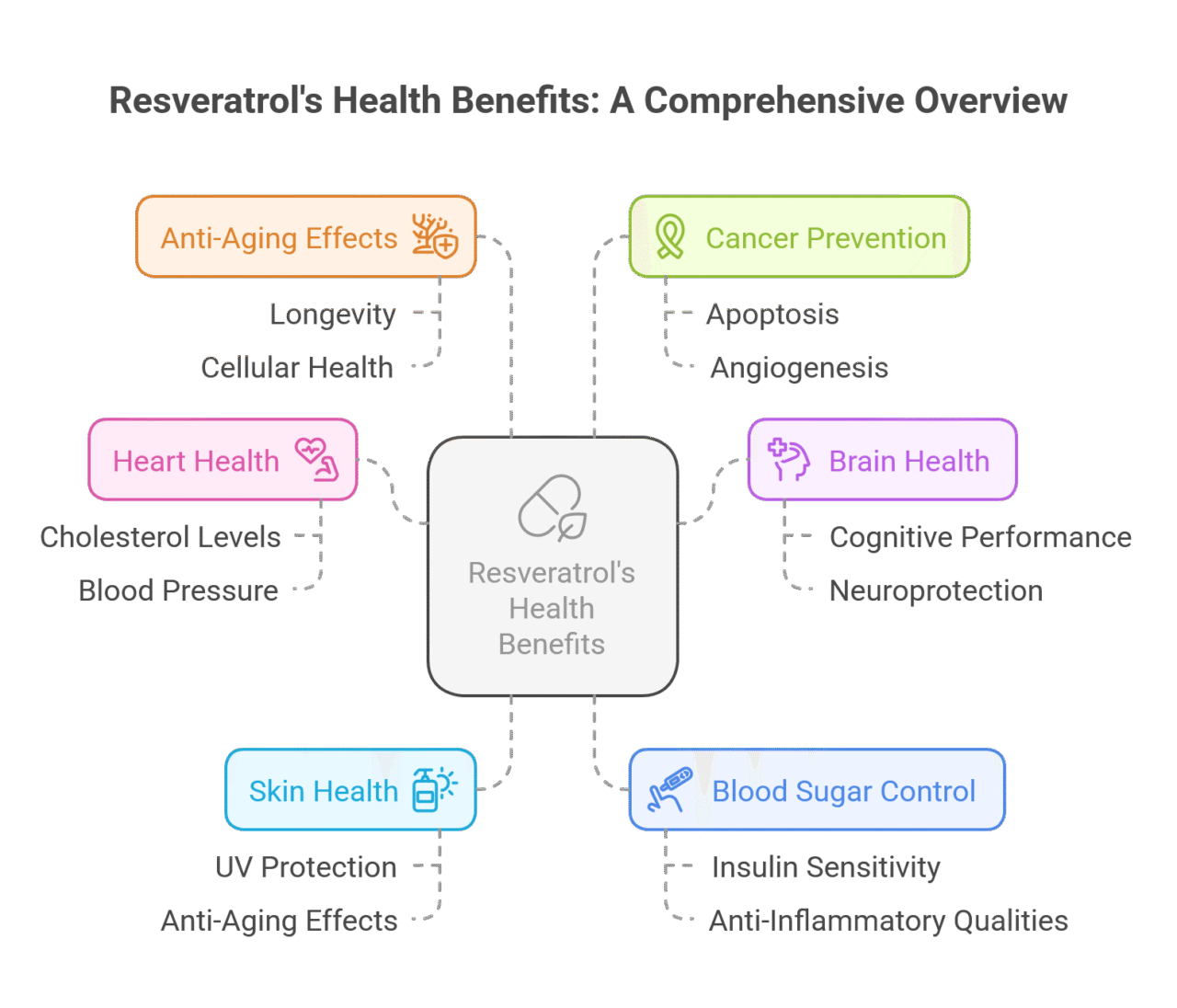
Extensive research done mainly in labs and with animals, along with results from clinical studies, shows many possible health benefits of resveratrol. This makes it a strong candidate for improving overall well-being. So, what are these benefits?
Promising results suggest that resveratrol may help heart health and potentially extend the life span. It could reduce the risk of heart disease by lowering blood pressure and improving cholesterol levels. Additionally, the consumption of wine might also support brain health, potentially protecting against cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases. Studies even suggest that it could improve insulin sensitivity. , as discussed in the Br J Nutr. This is important for managing blood sugar and may help lower the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Antioxidant Effects: How Resveratrol Fights Oxidative Stress
Resveratrol has amazing health benefits because it is a powerful antioxidant. This means it helps fight off various diseases and keeps us healthy.
