
Introduction
L-Glutamine is an important amino acid that plays a key role in many functions of the body. It is not usually considered an essential amino acid, but during times of stress or illness, it becomes conditionally essential. This means that you may need to take dietary supplements to get enough of it. L-Glutamine is crucial for protein synthesis. It also helps support the immune and digestive systems. Whether you focus on health or fitness, L-Glutamine offers many benefits that fit different needs.
What is L-Glutamine?
L-Glutamine is a powerful amino acid that is very important for the body. It becomes even more crucial during high-stress times, like when you are sick, because the body may not make enough. As a conditionally essential amino acid, it does more than just help build protein. It also supports immune function and helps produce glucose.
This amino acid is part of many processes in the body, which ties its importance to health and physical performance. It helps in muscle recovery after workouts and supports gut health too. Because of these benefits, many people choose to take it as a dietary supplement. Plus, new research keeps showing more ways L-Glutamine may help, like in treating certain chronic diseases or in weight management.
Definition and Basic Information
L-Glutamine is a very important amino acid. It helps with protein synthesis and is vital for how the body works. Even though it is a nonessential amino acid, the body needs more of it during stress, illnesses, or intense exercise. This makes it a conditionally essential amino acid. It is a key part of proteins and glucose, which helps keep cells healthy.
This amino acid is also crucial for your immune system and gut health. It boosts gut function by providing energy to intestinal cells, which can help stop leaky gut syndrome. Additionally, L-Glutamine is important for supporting the immune system during recovery. It aids in metabolic processes, forming building blocks for other amino acids. Its wide-ranging benefits highlight its powerful role in the body.
L-Glutamine shows that it can adapt to different health issues and physical needs. It helps keep blood pH levels stable and supports red blood cells. This makes it essential for overall health.
Different Forms of Glutamine in the Body
Glutamine is important for many processes in the body. It helps with bodily functions in clear ways. Inside the body, it changes into different forms, with amino acids being key for protein synthesis. Red blood cells are essential for carrying nutrients and oxygen. They depend a lot on glutamine for energy and support.
Glutamine moves through blood cells, making sure it is available when the body is under stress or facing trauma. It helps produce glucose and supports immune function, especially when recovering from illness. Its ability to work within cells is crucial for sustaining life.
Glutamine also plays a role in communication between cells, especially in metabolic processes. It connects the functions of red blood cells with regulating energy production, which is essential for daily activities and athletic performance. This flexibility shows how important glutamine is for keeping the body balanced and healthy.
L-Glutamine vs. D-Glutamine
L-Glutamine and D-Glutamine have the same molecular structure, but they play different roles in the body. L-Glutamine is the form that works actively. It helps with metabolic processes, protein synthesis, and energy production in humans. D-Glutamine, on the other hand, does not offer any functional benefits for these needs.
L-Glutamine is important for the immune function and helps in muscle recovery. It is the best form for gut health. It supports the intestinal wall, helping to prevent digestive issues and leaky gut. In contrast, D-Glutamine has very limited use.
Most research looks at L-Glutamine because it is involved in building protein, increasing muscle mass, and providing nutrients for cell repair. Its presence in dietary supplements shows how important it is for metabolic processes. D-Glutamine does not play the same role.
|
Feature |
L-Glutamine |
D-Glutamine |
|---|---|---|
|
Basic Identity |
An amino acid |
An amino acid |
|
Chirality |
L-isomer (Levorotatory stereoisomer) |
D-isomer (Dextrorotatory stereoisomer) |
|
Structure |
Naturally occurring configuration in humans/animals |
Mirror image of L-Glutamine |
|
Biological Occurrence |
Abundant in nature; most abundant free amino acid in human blood and muscle |
Rare in nature, especially in higher organisms. Found in some bacterial cell walls or synthesized by certain microbes |
|
Role in Protein Synthesis |
Incorporated into proteins by ribosomes |
Not incorporated into proteins by human/animal ribosomes |
|
Metabolic Role |
Crucial metabolic fuel (especially for gut & immune cells), nitrogen transport, neurotransmitter precursor (glutamate, GABA), glutathione synthesis |
Generally considered biologically inactive or poorly metabolized in humans. May interfere with L-glutamine pathways |
|
Human Body Utilization |
Readily utilized and essential for many functions |
Poorly utilized or recognized by human metabolic pathways |
|
Dietary Sources |
Found naturally in protein-rich foods (meat, dairy, eggs, beans, etc.) |
Not typically found in natural food sources for humans |
|
Supplementation |
Widely available and used as a dietary supplement (sports nutrition, gut health, clinical support) |
Not used as a dietary supplement. Can be an impurity in L-Glutamine supplements |
