
Introduction to N-Acetyl Cysteine (NAC)
N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) is a strong antioxidant supplement with various clinical applications. It offers many health benefits. NAC helps fight oxidative stress by neutralizing harmful free radicals. This makes it important for our overall health. Researchers have studied NAC for treating different issues like acetaminophen poisoning, chronic bronchitis, and respiratory diseases. It can also boost glutathione levels and protect our cells from damage. Because of these effects, NAC has gained attention for its positive impact on human health.
Definition and Overview
Acetyl cysteine, also known as NAC, is a strong antioxidant. It helps protect our cells from damage caused by free radicals. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can harm our cells and lead to oxidative stress. This process can cause health problems, including aging, heart disease, and some types of cancer.
Oxidative stress happens when free radicals are produced faster than our body can fight them off. NAC helps fix this by neutralizing free radicals. This keeps a healthy balance and protects our cells from harm.
NAC’s protective effect is very important today. We face many environmental toxins, pollutants, and stress. All these factors can increase the production of free radicals.
NAC as a Supplement and Prescription Medication
In the United States, NAC is available as both a prescription medicine and a dietary supplement. As a medication approved for drug administration, it is mainly used to treat acetaminophen poisoning. It works by helping to increase glutathione levels in the liver, which is important for removing acetaminophen from the body.
NAC is also given for its ability to thin mucus. This makes it helpful for people with lung issues like chronic bronchitis and cystic fibrosis.
As a dietary supplement, NAC is often promoted for its antioxidant benefits. It is said to support the immune system, liver function, and brain health. However, it is crucial to understand that the FDA has changed its position on NAC as a dietary supplement, and its regulatory status may change again.
Mechanisms of Action: How NAC Works in the Body
NAC helps improve health in several ways. First, it works as a building block for glutathione and also directly fights free radicals. Together, these actions keep our cells safe from damage.
Additionally, NAC has anti-inflammatory effects. It can lower too much inflammation in the body. By changing how some signals work in the inflammation process, NAC can lessen inflammation linked to many long-term health problems.
NAC as a Precursor to Glutathione
One important job of NAC is to help make glutathione. People call glutathione the “master antioxidant” because it is great at fighting oxidative stress. It helps remove free radicals, cleans out harmful things, and supports the immune system.
But things like stress, bad diets, pollution, and getting older can lower our glutathione levels. That is where NAC becomes really useful.
When we take NAC as a supplement, we give our bodies what they need to create more glutathione. This helps our bodies fight oxidative stress and keep cells healthy. Research has highlighted the effects of NAC on glutathione levels, showing how important it is for our overall well-being.
Antioxidant and Free Radical Scavenging Effects
NAC does more than help make glutathione. It also acts as a strong antioxidant. This means it can neutralize free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can harm our cells. Free radicals come from normal body processes. Our bodies usually manage them well. But things like pollution, smoking, and UV rays can create too many free radicals. This leads to oxidative stress.
This is where NAC is useful. It helps to get rid of these reactive molecules. By doing this, NAC protects our cells from damage. This support helps our overall health and may lower the chances of chronic diseases.
Mucolytic Properties and Respiratory Benefits
NAC helps with mucus problems because it can break down mucus. This makes it helpful for treating respiratory diseases. It works by breaking the bonds in mucus, which makes it thinner and easier to cough up.
This ability to thin mucus is very helpful for people with chronic bronchitis, cystic fibrosis, and COPD. In these conditions, thick mucus can block airways and hurt lung function. With NAC, clearing mucus can become easier. This improves breathing, lowers coughing, and boosts overall lung function.
NAC also has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. These benefits can support respiratory health. They may help reduce swelling in the airways, which can improve lung function and lessen respiratory symptoms.