Oxidative stress happens when there are too many free radicals and not enough antioxidants. This stress can lead to chronic diseases. Resveratrol helps to reduce oxidative stress by neutralizing harmful free radicals. This helps protect our cells and tissues from damage.
Studies show that resveratrol can benefit many organs, like the heart, brain, and liver. For example, research suggests that resveratrol may help protect the liver from damage caused by toxins. This could lower the risk of liver disease.
Resveratrol for Heart Health: Cholesterol, Blood Pressure & Inflammation
Resveratrol seems to be a helpful friend for keeping the heart healthy. Research shows it might help prevent and manage heart disease.
Many studies suggest that resveratrol can support heart health. It does this by improving how blood vessels work and reducing inflammation. It encourages the making of nitric oxide. This is a molecule that helps relax blood vessels. As a result, blood flow improves, which may lower the chances of coronary artery disease.
In addition, resveratrol may assist with cholesterol levels. It helps reduce the oxidation of LDL cholesterol, known as “bad” cholesterol. This oxidation process can lead to plaque build-up in arteries, which is a significant risk factor for heart disease.
Resveratrol and Brain Health: Cognitive Benefits & Neuroprotection
Resveratrol is known for more than just helping the heart. Studies show it could also help keep your brain healthy. This might lead to better thinking skills and protect against problems that come with getting older.
Research indicates that resveratrol has good effects on cerebral blood flow to the brain, which can enhance cognitive performance and improve how well we think and remember. It may also help defend brain cells against oxidative stress, which is something that can lead to brain diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
Even though studies in people are still new, good results from animal studies hint that resveratrol could slow down brain decline. It may also lower the chance of getting these serious brain issues.
Resveratrol for Blood Sugar Control & Insulin Sensitivity
Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is very important for your health. Resveratrol may help with glucose control, especially for people who are at risk for or have type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Studies show that resveratrol could make the body more sensitive to insulin in diabetic patients. Insulin is the hormone that keeps blood sugar in check. When resveratrol boosts insulin sensitivity, it helps cells use glucose better. This can lead to lower blood sugar levels and better glycemic control.
On top of that, resveratrol has anti-inflammatory qualities. These qualities might also help with blood sugar regulation because long-term inflammation can lead to insulin resistance and diabetes.
Resveratrol Benefits for Skin: UV Protection & Anti-Aging Effects
Resveratrol does more than help inside the body; it also benefits our skin, which is the largest organ we have. This powerful antioxidant has gained a lot of interest in skincare because it helps fight the harmful effects of UV rays.
When our skin is exposed to the sun, it creates free radicals. These lead to oxidative stress, which can cause early aging, wrinkles, and age spots. Resveratrol, as a strong antioxidant, helps neutralize these free radicals and protects skin cells from the damage done by UV rays.
There’s a need for more research, but early studies show that using skincare products with resveratrol may help improve skin elasticity, lessen wrinkles, and defend against sun damage.
Anti-Aging Effects: Resveratrol for Longevity and Cellular Health
The search for a longer life has excited people for many years. Resveratrol is becoming a possible important factor in this search. It can help fight oxidative stress, lower inflammation, and change gene expression. This has made many people interested in its anti-aging effects.
Studies on different living things, from yeast to mice, show that resveratrol might help extend their lifespan. The ways it works are complex, but they include activating certain genes linked to living longer and cell repair.
It’s important to remember that these results are still early, and how they apply to humans is still being studied. Still, people remain curious about resveratrol’s role in promoting healthy aging and a longer life.
Resveratrol and Cancer Prevention: Current Evidence & Studies
The possible effects of resveratrol in preventing cancer have gained a lot of attention from scientists. Studies on cells and animals indicate that the properties of resveratrol might stop the growth and spread of different types of cancer cells, such as breast cancer, colon cancer, and prostate cancer.
Researchers believe that resveratrol’s ability to cause apoptosis, or programmed cell death, helps keep cancer cells from growing out of control. It also might help block angiogenesis, which is when new blood vessels form to feed tumors, basically cutting off their food supply.
Although there are not many human studies yet, these early findings show that resveratrol could be a good option for cancer prevention. More research is needed, though, to confirm how well it works and if it is safe for people.