|
Research Focus |
Extensively researched for its physiological roles and therapeutic potential |
Much less researched. Sometimes studied for specific microbial processes or as a non-metabolizable control |
|
Primary Significance |
Biologically active and essential form in humans |
Primarily relevant in specific microbial contexts or as a chemical isomer |
Health Benefits of L-Glutamine
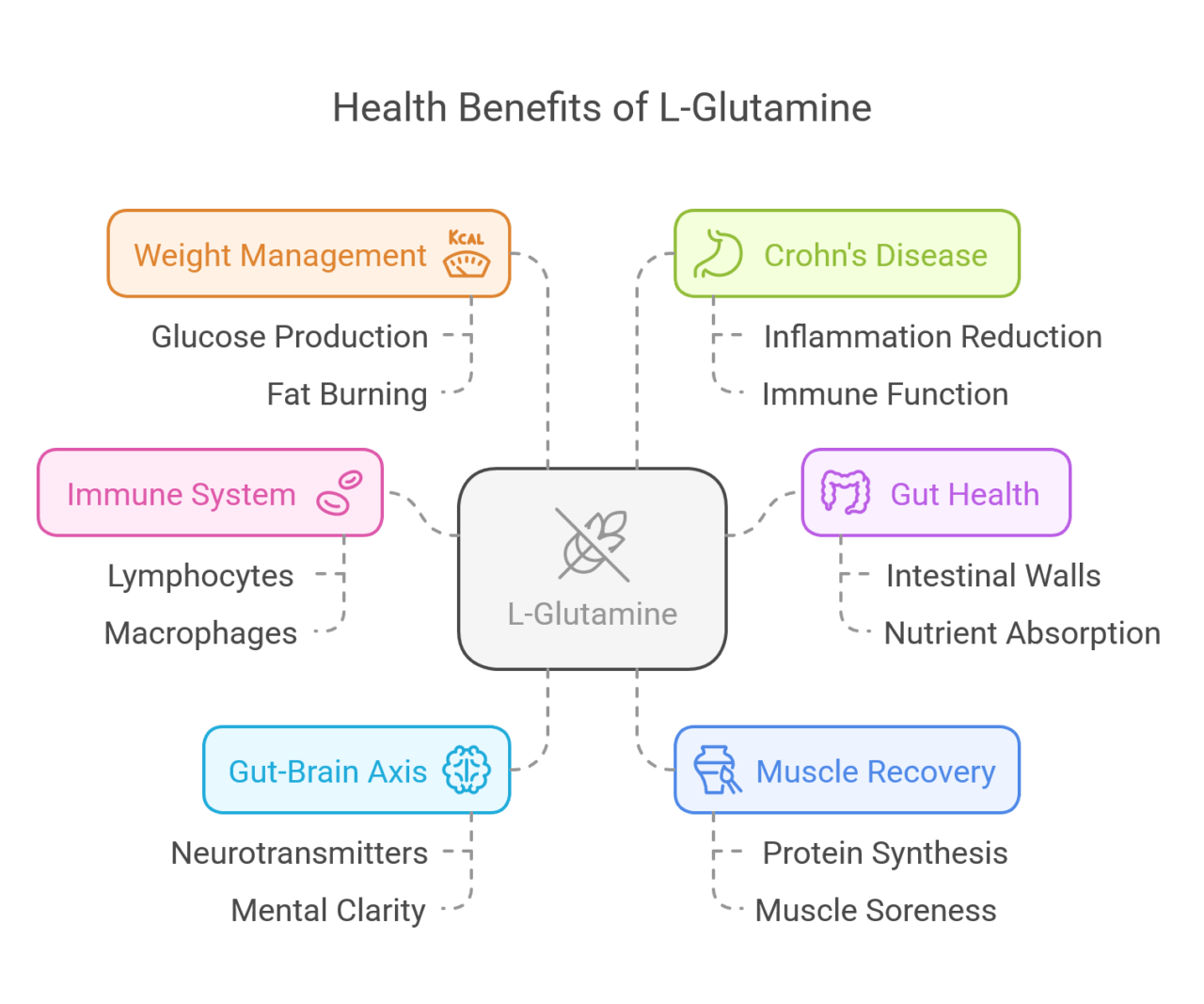
L-Glutamine provides many health benefits. It is important for good performance and recovery. For immune function, it helps cells like lymphocytes and macrophages work well against germs. It also improves gut health by making the stomach barriers stronger.
Other benefits include improving mental clarity because of the connection between the gut and brain. It also helps with weight management because of its part in metabolic processes. Additionally, it helps with muscle recovery, making it essential for fitness and overall well-being.
Enhances Immune System Function
The immune system works best when it is efficient. L-Glutamine plays an important role in keeping it that way. This amino acid acts as food for immune cells like lymphocytes and macrophages. This helps them fight infections strong. Glutamine also helps red blood cells deliver important nutrients that boost immune function, especially during physical stress.
When you are sick or under a lot of stress, your body needs more glutamine. This shows how important it is for recovery. It helps the immune system recover, especially after surgery or injury, when the need goes way up. Plus, glutamine helps metabolic processes that are important for fighting off germs.
Taking L-Glutamine can really help with immune efficiency. It supports recovery during health challenges and builds strength against them. It is clear that L-Glutamine not only strengthens immunity but also helps with the function of red blood cells.
Supports Gut Health
L-Glutamine is very important for gut health. It provides energy to the cells in the intestines. These cells rely on glutamine, helping keep the gut function stable and supporting the digestive system. Strengthening the intestinal walls can reduce issues like leaky gut syndrome, which may lead to long-term health problems.
The amino acid helps with nutrient absorption and lowers inflammation in the gut. This can lessen negative digestive symptoms, such as bloating or diarrhea, which often happen during stress. Moreover, this nutrient plays a vital role in metabolic processes in the gut. It helps restore balance and keeps the gut ecosystem healthy.
In conditions like Crohn’s disease or irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), glutamine supplementation can help improve gut health and ease symptoms. It is also important for stabilizing repair mechanisms in the digestive system, helping to prevent long-term gut-related problems.
Role in the Gut-Brain Axis
Modern research is showing how our gut and brain are connected. L-Glutamine is an important nutrient that links these two systems. It helps keep the gut healthy, which in turn boosts brain function by improving nutrient absorption and keeping metabolism balanced. L-Glutamine helps protect the gut walls and reduces inflammation that can harm brain health due to metabolic processes.
This amino acid helps make neurotransmitters, which are essential for communication between gut function and clear thinking. It also supports the brain’s performance, especially during stress or mental fatigue. This connection between gut and brain health shows how important L-Glutamine is for overall wellness.
By improving both gut health and mental sharpness, L-Glutamine strengthens the link between the mind and body. Its nutritional benefits help increase daily performance and tackle health issues by playing many different roles.
Promotes Muscle Recovery and Growth
Muscle growth and recovery depend a lot on protein synthesis. This makes L-Glutamine very important for people who are active. After workouts, higher levels of glutamine help fix muscle fibers and reduce soreness. This speeds up recovery and improves athletic performance.
This amino acid helps build muscle mass by giving the essential material needed for proteins. Good levels of glutamine in our bodies also support immune function after exercise. This helps the body recover well.
Moreover, L-Glutamine boosts metabolism and helps move nutrients to tired muscles, speeding up recovery. These advantages make it a key part of fitness routines. Athletes often use dietary supplements of L-Glutamine to support endurance training and strength-building exercises.
Potential Role in Weight Management
L-Glutamine is helpful for managing weight. It helps balance metabolic processes in the body. By controlling how much glucose is produced, it can reduce strong cravings for sugar. This leads to maintaining a healthy weight. It also targets belly fat, making it useful for losing fat.
This amino acid increases fat burning during exercises, which helps with weight loss. Taking glutamine can also lower inflammation in people who are overweight. This is good for normal body functions that are related to weight control.
Additionally, glutamine benefits gut health. It strengthens the barriers in the intestines that help with absorbing nutrients and digestion. With its ability to enhance metabolism, glutamine is a great support for weight loss and improving body shape over time.