Health Benefits of NAC
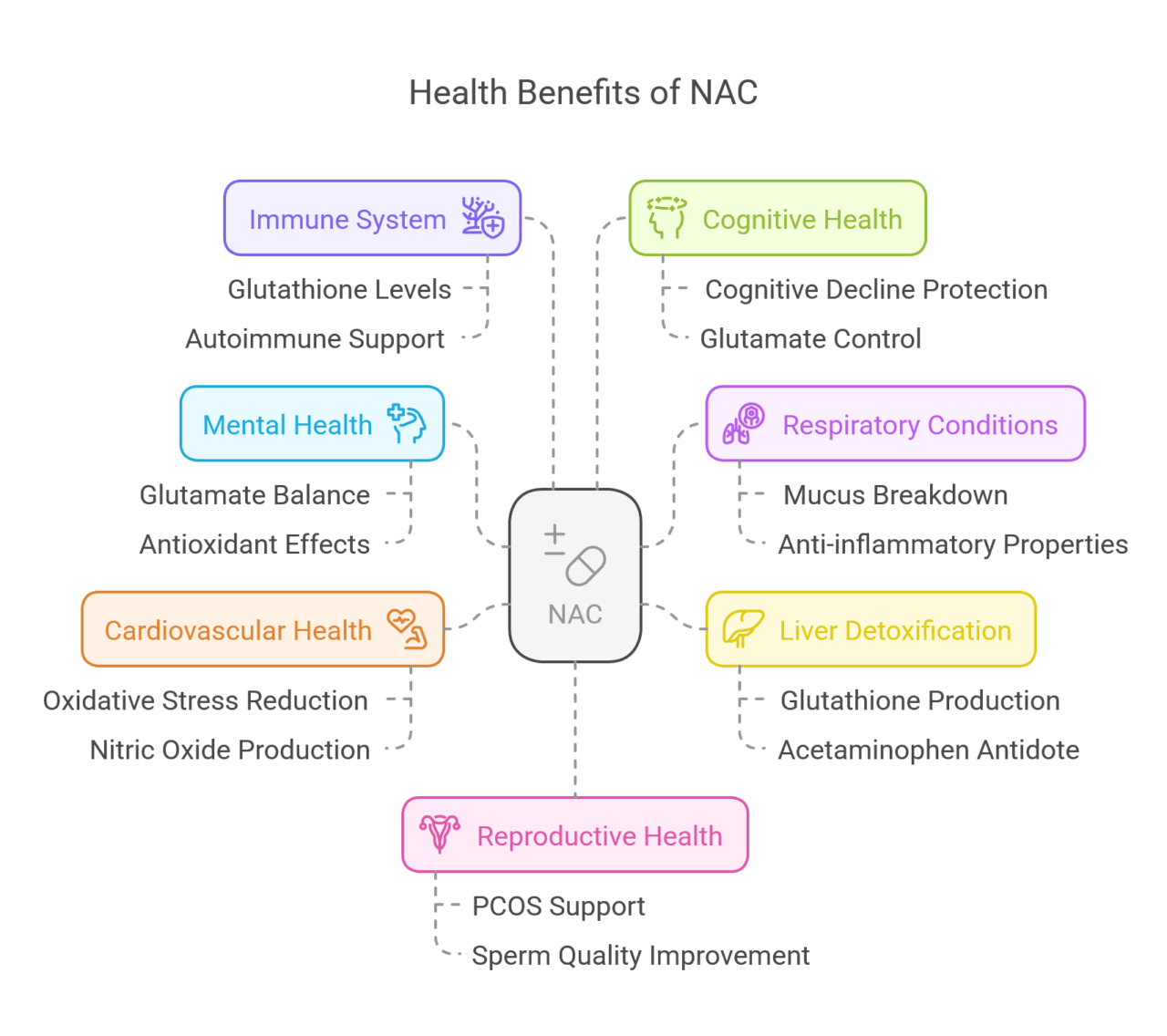
NAC may offer many health benefits. Researchers have looked into it a lot. They see good results in mental health, lung support, liver cleansing, and heart health. Because NAC works in different ways, it could help with many health problems.
We may need more studies to learn all the benefits, but current findings show that NAC can be helpful for better health and wellness.
Mental Health and Mood Support
Emerging research shows that NAC might help support mental health. Studies have looked into how it can ease symptoms of different psychiatric disorders, like bipolar depression, bipolar disorder, depression, and anxiety. The specific ways NAC works are still being studied, but it seems to affect glutamate levels in the brain, which is thought to be important.
Glutamate is a neurotransmitter that helps with learning, memory, and mood. If glutamate levels are not balanced, it can lead to mental health issues and potential brain damage. NAC seems to help balance these levels, which may reduce symptoms.
In addition, NAC has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. These properties can help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in the brain. This may protect brain cells and improve brain function, which is essential for good mental health and quality of life.