Top Natural Sources of Resveratrol: Grapes, Wine, Berries & More

Adding resveratrol to your diet can be an easy way to improve your health and enjoy its benefits. Luckily, there are many tasty and common foods that are great sources of this strong compound.
Grapes, especially red grapes, have a lot of resveratrol. The highest amounts are found in the skins and seeds. Red wine, which comes from fermented grapes, also has a good amount of resveratrol. This is especially true for red wines made with thicker-skinned grapes.
Grapes as a Natural Source of Resveratrol
When you are looking for natural sources of resveratrol, think of the grape (Vitis vinifera). This simple fruit can be eaten fresh, dried as raisins, or turned into juice and wine. It is full of resveratrol, especially in its skin and seeds.
Red grapes usually have more resveratrol than green grapes because of their dark skin. Muscadine grapes, which come from the southeastern United States, are known for having even more resveratrol.
Eating grapes, whether fresh as a snack or added to salads and desserts, is a tasty and healthy way to get more resveratrol. Drinking unsweetened grape juice, especially if it is made from Concord grapes, can also give you a strong amount of this healthy substance.
Red Wine: Resveratrol Content & Health Impact
The link between red wine and good health, especially heart health, has been talked about a lot. Many people believe that drinking red wine in moderation can be good for you. However, it’s important to keep a balanced view on this topic.
The possible health benefits of red wine are often related to a compound called resveratrol. This compound comes from the skins of grapes and gets into the wine during the fermentation process. It can add to the wine’s taste and may have some health benefits.
Still, it’s very important to focus on moderation. Drinking too much wine, or any type of alcohol, can be harmful to your health. Enjoying a glass of red wine now and then can be part of a healthy lifestyle. However, it should not be seen as the main source of resveratrol or a substitute for other healthy habits.
Japanese Knotweed: Potent Source of Supplement-Grade Resveratrol
Japanese knotweed, also known as Polygonum cuspidatum, might not be a usual cooking ingredient, but it should be known for having a lot of resveratrol. This plant grows quickly and is often seen as an invasive species, but its high resveratrol content is making it popular.
Extracts from Japanese knotweed are often used to make resveratrol supplements. These supplements provide a strong dose of resveratrol. You can find them in different forms like capsules, tablets, and powders.
It’s important to be careful with resveratrol supplementation. Always talk to a healthcare professional about the right dosage and possible interactions with your medications.
Berries High in Resveratrol: Blueberries, Raspberries & More
Berries are well-known for being packed with antioxidants and their tasty flavors. They are also high in resveratrol, which adds to their many health benefits. By including these small but powerful fruits in your diet, you can enjoy great flavor and benefit from this strong compound.
Blueberries, raspberries, and mulberries are some of the best berries for resveratrol. These tasty fruits offer resveratrol along with a lot of other antioxidants, vitamins, and fiber. This is why they are seen as nutritional powerhouses.
Eating berries regularly can lead to many health benefits. This includes lower cardiovascular risk factors, better blood sugar control, and improved cognitive function. This makes them a great addition to any healthy diet.
Nuts with Resveratrol: Peanuts, Pistachios, Walnuts
Nuts are a tasty snack that can also be used in many dishes. They give a nice crunch and are a good source of resveratrol, which helps keep your heart healthy. Eating different kinds of nuts can give you important nutrients, including this strong antioxidant.
Peanuts are technically legumes but are often found with nuts. They have a good amount of resveratrol. Other nuts, like pistachios and walnuts, have resveratrol too, but in smaller amounts. Eating a handful of nuts every day can be a yummy and healthy way to get more nutrition in your diet.
Nuts have more than just resveratrol. They are also full of healthy fats, fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Eating nuts may help lower cholesterol, improve blood sugar levels, and could protect against fatty liver disease.