Use in Crohn’s Disease Management
Crohn’s disease is marked by long-lasting inflammation in the digestive system. So, managing this condition is very important for good health. L-glutamine is a special type of amino acid that helps gut function. It supports the intestinal barrier and helps reduce something known as “leaky gut.” Clinical trials have shown positive effects on inflammation and immune function in people with Crohn’s disease. This suggests that glutamine supplementation could help lessen abdominal pain and improve how nutrients are absorbed. Remember, it is important to talk to healthcare professionals before starting glutamine supplementation for the best medical advice.
L-Glutamine and Fitness

L-glutamine is an important amino acid in fitness. It helps with muscle recovery and boosts athletic performance. This amino acid is conditionally essential, meaning it plays a key role in protein synthesis. It helps build muscle mass and reduces the breakdown of protein after exercise. L-glutamine also manages oxidative stress and supports gut health. This can help improve energy levels during workouts. By using dietary supplements or getting L-glutamine from natural sources, athletes can enhance their training and recovery for better results.
Role in Muscle Building
Building muscle effectively needs amino acids, especially L-glutamine. This important amino acid helps with protein synthesis. It supports muscle recovery by reducing soreness and speeding up healing after tough workouts. L-glutamine is also a key energy source for muscle cells. It plays a role in keeping nitric oxide levels stable, which helps blood flow and nutrient delivery. Having enough L-glutamine also boosts immune function. This is very important for athletes who deal with oxidative stress from intense training.
Impact on Athletic Performance
Supplementing with L-glutamine can really help improve athletic performance. It supports muscle recovery and boosts endurance. This amino acid is important for protein synthesis, which helps repair muscles after tough workouts. It might also reduce oxidative stress caused by exercise. This means athletes can train more without dealing with painful muscle soreness. Plus, L-glutamine can improve immune function, which helps athletes keep training without taking time off due to illness or injury. In short, this amino acid can be a great part of an athlete’s nutrition plan.
Dosage Recommendations for Athletes
For athletes looking to improve their performance and recovery, it’s often suggested to take 5 to 10 grams of L-Glutamine each day. This amount can be split into several doses, preferably taken after workouts to help with muscle recovery and protein synthesis. Athletes who train hard or compete in endurance events might need a bit more, up to 20 grams a day. Everyone’s needs can be different based on their weight, how active they are, and any health issues. It’s important to talk with a healthcare provider before starting to take any supplements.
Natural Sources of L-Glutamine

L-Glutamine is found in many foods that are good for your health and provide amino acids. You can get it from beef, chicken, fish, eggs, dairy products, and some legumes. These foods help with protein synthesis and support muscle recovery. Vegetables like spinach, cabbage, and parsley also have this important compound. Plus, your body can make glutamine on its own. This is especially important during times of extra stress, like when you are sick or exercising hard. This helps keep your immune system strong.
Dietary Sources
Many foods are great sources of this important amino acid. Meat, fish, and dairy products help make protein and are good for muscle health. If you prefer plant-based options, beans, lentils, and nuts are also rich in L-Glutamine. This is especially useful for vegetarians or vegans. Eating these foods can boost gut function and support your immune system. They also help you get a wider range of nutrients for better health.
Endogenous Production
L-Glutamine is a conditionally essential amino acid. This means that sometimes, the body needs more than it can make. The body mostly makes it in the muscles. It is important for many metabolic processes. It helps with protein synthesis and supports the immune system. When the body is under stress, like during infections or severe burns, the need for glutamine goes up. This is why using dietary supplements or eating foods that contain glutamine is important to keep gut health and overall well-being at good levels.
Table: Top Food Sources of L-Glutamine
|
Food Category |
Specific Foods |
Why Rich in L-Glutamine? |
Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Animal-Based |
Beef, chicken, pork, fish (cod, salmon), eggs, dairy (milk, yogurt, cheese) |
High in complete proteins; contains all essential amino acids |
Muscle growth, immune support, gut health |
|
Plant-Based |
Beans (black, kidney), lentils, tofu, tempeh, spinach, cabbage, parsley |
Plant proteins with moderate glutamine; ideal for vegetarians |
Supports digestion, vegan-friendly, fiber-rich |
|
Bone Broth |
Homemade chicken/beef bone broth |
Slow cooking releases glutamine from bones/cartilage |
Joint and gut lining repair, immune function |
|
Fermented Foods |
Miso, kimchi, sauerkraut |
Fermentation boosts free glutamine content |
Gut microbiome balance, anti-inflammatory |
|
Nuts & Seeds |
Almonds, pumpkin seeds, peanuts |
Contains some glutamine but lower than animal sources |
Brain and heart health, plant-based protein |
L-Glutamine Supplementation
Individuals who want to boost their fitness often look into glutamine supplementation. This amino acid is important for muscle recovery and overall health. It helps reduce oxidative stress after tough workouts, supports immune function, and lessens muscle soreness. Athletes with tough training schedules need to take guided doses. This helps them get the most benefits and avoid adverse effects. Talking to healthcare professionals can lead to good dosage recommendations based on personal needs. This ensures safety and enhances performance in different activities. Using l-glutamine carefully may lead to better results.
When Supplementation Is Needed
Supplementation can be important in some health situations. This is especially true for people with weak gut health or conditions like inflammatory bowel disease. Clinical trials show that those who have surgery or are dealing with severe burns can gain a lot from glutamine supplementation. It helps with immune function and recovery. Athletes who train hard may also find that supplementation helps their muscle recovery and reduces oxidative stress after workouts. If you notice symptoms like abdominal pain or other digestive issues, it may be a sign that you need extra support.
Dosage Recommendations
Determining the right amount of L-Glutamine is important for getting its health benefits without causing any bad effects. For people with gut issues, like Crohn’s disease, a common suggestion is to take between 5 and 30 grams a day. It’s best to split this into several smaller doses for better absorption. Healthy adults who do intense exercise might also benefit from a similar amount, which is usually around 10 to 20 grams each day. But, it’s important to talk to a healthcare provider to customize the dosage for your specific health needs and to get the best results.