NAC for Respiratory Conditions
NAC has been known for its help in managing lung issues for a long time. It helps break down mucus, and its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties make it helpful for people with chronic bronchitis, cystic fibrosis, and other respiratory diseases.
For those with chronic bronchitis, NAC can thin out mucus. This makes it easier to cough up and clear the airways. It can reduce coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath, which can make you feel better overall.
NAC’s antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects can also assist in reducing the swelling in the airways. This can help lower lung damage and improve lung function over time, potentially protecting against bone marrow toxicity. While we need more studies, NAC looks promising for managing respiratory diseases and enhancing the quality of life for people affected.
Liver Detoxification and Protection
The liver is our main organ for detoxification. It needs a substance called glutathione to help keep us safe and to cleanse itself. NAC is important because it helps make glutathione, which is key for liver health and protection from harm. This is especially true if someone has taken too much acetaminophen. In those situations, NAC is used as a common treatment to avoid serious liver injury.
Acetaminophen is a popular pain reliever, but taking too much can really hurt the liver. NAC works as an antidote by bringing back glutathione levels in the liver. These levels drop when acetaminophen is broken down in the body. By getting glutathione back, NAC helps in the treatment of acetaminophen and tackles the harmful effects of acetaminophen and stops or lessens liver injury.
On top of that, NAC has properties that fight off harmful molecules and reduce inflammation. This means it can give extra support to the liver. By lowering oxidative stress and inflammation, NAC can help stop or slow down problems like fatty liver disease and alcoholic liver disease.
Cardiovascular Health Effects
NAC may help improve heart health. Studies suggest it could lower the chance of heart disease and reduce heart disease risk. It targets key issues like oxidative stress, inflammation, and blood vessel health.
Oxidative stress is a big player in heart diseases. NAC fights free radicals. By doing this, it protects the heart and blood vessels from damage. This may help decrease the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other heart problems.
NAC could also help blood vessel health by increasing nitric oxide production. Nitric oxide helps relax and widen blood vessels. This leads to better blood flow and lower blood pressure. These benefits could make NAC effective in lowering the risk of heart disease.
Immune System Support and Modulation
NAC is important for our immune system. It helps both our basic and advanced immune responses. A strong immune system is key for fighting infections. At the same time, having a balanced immune response can help stop autoimmune disorders. NAC helps our immune health because it raises the levels of glutathione, which is needed for immune cells to work well.
Glutathione acts as a strong antioxidant. It protects immune cells from harm caused by reactive oxygen species (ROS) during immune responses and helps prevent cell death. NAC supports the immune cells by boosting glutathione levels. This support helps immune cells fight off germs effectively.
Also, some clinical trials have looked at NAC’s role in helping with autoimmune conditions. While we need more studies, some suggest that NAC could help balance the immune response in certain autoimmune diseases. This might reduce inflammation and lessen symptoms.
Cognitive and Neurological Health
NAC is not just good for physical health; it may also help brain health. Studies show that NAC could protect against cognitive decline and might improve how the brain works in some cases. This happens because NAC has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and effects on glutamate that protect the brain.
Oxidative stress and inflammation are major causes of brain diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. By reducing oxidative stress and inflammation in the brain, NAC might help keep neurons safe and could slow the progression of these serious illnesses associated with Parkinson’s disease.
Also, NAC can help control glutamate levels in the brain, which may support cognitive function. Glutamate is important for learning and memory, but too much of it can harm the brain. NAC’s ability to control glutamate may help keep it at healthy levels, protecting brain cells and supporting overall cognitive health.
Reproductive and Fertility Benefits
NAC has caught attention for its possible benefits in improving reproductive health and fertility for both men and women. It works as an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent. Plus, it may help with insulin sensitivity. These features might positively affect reproductive function.
For women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), which can impact fertility, NAC might help with ovulation and menstrual cycles. PCOS is linked to insulin resistance. NAC’s ability to improve insulin sensitivity could lead to some of these benefits.
NAC has also been studied for helping sperm quality in men with infertility issues. Oxidative stress is a known issue that affects sperm health. NAC’s antioxidant properties might protect sperm cells from damage. This could improve how well they move and their overall health.
NAC for Specific Populations and Lifestyles
The possible benefits of NAC can help different groups of people. Athletes and active individuals may use NAC for better muscle recovery. NAC can help reduce muscle damage and soreness caused by exercise. This could lead to quicker recovery times.