Table: Comparing Key Natural Food Sources of Resveratrol
| Food Source | Primary Resveratrol Location/Form | Typical Resveratrol Yield | Additional Notes/Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Red Grapes | Skins and seeds | High | Eat whole fruit for fiber and additional antioxidants |
| Red Wine | Derived from grape skins during fermentation | Moderate (variable) | Consume in moderation due to alcohol content |
| Concord Grape Juice | Skin (from pressed Concord grapes) | Moderate | Non-alcoholic alternative to wine; higher resveratrol than regular grape juice |
| Japanese Knotweed | Root extract (used in supplements) | Very High (concentrated) | Potent; used for consistent supplemental dosage |
| Blueberries | Skin | Moderate | Also rich in anthocyanins and vitamin C |
| Raspberries | Skin | Lower-Moderate | Also contains ellagic acid; good source of fiber |
| Mulberries | Skin | Moderate | High in resveratrol among berries; also a source of vitamin C |
| Peanuts | Skin | Moderate | Affordable source; contains other phytonutrients |
| Pistachios | Skin (thin layer around the nut) | Lower | Good source of healthy fats and micronutrients |
| Walnuts | Skin (papery layer around the nut) | Lower | Trace resveratrol content; high in omega-3s and polyphenols |
Is Resveratrol Safe? Side Effects, Drug Interactions & Precautions

Resveratrol, found in food and supplements, is usually safe for most people when taken in moderate amounts. Still, it’s important to know about possible side effects, adverse effects, and interactions with drugs to ensure safe use.
Most people can tolerate resveratrol well. However, some may feel mild side effects. These mainly include stomach issues, like nausea, diarrhea, and cramps. These problems usually go away on their own. But those with existing stomach issues may be more likely to experience these side effects and should be careful.
Resveratrol Side Effects: What to Expect
Resveratrol is mostly safe to use, especially when you get it from natural foods and in moderate amounts. But like any active compound, taking high doses, especially through supplements, might cause some side effects.
The side effects of resveratrol often affect the stomach. Common issues include nausea, diarrhea, stomach cramps, and indigestion. How serious or common these side effects are can depend on the dose taken and how sensitive a person is.
In rare cases, some people might have allergic reactions to resveratrol. This could show up as skin rashes, itching, or swelling. If these allergic reactions happen, it is very important to stop taking resveratrol and get medical help immediately.
Resveratrol is generally safe when taken in moderation, but higher doses—especially from supplements—can lead to digestive discomfort or rare allergic reactions.
| Side Effect | How Common? | Potential Severity | Notes / Risk Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digestive upset (nausea, diarrhea, stomach cramps, indigestion) | Occasional (more common with high-dose supplements) | Mild to moderate | More likely at high supplemental doses; usually resolves on its own |
| Allergic reactions (rash, itching, swelling) | Rare | Mild to severe | More likely if allergic to source foods (e.g., peanuts, berries); seek immediate medical attention if severe |
| Headache | Rare | Mild | Most reported with supplements; typically transient |
| Changes in blood pressure | Rare | Mild to moderate | May lower blood pressure; caution with antihypertensive meds |
| Interaction with blood thinners (e.g., warfarin, aspirin) | Uncommon (with supplements) | Moderate to severe | Can increase bleeding risk; consult doctor if on these medications |
| Potential liver impact (with very high doses) | Very rare (high-dose supplements) | Moderate to severe | Monitor if liver disease is present; discuss with healthcare provider |
| Joint or muscle pain | Very rare | Mild | Isolated reports, mostly in high-dose users |
Risks of High-Dose Resveratrol Supplements
Resveratrol from natural food sources is usually safe for most people. However, you should be careful when thinking about taking resveratrol supplements. Taking high doses of resveratrol over a long time may come with risks.
If you have any liver disease, you need to be cautious with resveratrol supplements. High doses can make liver damage worse. It’s important to talk to a doctor to see if resveratrol supplementation is safe for you, based on your health.
Also, if you have metabolic disorders like metabolic syndrome, check with your doctor before using resveratrol supplements. High doses may affect how your body processes certain things.
Who Should Not Take Resveratrol? Precautions & Contraindications
Some groups of people need to be careful when thinking about taking resveratrol supplements for disease prevention. This is because these supplements could interact with their health issues or their medicines.
Pregnant and breastfeeding women should not take resveratrol supplements. We don’t know enough about how it affects the development of babies and infants. However, getting resveratrol from food in moderate amounts is usually safe during pregnancy. It’s good to talk to a doctor before making any changes to your diet.
Older adults, especially those who take many different medications, should be careful about resveratrol supplements. There could be drug interactions. It’s important to talk to a healthcare professional to understand the risks and benefits.