Available Supplement Forms
There are many types of L-Glutamine supplements to meet different needs and likes. They usually come in powders, capsules, and pills. This variety makes them easy to use for different lifestyles. The oral powder form is very popular. It can be mixed with drinks, making it easy to take after exercising. Some also come in liquid form, which helps the body absorb them faster. There are also dietary supplements that combine L-Glutamine with other amino acids or minerals. This can help with muscle recovery and improve immune function. Choosing the right type can make sure you get the best benefits, especially for people with certain health issues.
|
Supplement Form |
Description |
Pros / Advantages |
Cons / Considerations |
Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Powder |
Fine, loose L-Glutamine powder, typically mixed with water, juice, or shakes. |
– Most cost-effective per gram |
– Requires mixing (less convenient) |
Post-workout recovery or therapeutic doses |
|
Capsules |
L-Glutamine powder enclosed in a gelatin or vegetarian shell. Swallowed whole. |
– Convenient and portable |
– Less cost-effective per gram |
Daily maintenance or travel-friendly option |
|
Tablets |
Compressed L-Glutamine powder, often with binders/fillers. Swallowed whole. |
– Convenient and portable |
– Can be large and harder to swallow |
Routine supplementation for general wellness |
|
Liquid (Less Common) |
L-Glutamine dissolved or suspended in a liquid base. |
– Potentially faster absorption |
– Often more expensive |
For people who have difficulty swallowing pills |
Potential Side Effects and Precautions

Supplementation can cause mild side effects for some people. This includes digestive issues, like abdominal pain or bloating. While it is usually safe, taking too much can lead to adverse effects, such as headaches and muscle soreness. People with certain health problems, especially those related to the digestive system or kidneys, should be careful. It’s important to talk to a healthcare professional before adding L-Glutamine to your routine. This helps ensure safe and effective use. Always watch for unusual symptoms and stop using it if any severe reactions happen.
Common Side Effects
L-glutamine is often thought to be safe. However, it can cause side effects in some people. You might have digestive problems, like abdominal pain and diarrhea, especially if you take higher doses. Some users could also feel mild symptoms in their nerves, such as headaches or dizziness. These side effects usually go away if you keep taking it or adjust the dosage properly. It’s really important to talk to a healthcare provider before you start using glutamine supplementation. This is especially important for those with chronic health issues. They can help make sure it’s safe and effective for you.
Medication Interactions
Some medications can change how L-Glutamine works. They might make it less effective or increase the chance of side effects. This is especially true for drugs that affect the immune system because L-Glutamine can change immune function. If you are on chemotherapy or other cancer treatments, it is important to talk to your doctor. This is because your body might react differently to glutamine supplementation. Always discuss any dietary supplements, like L-Glutamine, with a healthcare provider. This will help you avoid adverse effects and make sure the supplement fits your health needs.
Toxicity and Overdose
L-Glutamine is considered safe if used correctly. However, taking too much can be harmful and may lead to an overdose. Signs of an overdose can include abdominal pain, nausea, and other problems with the digestive system. It is important to watch how much you take, especially if you have health issues or are on medicines that affect your immune function or digestive system. Talking to a healthcare professional before starting this supplement can help reduce risks and check for any adverse effects. Also, knowing how it works can help you use it safely and enjoy its benefits.
Who Should Avoid L-Glutamine
Certain people might want to think about not using L-Glutamine supplements. Those who have liver issues should be careful. When the liver does not work well, it can change how our bodies process amino acids. Also, people with certain metabolic disorders related to amino acids could have bad reactions. Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should talk to a doctor before adding these supplements to their routine. Lastly, anyone who is allergic to glutamine or its parts should avoid it to stop any allergic reactions. Always ask for medical advice for help that fits your needs.
L-Glutamine Deficiency

A lack of L-glutamine can happen for a few reasons. Serious illness or stress can require more of this important amino acid. You might notice signs like fatigue, weak muscles, or a lower immune function, telling you that you may need to change your diet or add supplements. Doctors usually check for low glutamine levels through clinical evaluations and blood tests. To fix this deficiency, you could eat more foods that are high in glutamine or take glutamine supplements. This can help your muscle recovery and support gut health, which is good for your overall well-being.
Causes of Deficiency
Some things can cause a lack of this important amino acid. Stressful situations, like surgery or severe burns, lower glutamine levels a lot. The body uses it to heal and support immune function. Also, health problems, such as chronic diseases or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), can make it hard to absorb glutamine in the digestive system, leading to low amounts. High-intensity exercise can raise the need for glutamine, especially in athletes. This need might not be met by diet alone.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Symptoms of low L-Glutamine levels can include tiredness, weak muscles, and getting sick often because the immune system does not work well. People with diseases like Crohn’s disease or sickle cell anemia may also have stomach problems, like abdominal pain or bloating. This happens because their digestive system struggles to take in nutrients properly. To diagnose low levels, doctors usually check what you eat and your medical history. They also do blood tests to look at amino acid levels. Findings from clinical trials may help us understand more about symptoms related to glutamine deficiency.
How to Address Low Glutamine Levels
Addressing low glutamine levels can be done in different ways. Using dietary supplements like oral powders that are high in this important amino acid can really help. Foods such as meat, dairy, and legumes also play a good role. Plus, doing specific exercises that help with muscle recovery may increase the body’s natural production. It is important to talk to healthcare professionals, especially if there are other health issues. They can help create a plan that improves immune function and supports gut health. Watching and making changes based on clinical trials can cause noticeable improvements.
Table: Common Triggers Behind Low L-Glutamine Levels
|
Category |
Specific Causes |
Mechanism/Explanation |
|---|---|---|
|
Dietary Insufficiency |
– Low-protein diet |
Reduced intake of glutamine-rich foods (meat, fish, eggs, dairy) |
|
Increased Demand |
– Intense exercise/athletic training |
Higher glutamine utilization for muscle repair, immune function, and stress response |
|
Digestive Disorders |
– Leaky gut syndrome |
Impaired gut absorption and increased intestinal glutamine consumption |
|
Medical Conditions |
– Cancer/cachexia |
Hypermetabolic states deplete glutamine stores |
|
Aging |
– Natural decline in muscle mass (sarcopenia) |
Lower endogenous production |
Conclusion
Adding L-Glutamine to your daily routine can offer many health and fitness benefits. This amino acid is important for muscle recovery, helps build proteins, and can improve your athletic performance. Knowing how it works and getting enough from food or supplements can help boost your immune function and digestive health. Like any supplement, it’s important to be aware of possible side effects and to use the right doses. This way, you can enjoy the positive effects while keeping risks low. Including L-Glutamine in your routine may help you reach your health and fitness goals.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is L-Glutamine safe to take every day?
L-glutamine is usually safe for daily use if you follow the recommended doses. Still, if you have specific health issues or take certain medicines, talk to a doctor before starting to take it. This way, you can avoid any side effects or interactions. Always focus on being safe and using it in moderation.