Older adults may also find NAC useful for brain health. As people get older, their brains can face more oxidative stress and inflammation. This can lead to problems with thinking and memory.
NAC in Sports and Exercise Recovery
Athletes and fitness fans are always looking for ways to improve sports recovery and boost their performance. NAC has come up as a helpful natural option. Studies suggest it might lessen muscle damage from tough workouts and speed up recovery, helping athletes get back to training more quickly.
When we take part in intense exercise, our bodies create more reactive oxygen species (ROS). This can cause oxidative stress and harm our muscles. This oxidative stress leads to soreness, tiredness, and slow recovery. NAC, being a strong antioxidant, can help fight off these ROS and lessen damage to muscle tissue.
By reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, NAC can help shorten recovery time. This means athletes can return to training quicker and might even improve their overall performance. However, we need more research to find out the best doses and timing for NAC supplementation based on different sports and activities.
Table: NAC vs. Other Exercise Supplements
| Supplement | Function | Target Audience | Key Benefit | Common Side Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAC (N-Acetyl Cysteine) | Antioxidant, reduces oxidative stress, aids recovery | Endurance athletes, high-intensity trainers, older adults | Reduces muscle fatigue, supports faster recovery | Mild GI upset (nausea, bloating), headache |
| BCAAs (Branched-Chain Amino Acids) | Stimulates muscle protein synthesis, reduces muscle breakdown | Bodybuilders, strength athletes, people cutting fat | Preserves lean muscle mass, reduces soreness | Fatigue, imbalance with long-term use |
| Creatine | Boosts ATP production, enhances strength and power | Powerlifters, sprinters, CrossFit athletes | Increases strength, power, and muscle mass | Water retention, GI discomfort, possible cramping |
| Glutamine | Supports immune function and gut health, may aid recovery | Endurance athletes, those under heavy training loads | Reduces muscle soreness, supports gut repair | Generally well tolerated, possible bloating |
NAC and Alcohol Use: Liver and Detox Effects
Alcohol use, even a little bit, can harm the liver, which helps to clean toxins from our body. For most healthy adults, occasional drinking may not be a big deal. However, drinking too much or too often can really hurt the liver. People are starting to look into how NAC might help reduce the negative effects of alcohol on the liver.
When we drink, our body creates harmful substances like acetaldehyde. These can cause oxidative stress and liver injury. NAC can help raise glutathione levels and work as an antioxidant. This may help protect the liver from damage that comes from drinking.
We still need more studies, especially with people, to understand things better. The current information suggests that NAC may help the liver by supporting detoxification processes and lowering oxidative stress from alcohol use.
Dietary Factors That Influence NAC Efficacy
While using NAC can help, it’s important to understand how our diet affects its effectiveness. What we eat affects how our body absorbs and uses NAC supplementation.
Getting enough protein is very important because NAC comes from the amino acid L-cysteine. Eating a balanced diet with protein-rich foods like poultry, fish, eggs, beans, and lentils gives our body what it needs to make NAC.
Also, some nutrients can help NAC work better. For example, vitamin C is a potent antioxidant that helps boost NAC’s antioxidant power. Adding foods high in vitamin C, like citrus fruits, berries, and leafy greens, can make the benefits of NAC supplementation even stronger.
NAC Use in Older Adults and Brain Function
Maintaining brain health is very important as we grow older. Older people may face more oxidative stress. This happens because their natural defenses against it get weaker with age. NAC is getting attention for its potential benefits for brain health, especially for older adults.
NAC has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. It also helps manage glutamate levels. These features might protect the brain. By reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, NAC could help keep brain cells healthy. This may support overall cognitive health in older people.
Some studies show that NAC might help improve memory, attention, and overall thinking skills. This could be especially true for people with mild cognitive impairment.
Natural Food Sources of NAC (Cysteine)

N-Acetyl Cysteine (NAC) is found in many natural foods that are high in cysteine, which is what NAC comes from. Good sources of cysteine include poultry, yogurt, cheese, eggs, oats, garlic, and broccoli. Eating these foods can promote your overall health. They can also help improve your body’s antioxidant defense system. This fights oxidative stress and supports different body functions. By adding more cysteine-rich foods to your meals, you can enjoy the benefits of NAC while fighting free radicals and other harmful things naturally.
Foods Rich in Cysteine
Eating foods high in cysteine is an important way to help your body make glutathione. Cysteine is a semi-essential amino acid, which means our body can make it, but we also need to get enough from our diet, especially when we need more.