Resveratrol supplements may not be suitable for everyone, especially those with specific health conditions or life stages—here’s who should avoid or use them with caution.
| Group | Recommendation | Reason / Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Pregnant Women | Avoid resveratrol supplements | Insufficient safety data; potential effects on fetal development are unknown |
| Breastfeeding Women | Avoid resveratrol supplements | Limited research; uncertain impact on infant health via breast milk |
| Pregnant/Breastfeeding (Food) | Moderate intake from natural food sources is generally safe | Whole foods like grapes and berries are low risk when consumed in typical amounts |
| Older Adults (Taking Multiple Medications) | Use caution; consult a healthcare provider | May interact with multiple medications; risk of cumulative side effects |
| People on Prescription Medications | Consult a doctor before use | Risk of interactions, especially with blood thinners and liver-metabolized drugs |
| People with Liver Disease | Avoid or use only under medical supervision | May worsen liver function; resveratrol is metabolized in the liver |
| People Scheduled for Surgery | Stop use at least 2 weeks before surgery | May increase bleeding risk due to effects on blood clotting |
| People with Hormone-Sensitive Conditions | Consult a healthcare provider | May act as a phytoestrogen; possible effects on hormone-sensitive conditions |
Resveratrol Interactions with Medications & Blood Thinners
Resveratrol has many biological functions. Because of this, it can interact with some medications. This is especially true for those that the liver processes or that influence blood clotting.
If you take medications like aspirin or warfarin, you need to be careful with high doses of resveratrol. It might make these medications work stronger, which could increase the risk of bleeding.
Also, resveratrol can mix with other drugs processed by the liver. This may change how well they work or raise the chances of side effects. It’s important to talk to a healthcare professional to check for possible interactions and change your medication doses if needed.
Below is a summary of common medications that may interact with resveratrol and what precautions to take.
| Medication Type | Interaction Risk | Potential Effect | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blood thinners (e.g., warfarin, aspirin, clopidogrel) | High | May enhance anticoagulant effects, increasing bleeding risk | Avoid high-dose supplements; consult your doctor before use |
| NSAIDs (e.g., ibuprofen, naproxen) | Moderate | May increase risk of stomach bleeding or irritation, especially with supplements | Use with caution; monitor for GI symptoms |
| Antihypertensives (e.g., ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers) | Possible | May enhance blood pressure-lowering effects | Monitor blood pressure regularly |
| Statins (e.g., atorvastatin, simvastatin) | Possible | May alter drug metabolism and increase side effects | Use with medical supervision |
| Drugs metabolized by the liver (CYP450 enzymes; e.g., certain antidepressants, antiepileptics, immunosuppressants) | Variable | May interfere with liver enzyme activity, altering drug concentration in the blood | Ask a healthcare provider before combining |
| Hormonal therapies (e.g., tamoxifen, hormone replacement therapy) | Theoretical | May interfere due to possible estrogenic (phytoestrogen) effects | Discuss with your healthcare provider |
Resveratrol: Food, Drink & Supplement Interactions
While resveratrol doesn’t have major food interactions, you should think about where it comes from when adding it to your diet.
Drinking red wine, a key source of resveratrol, in large amounts can cause health issues because of the alcohol. It’s important to enjoy drinks in moderation.
Grapefruit can affect some medicines but doesn’t directly interact with resveratrol. Still, be aware of possible issues if you have grapefruit while taking medicines broken down by the same liver enzymes as resveratrol.
Below is a breakdown of how resveratrol interacts with common foods, drinks, and supplements you might take alongside it.
| Item | Category | Interaction Type | Effect / Details | Recommendation / Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Red Wine | Drink | Alcohol-related | Source of resveratrol, but excess alcohol may harm liver and negate benefits | Enjoy in moderation; benefits don’t require large amounts of wine |
| Grapefruit | Food / Drink | Indirect (enzyme interaction) | May interfere with metabolism of medications processed by CYP3A4 enzymes | Be cautious if on medications affected by grapefruit |
| High-fat meals | Food | Absorption synergy | Fat enhances resveratrol absorption (bioavailability) | Take with a small amount of healthy fat |
| Iron supplements | Supplement | Theoretical (absorption interference) | Polyphenols like resveratrol may reduce iron absorption | Avoid taking at the same time as iron |
| Curcumin | Other Supplement | Synergy | May enhance antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects | May be beneficial together; consult healthcare provider |
| Quercetin | Other Supplement | Variable synergy / competition | May compete for absorption; synergy varies | Space out doses or consult healthcare provider |
| Vitamin C | Vitamin | Synergy | Combined antioxidant support against oxidative stress | Often used together in anti-aging supplements |
| Vitamin E | Vitamin | Synergy | Enhances antioxidant network; may support cardiovascular health | Found in heart-health formulations |
| Selenium | Mineral | Synergy | Both reduce oxidative stress and inflammation | Often paired in anti-aging formulas |
| L-Carnitine | Amino Acid | Synergy | May enhance mitochondrial function and energy metabolism | Popular in anti-aging and energy blends |
| Glutathione | Amino Acid | Synergy | Supports cellular antioxidant defense | Common in detox and longevity stacks |
| Green Tea Extract | Other Antioxidant | Synergy | Amplifies anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects | Widely used in anti-aging combinations |
| Dark Chocolate | Food | Positive synergy | Contains polyphenols and flavonoids that may complement resveratrol | Eat in moderation; choose high-cacao content |
| Blueberries | Food | Synergy | Natural antioxidant source that complements resveratrol | Can enhance polyphenol diversity in diet |
How to Take Resveratrol: Foods, Supplements & Daily Tips

Adding resveratrol to your life is not hard. You don’t need to make big changes. Just a few simple tips about your diet and lifestyle can help you get more of this good compound. It might even improve how you feel overall.