Is L-Glutamine safe for long-term use?
Using L-glutamine for a long time is usually safe for most people. Still, it is important to talk to a doctor before starting the supplement. This is especially true for anyone with health issues or those on medications that could mix with glutamine. Always follow the recommended doses.
When is the best time to take L-Glutamine?
The best time to take L-glutamine is after a workout or right before bed. After you exercise, it helps with recovery and muscle repair. Taking it before you sleep aids in overnight recovery. Being consistent with the timing can help both athletes and those who want to improve their health.
Are there any risks of taking L-Glutamine with other supplements?
L-glutamine is usually safe to use. However, combining it with some supplements can pose risks. These interactions might cause stomach problems or change how well you absorb nutrients. It is important to talk to a healthcare professional before mixing L-glutamine with any other supplements. This will help you stay safe and make sure it works well for you.
Can L-Glutamine help with leaky gut?
L-glutamine might help gut health. It can strengthen the intestinal barrier and lower inflammation. This may reduce symptoms of leaky gut syndrome. But more studies are needed to prove how effective it is for this specific issue. Always talk to a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement.
Can L-Glutamine help with weight loss?
L-Glutamine might help with weight loss by boosting metabolism and lowering cravings. It doesn’t directly burn fat, but it helps keep muscles and aids recovery. This can make you more active, which may help you burn more calories while exercising. Always talk to a healthcare professional before taking any supplements.
Are there any risks associated with L-Glutamine supplementation?
L-glutamine supplementation is usually safe. However, some people might have side effects. This can include stomach issues or allergies. It is important to talk to your doctor, especially if you have health problems or are on medications. This can help avoid any possible interactions.
Can vegetarians get enough L-Glutamine from their diet?
Yes, vegetarians can get enough L-glutamine from many plant-based foods like beans, lentils, spinach, and cabbage. These foods might have less L-glutamine than animal products. However, if you combine them with other protein-rich vegetarian options, you can meet your daily needs well.
Introduction
L-Glutamine is an important amino acid that plays a key role in many functions of the body. It is not usually considered an essential amino acid, but during times of stress or illness, it becomes conditionally essential. This means that you may need to take dietary supplements to get enough of it. L-Glutamine is crucial for protein synthesis. It also helps support the immune and digestive systems. Whether you focus on health or fitness, L-Glutamine offers many benefits that fit different needs.
What is L-Glutamine?
L-Glutamine is a powerful amino acid that is very important for the body. It becomes even more crucial during high-stress times, like when you are sick, because the body may not make enough. As a conditionally essential amino acid, it does more than just help build protein. It also supports immune function and helps produce glucose.
This amino acid is part of many processes in the body, which ties its importance to health and physical performance. It helps in muscle recovery after workouts and supports gut health too. Because of these benefits, many people choose to take it as a dietary supplement. Plus, new research keeps showing more ways L-Glutamine may help, like in treating certain chronic diseases or in weight management.
Definition and Basic Information
L-Glutamine is a very important amino acid. It helps with protein synthesis and is vital for how the body works. Even though it is a nonessential amino acid, the body needs more of it during stress, illnesses, or intense exercise. This makes it a conditionally essential amino acid. It is a key part of proteins and glucose, which helps keep cells healthy.
This amino acid is also crucial for your immune system and gut health. It boosts gut function by providing energy to intestinal cells, which can help stop leaky gut syndrome. Additionally, L-Glutamine is important for supporting the immune system during recovery. It aids in metabolic processes, forming building blocks for other amino acids. Its wide-ranging benefits highlight its powerful role in the body.
L-Glutamine shows that it can adapt to different health issues and physical needs. It helps keep blood pH levels stable and supports red blood cells. This makes it essential for overall health.
Different Forms of Glutamine in the Body
Glutamine is important for many processes in the body. It helps with bodily functions in clear ways. Inside the body, it changes into different forms, with amino acids being key for protein synthesis. Red blood cells are essential for carrying nutrients and oxygen. They depend a lot on glutamine for energy and support.
Glutamine moves through blood cells, making sure it is available when the body is under stress or facing trauma. It helps produce glucose and supports immune function, especially when recovering from illness. Its ability to work within cells is crucial for sustaining life.
Glutamine also plays a role in communication between cells, especially in metabolic processes. It connects the functions of red blood cells with regulating energy production, which is essential for daily activities and athletic performance. This flexibility shows how important glutamine is for keeping the body balanced and healthy.
L-Glutamine vs. D-Glutamine
L-Glutamine and D-Glutamine have the same molecular structure, but they play different roles in the body. L-Glutamine is the form that works actively. It helps with metabolic processes, protein synthesis, and energy production in humans. D-Glutamine, on the other hand, does not offer any functional benefits for these needs.
L-Glutamine is important for the immune function and helps in muscle recovery. It is the best form for gut health. It supports the intestinal wall, helping to prevent digestive issues and leaky gut. In contrast, D-Glutamine has very limited use.
Most research looks at L-Glutamine because it is involved in building protein, increasing muscle mass, and providing nutrients for cell repair. Its presence in dietary supplements shows how important it is for metabolic processes. D-Glutamine does not play the same role.
|
Feature |
L-Glutamine |
D-Glutamine |
|---|---|---|
|
Basic Identity |
An amino acid |
An amino acid |
|
Chirality |
L-isomer (Levorotatory stereoisomer) |
D-isomer (Dextrorotatory stereoisomer) |
|
Structure |
Naturally occurring configuration in humans/animals |
Mirror image of L-Glutamine |
|
Biological Occurrence |
Abundant in nature; most abundant free amino acid in human blood and muscle |
Rare in nature, especially in higher organisms. Found in some bacterial cell walls or synthesized by certain microbes |
|
Role in Protein Synthesis |
Incorporated into proteins by ribosomes |
Not incorporated into proteins by human/animal ribosomes |
|
Metabolic Role |
Crucial metabolic fuel (especially for gut & immune cells), nitrogen transport, neurotransmitter precursor (glutamate, GABA), glutathione synthesis |
Generally considered biologically inactive or poorly metabolized in humans. May interfere with L-glutamine pathways |
|
Human Body Utilization |
Readily utilized and essential for many functions |
Poorly utilized or recognized by human metabolic pathways |
|
Dietary Sources |
Found naturally in protein-rich foods (meat, dairy, eggs, beans, etc.) |
Not typically found in natural food sources for humans |
|
Supplementation |
Widely available and used as a dietary supplement (sports nutrition, gut health, clinical support) |
Not used as a dietary supplement. Can be an impurity in L-Glutamine supplements |
|
Research Focus |
Extensively researched for its physiological roles and therapeutic potential |
Much less researched. Sometimes studied for specific microbial processes or as a non-metabolizable control |
|
Primary Significance |
Biologically active and essential form in humans |
Primarily relevant in specific microbial contexts or as a chemical isomer |
Health Benefits of L-Glutamine

L-Glutamine provides many health benefits. It is important for good performance and recovery. For immune function, it helps cells like lymphocytes and macrophages work well against germs. It also improves gut health by making the stomach barriers stronger.