Animal products are some of the best foods for cysteine. Foods like chicken and turkey, beef, pork, and fish have a lot of cysteine. Dairy products such as milk, yogurt, and cheese are also great choices.
If you eat a plant-based diet, you can find good sources of cysteine in legumes like lentils, beans, and peas. Nuts and seeds, especially sunflower seeds, are helpful too. Cabbage family vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower, and Brussels sprouts also have cysteine.
Cooking Methods That Preserve Cysteine
Eating foods that are high in cysteine is important. However, how we cook these foods can greatly affect the nutrients we get. Some cooking methods can cause nutrients to be lost. This means we might absorb less cysteine from our meals.
Choosing gentle cooking methods is crucial. Steaming is a great option. It helps keep the nutrients, including cysteine, intact. Poaching is another good technique. This method cooks food in warm liquid, helping to preserve its nutrients.
Try to avoid overcooking, as it can cause a lot of nutrient loss. When stir-frying or sautéing, use medium heat and keep the cooking time short. You can also use cooking liquids like broths or sauces. This will help capture any nutrients that come out during cooking.
NAC from Food vs. Supplements: Which is Better?
The long-standing discussion about food sources and supplements includes NAC (cysteine). Both can help increase our cysteine intake, but they have different strengths and considerations. The best options often include a healthy mix of both.
Getting nutrients from whole foods is encouraged. Foods give us a blend of vitamins, minerals, fiber, and phytonutrients that all work together to support our health. Eating foods high in cysteine as part of a balanced diet gives us cysteine and other great nutritional benefits.
Still, there are times when taking supplements can be needed or helpful. For certain health issues, like acetaminophen poisoning or lung disease, you may need special amounts of NAC. It might be hard to get these amounts through food alone. NAC supplements can provide a convenient and strong dose of cysteine, making it easier to reach the necessary levels when needed.
| Feature | Food Sources of Cysteine | NAC Supplements |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural foods (meat, legumes, etc.) | Synthetic supplement (NAC) |
| Bioavailability | Lower (depends on digestion, cooking) | Higher (direct absorption) |
| Additional Nutrients | Yes (vitamins, minerals) | No |
| Convenience | Requires meal planning | Easy and fast |
| Dosage Control | Difficult | Precise |
Choosing and Using NAC Supplements
Choosing NAC supplements can be tricky. There are many brands and types out there. It’s important to pick a high-quality supplement from a well-known maker.
Also, knowing about the different forms of NAC supplements, how much to take, and any possible interactions is key. This will help you use them safely and effectively.
Why Third-Party Testing Matters
In the world of dietary supplements, third-party testing is very important. Unlike prescription medications, which must meet strict FDA rules for safety, dietary supplements face looser regulations. This makes third-party testing essential for keeping products safe and of good quality.
Third-party testing means that independent labs check and confirm the quality and purity of dietary supplements. Trusted supplement companies willingly send their products to these labs. They want to make sure their products match what is on the label, are clean of harmful substances, and follow good manufacturing practices (GMP).
When you choose NAC supplements that have gone through third-party testing, you get extra peace of mind. It makes sure the product has the right ingredients in the right amounts and does not contain unsafe levels of things like heavy metals, pesticides, or germs.
How to Identify High-Quality NAC Brands
Finding good NAC brands in the complex supplement market can be tough. Many companies compete for your attention, making it hard to choose the right ones. Still, some important signs can help you find reliable brands.
First, choose brands that are open and provide clear labeling. Check for products that show the active ingredient (NAC) and its dosage per serving. Stay away from brands with proprietary blends because they often do not tell you how much of each ingredient is really in their products.
Next, look for brands that have certifications from trusted third-party testing groups. These certifications proof the quality, purity, and strength of supplements. If a product has certifications from groups like USP, NSF, or ConsumerLab, it means it has been thoroughly tested and meets high standards.
NAC Supplement Storage and Shelf-Life Tips
Proper storage of NAC supplements is very important. It helps keep the product good for a longer time and maintains its strength. Like other medicines or supplements, NAC can go bad if it’s not stored correctly. This can make it less effective.
You should always put NAC supplements in a cool, dry place. Keep them away from direct sunlight and heat. Heat and moisture can speed up how fast they spoil. It’s a good idea to keep them in their original containers. This helps protect them from light and humidity.