Start by eating foods that are high in resveratrol. Enjoy some grapes or berries as a snack. You can also add them to your breakfast cereal or mix them into your salads and smoothies. Drinking a glass of red wine now and then is nice too, as long as you do it in moderation.
Tips to Increase Resveratrol Intake: Diet, Meals & Recipes
Boosting your intake of resveratrol is easy to do with a few simple changes to your meals. Use these tips to enjoy the health benefits of this strong compound through better eating.
Begin your day with a breakfast that has resveratrol. Put some grapes or berries in your cereal, yogurt, or oatmeal. You can also blend them into a smoothie with spinach, almond milk, and protein powder for a tasty and healthy morning drink.
Add resveratrol-rich foods to your main meals. Toss grapes into salads, chicken salads, or grain bowls for extra flavor and crunch. Use berries in your desserts too, like on yogurt parfaits, chia pudding, or oatmeal.
Resveratrol: Food Sources vs Supplements – Which is Best?
When it comes to enjoying the benefits of resveratrol, many wonder if food sources are better than supplements. The answer depends on their different benefits.
Getting resveratrol from food lets you consume it in its natural state. You also gain other helpful nutrients like vitamins, minerals, and fiber. These nutrients can work together with resveratrol, possibly helping your body absorb it better.
On the other hand, if you can’t eat many resveratrol-rich foods because of diet restrictions or preferences, supplements are a good option. Resveratrol supplements offer a strong dose of the compound, which helps in keeping a steady intake. However, it is important to choose good brands and talk to a healthcare expert about the right amount to take. Be careful to consider any possible interactions with other medications.
Deciding between food sources and supplements? Here’s a comparison:
| Factor | Food Sources | Supplements |
|---|---|---|
| Resveratrol Concentration | Generally lower and variable | Higher and standardized |
| Bioavailability / Synergy | Natural matrix; potential synergy with other phytonutrients | Isolated compound; bioavailability varies by formulation (e.g., micronized, liposomal) |
| Nutrient Profile | Whole food benefits (fiber, vitamins, minerals, antioxidants) | Primarily resveratrol; often lacks co-factors found in natural sources |
| Dosage Control | Difficult to measure or control precise intake | Precise and consistent dosage per serving |
| Cost | Can be part of a regular diet; no extra cost for most people | Can be an added expense depending on quality and dosage |
| Potential for Additives / Fillers | Naturally occurring; no added substances | May contain fillers, preservatives, or binders; choose trusted brands |
| Safety / Side Effects | Generally safe; rare side effects, but possible allergies (e.g., peanuts, berries) | Possible side effects with high doses; may interact with medications |
| Suitability for Special Diets | Naturally vegan and gluten-free; some foods (like grape juice) may be high in sugar | Vegan and allergen-free options available; always check for gelatin capsules or animal-based additives |
Combining Resveratrol with Healthy Lifestyle for Maximum Benefits
Resveratrol can give you some health benefits, but it’s important to see it as part of a larger health plan. Using it with a balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle will help you get the most from it and improve your well-being.
Aim to have a balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. This mix of foods offers many nutrients that help your health work better.
Keep in mind that resveratrol is not a quick fix. It works best when combined with other healthy habits, such as regular exercise, managing stress, getting enough sleep, and not smoking.