Other benefits include improving mental clarity because of the connection between the gut and brain. It also helps with weight management because of its part in metabolic processes. Additionally, it helps with muscle recovery, making it essential for fitness and overall well-being.
Enhances Immune System Function
The immune system works best when it is efficient. L-Glutamine plays an important role in keeping it that way. This amino acid acts as food for immune cells like lymphocytes and macrophages. This helps them fight infections strong. Glutamine also helps red blood cells deliver important nutrients that boost immune function, especially during physical stress.
When you are sick or under a lot of stress, your body needs more glutamine. This shows how important it is for recovery. It helps the immune system recover, especially after surgery or injury, when the need goes way up. Plus, glutamine helps metabolic processes that are important for fighting off germs.
Taking L-Glutamine can really help with immune efficiency. It supports recovery during health challenges and builds strength against them. It is clear that L-Glutamine not only strengthens immunity but also helps with the function of red blood cells.
Supports Gut Health
L-Glutamine is very important for gut health. It provides energy to the cells in the intestines. These cells rely on glutamine, helping keep the gut function stable and supporting the digestive system. Strengthening the intestinal walls can reduce issues like leaky gut syndrome, which may lead to long-term health problems.
The amino acid helps with nutrient absorption and lowers inflammation in the gut. This can lessen negative digestive symptoms, such as bloating or diarrhea, which often happen during stress. Moreover, this nutrient plays a vital role in metabolic processes in the gut. It helps restore balance and keeps the gut ecosystem healthy.
In conditions like Crohn’s disease or irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), glutamine supplementation can help improve gut health and ease symptoms. It is also important for stabilizing repair mechanisms in the digestive system, helping to prevent long-term gut-related problems.
Role in the Gut-Brain Axis
Modern research is showing how our gut and brain are connected. L-Glutamine is an important nutrient that links these two systems. It helps keep the gut healthy, which in turn boosts brain function by improving nutrient absorption and keeping metabolism balanced. L-Glutamine helps protect the gut walls and reduces inflammation that can harm brain health due to metabolic processes.
This amino acid helps make neurotransmitters, which are essential for communication between gut function and clear thinking. It also supports the brain’s performance, especially during stress or mental fatigue. This connection between gut and brain health shows how important L-Glutamine is for overall wellness.
By improving both gut health and mental sharpness, L-Glutamine strengthens the link between the mind and body. Its nutritional benefits help increase daily performance and tackle health issues by playing many different roles.
Promotes Muscle Recovery and Growth
Muscle growth and recovery depend a lot on protein synthesis. This makes L-Glutamine very important for people who are active. After workouts, higher levels of glutamine help fix muscle fibers and reduce soreness. This speeds up recovery and improves athletic performance.
This amino acid helps build muscle mass by giving the essential material needed for proteins. Good levels of glutamine in our bodies also support immune function after exercise. This helps the body recover well.
Moreover, L-Glutamine boosts metabolism and helps move nutrients to tired muscles, speeding up recovery. These advantages make it a key part of fitness routines. Athletes often use dietary supplements of L-Glutamine to support endurance training and strength-building exercises.
Potential Role in Weight Management
L-Glutamine is helpful for managing weight. It helps balance metabolic processes in the body. By controlling how much glucose is produced, it can reduce strong cravings for sugar. This leads to maintaining a healthy weight. It also targets belly fat, making it useful for losing fat.
This amino acid increases fat burning during exercises, which helps with weight loss. Taking glutamine can also lower inflammation in people who are overweight. This is good for normal body functions that are related to weight control.
Additionally, glutamine benefits gut health. It strengthens the barriers in the intestines that help with absorbing nutrients and digestion. With its ability to enhance metabolism, glutamine is a great support for weight loss and improving body shape over time.
Use in Crohn’s Disease Management
Crohn’s disease is marked by long-lasting inflammation in the digestive system. So, managing this condition is very important for good health. L-glutamine is a special type of amino acid that helps gut function. It supports the intestinal barrier and helps reduce something known as “leaky gut.” Clinical trials have shown positive effects on inflammation and immune function in people with Crohn’s disease. This suggests that glutamine supplementation could help lessen abdominal pain and improve how nutrients are absorbed. Remember, it is important to talk to healthcare professionals before starting glutamine supplementation for the best medical advice.
L-Glutamine and Fitness

L-glutamine is an important amino acid in fitness. It helps with muscle recovery and boosts athletic performance. This amino acid is conditionally essential, meaning it plays a key role in protein synthesis. It helps build muscle mass and reduces the breakdown of protein after exercise. L-glutamine also manages oxidative stress and supports gut health. This can help improve energy levels during workouts. By using dietary supplements or getting L-glutamine from natural sources, athletes can enhance their training and recovery for better results.
Role in Muscle Building
Building muscle effectively needs amino acids, especially L-glutamine. This important amino acid helps with protein synthesis. It supports muscle recovery by reducing soreness and speeding up healing after tough workouts. L-glutamine is also a key energy source for muscle cells. It plays a role in keeping nitric oxide levels stable, which helps blood flow and nutrient delivery. Having enough L-glutamine also boosts immune function. This is very important for athletes who deal with oxidative stress from intense training.
Impact on Athletic Performance
Supplementing with L-glutamine can really help improve athletic performance. It supports muscle recovery and boosts endurance. This amino acid is important for protein synthesis, which helps repair muscles after tough workouts. It might also reduce oxidative stress caused by exercise. This means athletes can train more without dealing with painful muscle soreness. Plus, L-glutamine can improve immune function, which helps athletes keep training without taking time off due to illness or injury. In short, this amino acid can be a great part of an athlete’s nutrition plan.