Always check the expiration date on the bottle. Follow the manufacturer’s storage instructions too. If you see any change in color, smell, or texture, it’s best to throw the product away. These changes might mean that the NAC is no longer good.
Practical Ways to Include NAC in Your Diet
Blending NAC into your daily diet is easy. You can use supplements to help, but adding foods high in cysteine can also help you get more NAC.
Start your day with a healthy breakfast full of protein and cysteine. Eggs are a great option; you can scramble them with spinach and mushrooms or make a vegetable omelet. Greek yogurt mixed with berries and topped with nuts is another good, cysteine-rich choice.
For lunch or dinner, eat lean proteins like chicken, fish, or beans. A grilled chicken salad with mixed greens and colorful veggies gives you protein and also adds antioxidants.
Dosage and Usage Guidelines

Finding the right NAC dosage relies on several factors. These include your health goals, personal needs, and whether you need it for general health or a specific health issue. It is important to talk to your healthcare provider. They can help you decide on a safe and effective dosage based on your medical history, current medications, and possible interactions.
Recommended NAC Dosages by Condition
Dosage recommendations for NAC can vary widely depending on the specific condition being addressed. While lower doses are often sufficient for general health support, therapeutic doses for specific conditions might require higher amounts. It’s crucial to consult with a qualified healthcare professional for personalized advice on NAC dosing.
The following table provides a general overview of dosage recommendations for common uses of NAC. However, this table is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice.
| Condition | Dosage Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Acetaminophen Overdose | Intravenous administration: Typically, a loading dose followed by a maintenance infusion. The dosage and duration vary based on the severity of the overdose, and close medical monitoring is crucial. |
| Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) | 600-1200 mg daily, divided into two doses |
| Cystic Fibrosis | 20-25 mg/kg body weight daily, divided into three or four doses |
| Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) | 600-1800 mg daily, divided into two or three doses |
| General Antioxidant Support | 500-1000 mg daily |
Always follow your healthcare provider’s guidance regarding NAC dosage. They can assess your individual needs and provide personalized recommendations for safe and effective use.
Common Forms of NAC Supplements
The supplement industry provides NAC in different forms. This gives consumers choices based on what they like and need. Knowing these forms and what they are like can help you pick the best option for you.
NAC usually comes in capsules or tablets. These options are easy to use and carry around. Capsules hold NAC in powder or granules, while tablets are made by pressing the powder into a solid.
NAC also comes in powder form. Powdered NAC is flexible. You can mix it into drinks or smoothies. This makes it easier to take for people who may have trouble swallowing pills. Some people even enjoy the taste and texture of powdered NAC more than the other forms.
| Form | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capsule | Powder inside gelatin shell | Easy to take, no taste | Slower absorption |
| Tablet | Compressed powder | Long shelf life | Harder to swallow |
| Powder | Loose form for mixing | Flexible dosing | May have taste/odor |
| IV | Medical use only | Immediate effect | Requires clinical setting |
Supplementation Tips and Best Practices
To get the most benefits from NAC supplementation, it’s important to follow some good practices. By doing this, you can use it well and increase your chances of seeing the results you want.
Start by taking a lower dose than what is suggested on the product label. Then, slowly increase it over time to see how your body reacts. While NAC is usually safe for most people, some might feel minor stomach issues, like nausea, upset stomach, or diarrhea, especially when taking higher doses.
The timing of when you take NAC can also make a difference. It’s best to take it on an empty stomach, either 30 minutes before or 2 hours after meals, to help your body absorb it better. If you find that NAC upsets your stomach when taken on an empty stomach, feel free to take it with food.
Morning vs. Evening NAC Dosing
When choosing when to take NAC, you should think about if you want to take it in the morning or evening. The best time to use NAC depends on your personal needs and goals.
Some people find that taking NAC in the morning, when their stomach is empty, helps it get absorbed better. It can also reduce should discomfort that sometimes happens with NAC supplementation.
On the other hand, some people like taking NAC in the evening. They believe it helps them relax and sleep better. Some users say that NAC makes them feel calmer, which may be because it affects glutamate levels in the brain.
NAC Timing for Exercise and Performance
For people looking to boost their athletic performance and get the most from their workouts, the timing of NAC supplementation is important. This timing can change based on the type and intensity of the exercise.
