
Embarking on a journey to better understand the role of Vitamin B in your overall wellness can be enlightening. You might have heard about its significance, but do you know the diverse types of Vitamin B and their unique contributions to your health? From Thiamin (B1) to Cyanocobalamin (B12), each vitamin plays a crucial role in your body’s functioning. In this blog, we will delve into the world of B-group vitamins, exploring their individual benefits and sources. We will also discuss when it might be necessary to consider Vitamin B supplements and how they differ from obtaining these essential nutrients through food. Get ready to unlock the secrets behind Vitamin B essentials for your well-being!
What is Vitamin B Complex? Benefits & Importance

B-group vitamins are a set of eight important nutrients needed for good health. Each B vitamin has its own chemical makeup and performs different tasks in the body. They usually work together to help with metabolic processes, change food into energy, and keep cells and organs working well.
These vitamins are very important for the nervous system. They help create neurotransmitters and keep nerve cells healthy. They also help make red blood cells, which move oxygen around the body. Plus, they are crucial for DNA synthesis and cell division, which are necessary for growth and repair.
8 Essential B Vitamins: Types & Their Roles
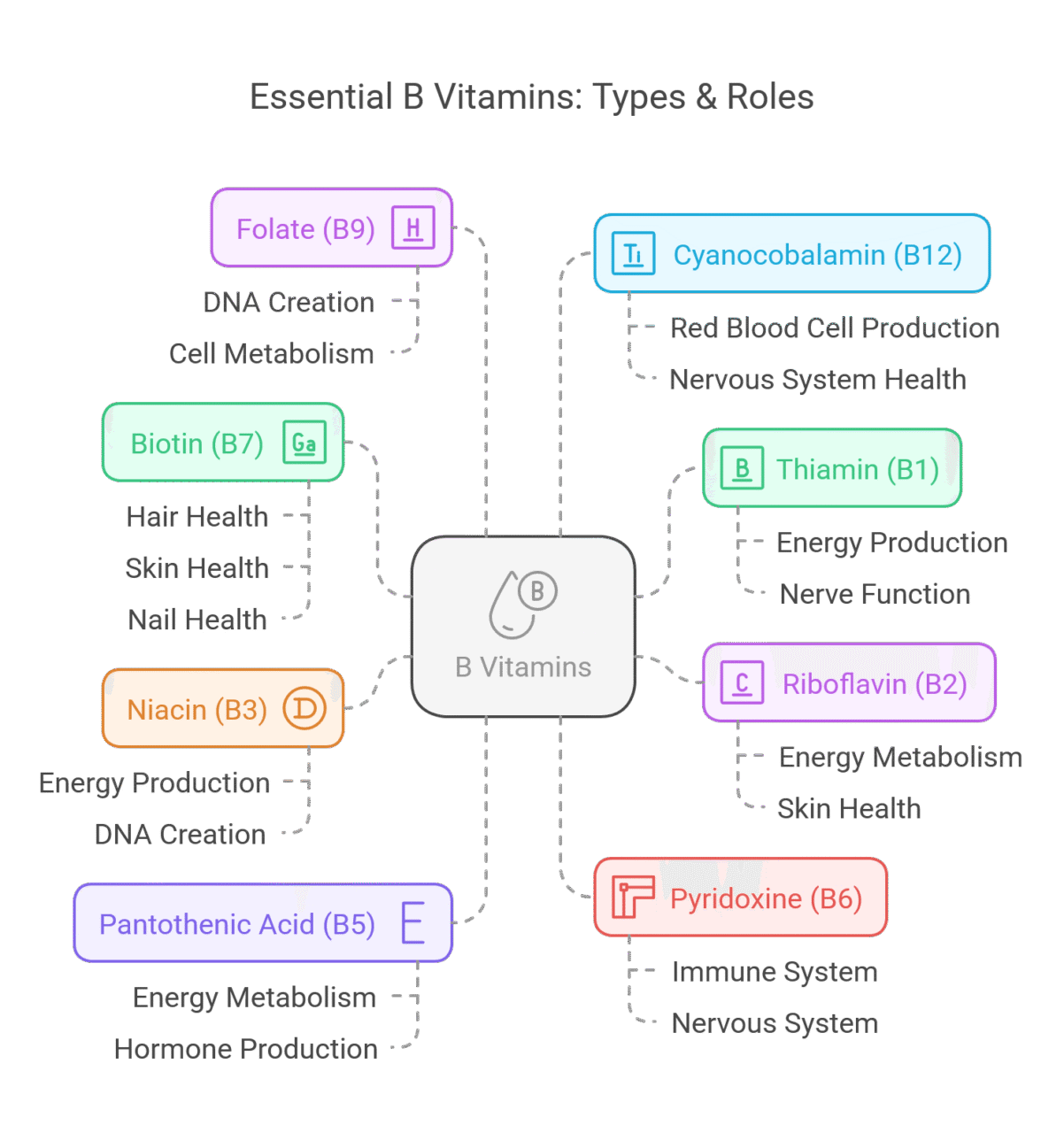
The B vitamin family has eight water-soluble vitamins. These are thiamin (B1), riboflavin (B2), niacin (B3), pantothenic acid (B5), vitamin B6 (pyridoxine), biotin (B7), folate or folic acid (B9), and cyanocobalamin (B12). Being water-soluble means that these vitamins do not stay in the body for a long time. Any extra amounts are usually released in urine. It is important to get these vitamins often through food or supplements.