Dosage Recommendations for Athletes
For athletes looking to improve their performance and recovery, it’s often suggested to take 5 to 10 grams of L-Glutamine each day. This amount can be split into several doses, preferably taken after workouts to help with muscle recovery and protein synthesis. Athletes who train hard or compete in endurance events might need a bit more, up to 20 grams a day. Everyone’s needs can be different based on their weight, how active they are, and any health issues. It’s important to talk with a healthcare provider before starting to take any supplements.
Natural Sources of L-Glutamine

L-Glutamine is found in many foods that are good for your health and provide amino acids. You can get it from beef, chicken, fish, eggs, dairy products, and some legumes. These foods help with protein synthesis and support muscle recovery. Vegetables like spinach, cabbage, and parsley also have this important compound. Plus, your body can make glutamine on its own. This is especially important during times of extra stress, like when you are sick or exercising hard. This helps keep your immune system strong.
Dietary Sources
Many foods are great sources of this important amino acid. Meat, fish, and dairy products help make protein and are good for muscle health. If you prefer plant-based options, beans, lentils, and nuts are also rich in L-Glutamine. This is especially useful for vegetarians or vegans. Eating these foods can boost gut function and support your immune system. They also help you get a wider range of nutrients for better health.
Endogenous Production
L-Glutamine is a conditionally essential amino acid. This means that sometimes, the body needs more than it can make. The body mostly makes it in the muscles. It is important for many metabolic processes. It helps with protein synthesis and supports the immune system. When the body is under stress, like during infections or severe burns, the need for glutamine goes up. This is why using dietary supplements or eating foods that contain glutamine is important to keep gut health and overall well-being at good levels.
Table: Top Food Sources of L-Glutamine
|
Food Category |
Specific Foods |
Why Rich in L-Glutamine? |
Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Animal-Based |
Beef, chicken, pork, fish (cod, salmon), eggs, dairy (milk, yogurt, cheese) |
High in complete proteins; contains all essential amino acids |
Muscle growth, immune support, gut health |
|
Plant-Based |
Beans (black, kidney), lentils, tofu, tempeh, spinach, cabbage, parsley |
Plant proteins with moderate glutamine; ideal for vegetarians |
Supports digestion, vegan-friendly, fiber-rich |
|
Bone Broth |
Homemade chicken/beef bone broth |
Slow cooking releases glutamine from bones/cartilage |
Joint and gut lining repair, immune function |
|
Fermented Foods |
Miso, kimchi, sauerkraut |
Fermentation boosts free glutamine content |
Gut microbiome balance, anti-inflammatory |
|
Nuts & Seeds |
Almonds, pumpkin seeds, peanuts |
Contains some glutamine but lower than animal sources |
Brain and heart health, plant-based protein |
L-Glutamine Supplementation
Individuals who want to boost their fitness often look into glutamine supplementation. This amino acid is important for muscle recovery and overall health. It helps reduce oxidative stress after tough workouts, supports immune function, and lessens muscle soreness. Athletes with tough training schedules need to take guided doses. This helps them get the most benefits and avoid adverse effects. Talking to healthcare professionals can lead to good dosage recommendations based on personal needs. This ensures safety and enhances performance in different activities. Using l-glutamine carefully may lead to better results.
When Supplementation Is Needed
Supplementation can be important in some health situations. This is especially true for people with weak gut health or conditions like inflammatory bowel disease. Clinical trials show that those who have surgery or are dealing with severe burns can gain a lot from glutamine supplementation. It helps with immune function and recovery. Athletes who train hard may also find that supplementation helps their muscle recovery and reduces oxidative stress after workouts. If you notice symptoms like abdominal pain or other digestive issues, it may be a sign that you need extra support.
Dosage Recommendations
Determining the right amount of L-Glutamine is important for getting its health benefits without causing any bad effects. For people with gut issues, like Crohn’s disease, a common suggestion is to take between 5 and 30 grams a day. It’s best to split this into several smaller doses for better absorption. Healthy adults who do intense exercise might also benefit from a similar amount, which is usually around 10 to 20 grams each day. But, it’s important to talk to a healthcare provider to customize the dosage for your specific health needs and to get the best results.
Available Supplement Forms
There are many types of L-Glutamine supplements to meet different needs and likes. They usually come in powders, capsules, and pills. This variety makes them easy to use for different lifestyles. The oral powder form is very popular. It can be mixed with drinks, making it easy to take after exercising. Some also come in liquid form, which helps the body absorb them faster. There are also dietary supplements that combine L-Glutamine with other amino acids or minerals. This can help with muscle recovery and improve immune function. Choosing the right type can make sure you get the best benefits, especially for people with certain health issues.
|
Supplement Form |
Description |
Pros / Advantages |
Cons / Considerations |
Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Powder |
Fine, loose L-Glutamine powder, typically mixed with water, juice, or shakes. |
– Most cost-effective per gram |
– Requires mixing (less convenient) |
Post-workout recovery or therapeutic doses |
|
Capsules |
L-Glutamine powder enclosed in a gelatin or vegetarian shell. Swallowed whole. |
– Convenient and portable |
– Less cost-effective per gram |
Daily maintenance or travel-friendly option |
|
Tablets |
Compressed L-Glutamine powder, often with binders/fillers. Swallowed whole. |
– Convenient and portable |
– Can be large and harder to swallow |
Routine supplementation for general wellness |
|
Liquid (Less Common) |
L-Glutamine dissolved or suspended in a liquid base. |
– Potentially faster absorption |
– Often more expensive |
For people who have difficulty swallowing pills |
Potential Side Effects and Precautions

Supplementation can cause mild side effects for some people. This includes digestive issues, like abdominal pain or bloating. While it is usually safe, taking too much can lead to adverse effects, such as headaches and muscle soreness. People with certain health problems, especially those related to the digestive system or kidneys, should be careful. It’s important to talk to a healthcare professional before adding L-Glutamine to your routine. This helps ensure safe and effective use. Always watch for unusual symptoms and stop using it if any severe reactions happen.
Common Side Effects
L-glutamine is often thought to be safe. However, it can cause side effects in some people. You might have digestive problems, like abdominal pain and diarrhea, especially if you take higher doses. Some users could also feel mild symptoms in their nerves, such as headaches or dizziness. These side effects usually go away if you keep taking it or adjust the dosage properly. It’s really important to talk to a healthcare provider before you start using glutamine supplementation. This is especially important for those with chronic health issues. They can help make sure it’s safe and effective for you.