Taking NAC before a workout is a popular approach, especially for endurance activities. If you consume NAC 30 to 60 minutes before exercising, it may raise glutathione levels in the muscles. This can help lower oxidative stress and prevent muscle damage during long exercise sessions. As a result, it might improve your endurance and lessen fatigue.
On the other hand, if you do strength training or high-intensity interval training (HIIT), it might be better to take NAC after your workout. After these types of exercises, the main aim is often to help muscle protein gain and support muscle growth.
Safety, Side Effects, and Interactions

NAC is usually safe for most people when taken properly. However, it’s important to know about possible side effects and interactions, just like with any other medicine. Knowing these things about NAC supplementation can help lower risks and make sure it is used safely and effectively.
Potential Side Effects of NAC
NAC is generally safe, especially when you take the right amount. But, like any supplement or medicine, it can have some side effects. Most of these side effects are not serious and usually go away on their own.
The most common effects of NAC are related to your stomach. You might feel nausea, upset stomach, diarrhea, or vomiting. These don’t usually last long as your body gets used to the supplement. To help reduce any stomach problems, you should start with a low dose and slowly increase it.
Sometimes, people might also feel headaches, tiredness, or have a skin rash. In rare cases, NAC can lead to more serious allergic reactions, like skin rashes, itching, facial swelling, or trouble breathing. If you notice any severe or ongoing side effects, stop taking NAC and get medical help right away.
Contraindications and Who Should Avoid NAC
NAC is usually safe for most people. However, there are some health warnings and contraindications that require careful attention. It is important to know these precautions to use NAC safely and correctly.
If you have bleeding disorders or take blood-thinning medicines, be careful with NAC supplementation. It can make bleeding time longer and increase the chance of bleeding issues. Talk to your doctor before using NAC if you have a bleeding disorder or take these medications.
Also, if you have kidney or liver disease, check with your healthcare provider first. They can help you understand the risks and benefits. Clinical studies on NAC might affect how some medicines work when treating these conditions.
NAC Drug and Supplement Interactions
Just like any supplement or medicine, safety is important with NAC. You should think about possible interactions with other drugs or supplements. Knowing these interactions can help avoid problems and improve treatment results.
NAC can change how some medications work. This can increase the risk of side effects. For example, NAC might make nitroglycerin, a drug for chest pain, work stronger. Using NAC with nitroglycerin could lower blood pressure too much, potentially leading to low blood pressure.
NAC can also affect certain antibiotics, making them less effective. If you are taking antibiotics, it’s best to take NAC at least two hours apart. This can help reduce any possible interactions.
Long-Term Use: Is Daily NAC Safe?
The question about using NAC for a long time and if taking it daily is safe is still being researched. Short-term use of NAC is generally safe for most people, but there isn’t much data on how it affects individuals over the long term.
Some studies suggest that using NAC long-term at moderate doses may be safe and well-tolerated for patients with neck cancer. For example, a study in the journal ‘Clinical Therapeutics’ showed that taking 600 mg of NAC daily for six months was safe for people with chronic bronchitis.
However, other studies point out possible negative effects that could come from a systematic review of high doses of NAC over a long period. These studies usually look at doses that are much higher than what is recommended for general health.
NAC Compared to Other Antioxidants
Antioxidants come in many forms with different ways of working and health benefits. NAC is a strong antioxidant that is often compared to other well-known antioxidants, with each one providing its own benefits.
Knowing these differences is important. It can help you choose the best antioxidant supplements that fit your health needs and goals.
NAC vs. Other Popular Antioxidants (Glutathione, Vitamin C, ALA)
When you compare NAC with other popular antioxidants like glutathione, vitamin C, and ALA, NAC stands out. NAC supplementation is helpful in treating acetaminophen poisoning, chronic bronchitis, and substance use disorders. Glutathione is important for detoxifying the body. Vitamin C is key for supporting the immune system. ALA is noted for its potential to reduce oxidative stress. Each antioxidant has its own unique benefits. They are all great for improving overall health and wellness.