Resveratrol Myths vs Facts: What Science Really Says

Resveratrol is becoming popular, but there are many misconceptions about it. It’s important to look at facts and evidence to understand its true limits.
Many people believe that resveratrol is a miracle cure that can prevent all diseases and stop aging. While some studies show it can boost health in some ways, we should be careful about trusting these claims too much.
Resveratrol Facts vs Myths: Scientific Review
Navigating the world of nutritional supplements can be tricky. You need to know the difference between real science and false claims.
Resveratrol seems to offer a lot of promise, but it has been the subject of many exaggerated claims. These often come from marketing tricks and personal stories.
It’s important to keep in mind that just because studies show a link between resveratrol intake and certain health benefits, it doesn’t mean that resveratrol actually causes these changes. There could be other reasons for these benefits. This shows we need more research to understand it better.
Addressing Common Misconceptions
Misunderstandings about resveratrol come from misreading research or applying results from animal studies to humans without thinking about how our bodies are different.
One common belief is that drinking a lot of red wine will give big health benefits because of resveratrol. While red wine has resveratrol, the amount can change a lot based on the type of grape and how the wine is made. Also, drinking too much alcohol can be very harmful, which cancels out any good effects.
Another wrong idea is that resveratrol supplements are a quick fix for weight loss. Some studies say resveratrol might help with metabolism and fat storage, but these effects are usually small and need more research.
Table: Resveratrol Myths vs Scientific Facts
| Myth | Scientific Fact |
|---|---|
| Resveratrol is a miracle cure that prevents all aging and diseases. | No supplement alone prevents aging or chronic disease; resveratrol shows promise but needs more research. |
| Drinking lots of red wine improves health because of resveratrol. | Red wine contains very little resveratrol; excessive alcohol harms health and outweighs potential benefits. |
| Resveratrol supplements are a substitute for a healthy lifestyle. | Supplements can support wellness, but diet, exercise, and sleep are still the foundation of good health. |
| All resveratrol supplements are equally effective. | Quality and bioavailability vary; choose third-party tested products with trusted formulations. |
| Resveratrol causes weight loss. | Evidence in humans is limited and inconsistent; it’s not an effective standalone weight-loss solution. |
| Resveratrol works the same in humans as in animals. | Most benefits were seen in animal and laboratory studies; human research is ongoing and results may differ. |
| The more resveratrol you take, the better. | High doses may cause side effects or interact with medications; more is not always better—stick to recommended amounts. |
| Resveratrol only comes from red wine. | It’s also found in grapes, berries, peanuts, and Japanese knotweed—red wine is not the only source. |
Latest Research & Clinical Studies on Resveratrol Benefits

The scientific community is still looking into the health benefits of resveratrol. They are running clinical trials and reviews to understand how it works and what it can treat.
Recent research has shown that resveratrol might help with different health problems. These include cardiovascular disease, brain disorders, cancer, and metabolic diseases. The ongoing clinical trials are important. They will help find the best doses, long-term effects, and any interactions that may happen.
How Resveratrol May Slow Aging: Research & Mechanisms
The idea that resveratrol can help slow aging has caught the interest of both scientists and the public. Research shows that resveratrol might affect aging at a cellular level. It does this by activating certain genes that play a role in living longer and repairing DNA.
Resveratrol is believed to activate a group of proteins called sirtuins, which include pathways linked to nitric oxide synthase activity. These proteins are important for controlling tasks in our cells, such as DNA repair, energy use, and inflammation. Each of these factors is important in the aging process.
Studies done on different living beings, like yeast and mice, have produced good results. They show that resveratrol administration can lengthen lifespan and improve healthspan, which is the time a person spends healthy. Still, to confirm these results in humans, more research is needed.
Resveratrol Clinical Studies: Cardiovascular Health & Blood Pressure
Cardiovascular disease is still a top cause of death around the world. This causes scientists to look into ways to prevent and treat it. Resveratrol has gained a lot of interest for its possible benefits for heart health.
Research shows that resveratrol might help cardiovascular health in different ways. It may lower, including the protective effects of resveratrol such as lowering blood pressure, improveimproving cholesterol levels, reducereducing inflammation, and boostboosting endothelial function, which is the inner lining of blood vessels.
Clinical trials have shown good signs, with resveratrol supplementation linked to better blood pressure and cholesterol levels. It also helps with other cardiovascular risk factors. But, more research is needed to find out the best doses, long-term effects, and how it might interact with other medications.