Medication Interactions
Some medications can change how L-Glutamine works. They might make it less effective or increase the chance of side effects. This is especially true for drugs that affect the immune system because L-Glutamine can change immune function. If you are on chemotherapy or other cancer treatments, it is important to talk to your doctor. This is because your body might react differently to glutamine supplementation. Always discuss any dietary supplements, like L-Glutamine, with a healthcare provider. This will help you avoid adverse effects and make sure the supplement fits your health needs.
Toxicity and Overdose
L-Glutamine is considered safe if used correctly. However, taking too much can be harmful and may lead to an overdose. Signs of an overdose can include abdominal pain, nausea, and other problems with the digestive system. It is important to watch how much you take, especially if you have health issues or are on medicines that affect your immune function or digestive system. Talking to a healthcare professional before starting this supplement can help reduce risks and check for any adverse effects. Also, knowing how it works can help you use it safely and enjoy its benefits.
Who Should Avoid L-Glutamine
Certain people might want to think about not using L-Glutamine supplements. Those who have liver issues should be careful. When the liver does not work well, it can change how our bodies process amino acids. Also, people with certain metabolic disorders related to amino acids could have bad reactions. Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should talk to a doctor before adding these supplements to their routine. Lastly, anyone who is allergic to glutamine or its parts should avoid it to stop any allergic reactions. Always ask for medical advice for help that fits your needs.
L-Glutamine Deficiency

A lack of L-glutamine can happen for a few reasons. Serious illness or stress can require more of this important amino acid. You might notice signs like fatigue, weak muscles, or a lower immune function, telling you that you may need to change your diet or add supplements. Doctors usually check for low glutamine levels through clinical evaluations and blood tests. To fix this deficiency, you could eat more foods that are high in glutamine or take glutamine supplements. This can help your muscle recovery and support gut health, which is good for your overall well-being.
Causes of Deficiency
Some things can cause a lack of this important amino acid. Stressful situations, like surgery or severe burns, lower glutamine levels a lot. The body uses it to heal and support immune function. Also, health problems, such as chronic diseases or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), can make it hard to absorb glutamine in the digestive system, leading to low amounts. High-intensity exercise can raise the need for glutamine, especially in athletes. This need might not be met by diet alone.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Symptoms of low L-Glutamine levels can include tiredness, weak muscles, and getting sick often because the immune system does not work well. People with diseases like Crohn’s disease or sickle cell anemia may also have stomach problems, like abdominal pain or bloating. This happens because their digestive system struggles to take in nutrients properly. To diagnose low levels, doctors usually check what you eat and your medical history. They also do blood tests to look at amino acid levels. Findings from clinical trials may help us understand more about symptoms related to glutamine deficiency.
How to Address Low Glutamine Levels
Addressing low glutamine levels can be done in different ways. Using dietary supplements like oral powders that are high in this important amino acid can really help. Foods such as meat, dairy, and legumes also play a good role. Plus, doing specific exercises that help with muscle recovery may increase the body’s natural production. It is important to talk to healthcare professionals, especially if there are other health issues. They can help create a plan that improves immune function and supports gut health. Watching and making changes based on clinical trials can cause noticeable improvements.
Table: Common Triggers Behind Low L-Glutamine Levels
|
Category |
Specific Causes |
Mechanism/Explanation |
|---|---|---|
|
Dietary Insufficiency |
– Low-protein diet |
Reduced intake of glutamine-rich foods (meat, fish, eggs, dairy) |
|
Increased Demand |
– Intense exercise/athletic training |
Higher glutamine utilization for muscle repair, immune function, and stress response |
|
Digestive Disorders |
– Leaky gut syndrome |
Impaired gut absorption and increased intestinal glutamine consumption |
|
Medical Conditions |
– Cancer/cachexia |
Hypermetabolic states deplete glutamine stores |
|
Aging |
– Natural decline in muscle mass (sarcopenia) |
Lower endogenous production |
Conclusion
Adding L-Glutamine to your daily routine can offer many health and fitness benefits. This amino acid is important for muscle recovery, helps build proteins, and can improve your athletic performance. Knowing how it works and getting enough from food or supplements can help boost your immune function and digestive health. Like any supplement, it’s important to be aware of possible side effects and to use the right doses. This way, you can enjoy the positive effects while keeping risks low. Including L-Glutamine in your routine may help you reach your health and fitness goals.
The content on WellwayHub.com is intended for general informational purposes only and should not be taken as medical advice. Please consult your doctor or a qualified health professional before making any changes to your health routine.
Some links on WellwayHub.com may be affiliate links. This means we may earn a small commission if you make a purchase through these links, at no extra cost to you. This helps support our mission to provide trusted wellness content.
Frequently Asked Questions
L-glutamine is usually safe for daily use if you follow the recommended doses. Still, if you have specific health issues or take certain medicines, talk to a doctor before starting to take it. This way, you can avoid any side effects or interactions. Always focus on being safe and using it in moderation.
Using L-glutamine for a long time is usually safe for most people. Still, it is important to talk to a doctor before starting the supplement. This is especially true for anyone with health issues or those on medications that could mix with glutamine. Always follow the recommended doses.
The best time to take L-glutamine is after a workout or right before bed. After you exercise, it helps with recovery and muscle repair. Taking it before you sleep aids in overnight recovery. Being consistent with the timing can help both athletes and those who want to improve their health.
L-glutamine is usually safe to use. However, combining it with some supplements can pose risks. These interactions might cause stomach problems or change how well you absorb nutrients. It is important to talk to a healthcare professional before mixing L-glutamine with any other supplements. This will help you stay safe and make sure it works well for you.
L-glutamine might help gut health. It can strengthen the intestinal barrier and lower inflammation. This may reduce symptoms of leaky gut syndrome. But more studies are needed to prove how effective it is for this specific issue. Always talk to a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement.
L-Glutamine might help with weight loss by boosting metabolism and lowering cravings. It doesn’t directly burn fat, but it helps keep muscles and aids recovery. This can make you more active, which may help you burn more calories while exercising. Always talk to a healthcare professional before taking any supplements.
L-glutamine supplementation is usually safe. However, some people might have side effects. This can include stomach issues or allergies. It is important to talk to your doctor, especially if you have health problems or are on medications. This can help avoid any possible interactions.
Yes, vegetarians can get enough L-glutamine from many plant-based foods like beans, lentils, spinach, and cabbage. These foods might have less L-glutamine than animal products. However, if you combine them with other protein-rich vegetarian options, you can meet your daily needs well.