| Antioxidant | Key Benefits | Mechanism | Best For | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAC (N-Acetyl Cysteine) | Boosts glutathione, detoxifies liver, supports respiratory health | Precursor to glutathione; breaks mucus bonds | Liver detox, COPD, mental health | May cause nausea; interacts with nitroglycerin |
| Glutathione | “Master antioxidant,” skin brightening, immune support | Directly neutralizes free radicals | Anti-aging, detox, skin health | Poor oral absorption (IV/liposomal forms better) |
| Vitamin C | Collagen synthesis, immune boost, iron absorption | Scavenges free radicals; regenerates vitamin E | Immunity, skin health, wound healing | High doses may cause diarrhea |
| CoQ10 | Cellular energy, heart health, migraine prevention | Supports mitochondrial function | Heart health, fatigue, statin users | Expensive; fat-soluble (take with meals) |
| Alpha-Lipoic Acid (ALA) | Blood sugar control, nerve protection | Works in water/fat; recycles other antioxidants | Diabetic neuropathy, weight loss | May lower blood sugar too much |
| Astaxanthin | UV protection, joint health, endurance | Crosses blood-brain barrier | Skin protection, athletes | Slow to show effects (takes weeks) |
| Resveratrol | Longevity, heart health, anti-inflammatory | Activates sirtuins (anti-aging genes) | Anti-aging, inflammation | Low bioavailability when taken alone |
Unique Properties That Set NAC Apart
NAC shares the spotlight with other antioxidants, but it has unique qualities that make it special and helpful for health. This quality makes it a great addition to our list of antioxidants, especially for certain health issues.
First, NAC helps to create glutathione. This is an important antioxidant that our bodies make naturally. However, stress, bad diets, and toxins can reduce its levels. NAC provides what is needed for the body to build glutathione again, helping to replace and boost our natural defenses.
Additionally, NAC helps with breathing issues. It has the ability to break down mucus, making it thinner and easier to get rid of. This is especially useful for health problems like chronic bronchitis and cystic fibrosis, where mucus can block the airways.
Efficacy, and Bioavailability Comparison
To understand how well antioxidants work and how the body uses them, we need to look at some important factors. Bioavailability is key here. It means how much of a nutrient or compound is absorbed by the body and used effectively.
NAC usually has good bioavailability after oral administration when you take it by mouth. This is especially true if you use capsules or tablets. It is absorbed well, which means the body can use it efficiently.
But there are things that can affect how well NAC is absorbed. The dosage, the form of the NAC, and individual health can all play a part. Taking NAC on an empty stomach might help your body absorb it better. If you have it with food, it might not be used as well.
Conclusion
NAC, short for N-Acetyl Cysteine, is a strong antioxidant that has many health benefits. It helps make glutathione, boosts mental health, supports lung health, helps detox the liver, and benefits heart health. NAC is useful for anyone, whether you are an athlete wanting to recover better, someone needing liver protection from alcohol, or a person looking to improve cognitive function. Adding NAC to your daily routine—through natural foods or good supplements—can be a great choice for your health. Make sure to watch for safety, stick to dosage rules, and check for any interactions to get the best from this powerful antioxidant. Stay updated, stay fit, and think about how NAC could help with your health needs.
The content on WellwayHub.com is intended for general informational purposes only and should not be taken as medical advice. Please consult your doctor or a qualified health professional before making any changes to your health routine.
Some links on WellwayHub.com may be affiliate links. This means we may earn a small commission if you make a purchase through these links, at no extra cost to you. This helps support our mission to provide trusted wellness content.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, you can take NAC every day. It is good for you because it has antioxidant qualities and helps with your overall health. Make sure to use the recommended amount that healthcare professionals suggest. This will give you the best results.
NAC can usually be taken with other supplements. However, it is a good idea to talk to a healthcare provider first. This helps to avoid any possible issues. If you are thinking about taking NAC with certain medications or antioxidants like glutathione, it is best to do it with professional help.
NAC usually starts to work within a few hours to a few days because it absorbs quickly. It gets into the blood fast and provides antioxidant and detoxifying benefits. If you use it regularly, you’ll see the best results over time.
NAC may help with weight loss by boosting metabolism and lowering oxidative stress. When we look at other antioxidants like glutathione, vitamin C, and ALA, NAC shows good potential for managing weight effectively.
NAC is usually safe for adults. However, children, pregnant women, and people with specific medical conditions should talk to a healthcare provider before using it. It’s important to think about individual health factors. Always seek professional advice when looking at NAC supplementation.
NAC is special because it helps increase glutathione levels, an important antioxidant in the body. Unlike vitamin C and ALA, NAC works directly to raise glutathione production. This provides unique support for detoxifying the body.