Resveratrol and Brain Health: Neuroprotective Clinical Evidence
The rise of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s shows the urgent need for effective ways to prevent and treat these conditions. Scientists are very interested in resveratrol for its possible benefits for brain health.
Studies say that resveratrol might help protect brain cells. It may defend against damage from oxidative stress, inflammation, and harmful protein buildup. These issues are common in neurodegenerative disorders.
Test results in animals look encouraging. Resveratrol appears to boost cognitive function. It may also lower amyloid plaque levels and protect brain cells in Alzheimer’s models. Still, more research is needed to apply these results to humans.
Anti-Cancer Effects of Resveratrol: Latest Scientific Findings
The search for good cancer treatments and ways to prevent it has led researchers to look into natural compounds like resveratrol. Studies in labs and with animals show that resveratrol may stop the growth and spread of different cancer cells, like breast cancer, colorectal cancer patients, and prostate cancer.
Resveratrol works against cancer by using several methods. It can cause apoptosis, which is programmed cell death in cancer cells. This helps keep those cells from growing too fast. Resveratrol may also stop angiogenesis, which is the creation of new blood vessels that give tumors the nutrients they need.
Although studies with humans are still limited, some small clinical trials have given hope for patients with colorectal cancer and men with prostate cancer. More research is needed to find the best dosages, learn about any long-term effects, and see how it interacts with regular cancer treatments.
Conclusion
Resveratrol is a strong antioxidant that can help your health in many ways. It supports heart and brain health and may even help with aging. You can find it in grapes, red wine, and berries, so adding these to your diet can boost your well-being. While there are supplements available, it is important to balance resveratrol with a healthy lifestyle. Be aware of possible interactions and take care if you are on medications. Research shows that resveratrol may have good effects on aging, heart health, and cancer prevention, which keeps scientists interested. It’s important to learn the truth about this antioxidant so you can make smart choices. Use resveratrol as a natural way to support a long and healthy life.
The content on WellwayHub.com is intended for general informational purposes only and should not be taken as medical advice. Please consult your doctor or a qualified health professional before making any changes to your health routine.
Some links on WellwayHub.com may be affiliate links. This means we may earn a small commission if you make a purchase through these links, at no extra cost to you. This helps support our mission to provide trusted wellness content.
Frequently Asked Questions
Resveratrol is a natural polyphenol found in red grapes, berries, peanuts, and Japanese knotweed. It’s commonly used in supplements for its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and potential anti-aging effects.
The benefits of resveratrol can start at different times, particularly after a few weeks of resveratrol supplementation. This depends on individual factors, the health issue being treated, and how much resveratrol you take. Studies on the clinical pharmacology of resveratrol show that some health improvements, like changes in biomarkers, may happen in just a few weeks. However, other benefits might need several months of regular use., particularly after days of resveratrol supplementation.
There is no official recommended daily dose of resveratrol, but most supplements provide between 100 mg and 500 mg per day. Clinical studies have used doses ranging from 150 mg to 1,000 mg daily, but higher doses may increase the risk of side effects. For general wellness, it’s best to start with the lowest effective dose and consult a healthcare provider to determine the right amount for your needs and health goals.
Some groups should stay away from resveratrol supplements because of possible risks. This includes women who are pregnant or breastfeeding, people with bleeding problems, and those taking blood-thinning drugs.
Yes, there are age restrictions for resveratrol supplementation. It is not usually recommended for children. Older adults should talk to a doctor before using it to ensure safe use and correct dosing. Always follow the intake guidelines found on the product label.
Resveratrol can affect how some medicines work. So, it’s very important to talk to your doctor before taking it with other drugs. This is especially true for blood thinners, NSAIDs, and some antidepressants.
Getting resveratrol from whole foods—like red grapes, berries, peanuts, and dark chocolate—is generally considered safest and offers the added benefits of fiber and other nutrients. However, supplements can provide higher, standardized doses for those who may not get enough from diet alone or have specific health goals. For most people, a balanced diet rich in natural sources is best, but supplements may be appropriate when recommended by a healthcare provider.
Some studies say resveratrol might help with metabolism and support small weight loss by reducing fat. But it isn’t a sure fix for obesity. We need more research to really know if it works as a tool for losing weight.
Red wine can be good for your heart health when you drink it in moderation. This means one glass a day for women and two glasses for men. However, drinking too much can be harmful. It is important to stick to dietary guidelines and focus on healthy habits overall.