Each B vitamin has its own important job in the body. If you do not get enough of any B vitamin, it can cause health issues. For example, pantothenic acid is important for energy production and making hormones. Folic acid is vital for cell growth and division, especially during pregnancy.
Vitamin B1 (Thiamin): Benefits, Foods & Deficiency Symptoms
Thiamin, or vitamin B1, is important for how our body gets energy and how our nerves work. It helps turn carbohydrates into energy. This vitamin is also needed for the nervous system to work properly. If someone does not get enough thiamin, they may develop serious issues, such as beriberi, which can harm their heart and muscles. To keep good health and energy levels, it is important to eat foods high in thiamin, like whole grains, pork, nuts, and seeds. This B vitamin is essential for our overall well-being and vitality.
Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin): Health Benefits & Food Sources
Riboflavin, or vitamin B2, is important for energy production and metabolism. It helps in forming red blood cells and keeps your skin healthy. If you do not get enough riboflavin, it can cause health problems like skin issues and anemia. You can find good sources of riboflavin in dairy products, whole grains, and leafy green vegetables. It is important to get enough riboflavin for your overall health and well-being.
Vitamin B3 (Niacin): Functions, Foods & Signs of Deficiency
Niacin, or vitamin B3, is important for making energy and creating DNA. It helps in forming red blood cells and supports the nervous system. You can find niacin in many foods, like meat, fish, and nuts. Not getting enough niacin can cause tiredness and skin problems. Including foods that are high in niacin in your diet can help you keep good health and feel better overall.
Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid): Role in Energy Metabolism
Pantothenic acid, or vitamin B5, is very important for energy production and how our bodies break down fats, proteins, and carbohydrates. It helps in forming red blood cells and keeps our digestive system healthy. You can find pantothenic acid in foods like whole grains, leafy green vegetables, and dairy products. Getting enough of this important B vitamin is key for good health and energy.
Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine): Benefits for Immune & Nervous Systems
Vitamin B6, or pyridoxine, is very important in many body processes. It helps make neurotransmitters and red blood cells. This vitamin is key for a healthy immune system and for your nervous system to work well. You can find good amounts of vitamin B6 in foods like poultry, fish, bananas, and chickpeas. If you don’t get enough vitamin B6, it may cause anemia and problems with your nerves. Getting the right amount of vitamin B6 is important for your health and well-being.
Vitamin B7 (Biotin): Benefits for Hair, Skin & Nails
Biotin, or vitamin B7, is very important for keeping your hair, skin, and nails healthy. This vitamin helps break down fats, carbohydrates, and proteins. This process supports energy metabolism in your body. If you don’t get enough biotin, you might have brittle nails, hair loss, or skin problems. Eating foods high in biotin, like eggs, nuts, and whole grains, can help you avoid these issues and promote good health. Before taking biotin supplements, make sure to talk to your healthcare provider to stay safe.
Vitamin B9 (Folate): Crucial for Pregnancy & Heart Health
Folate, also called folic acid or vitamin B9, is very important for making DNA and for cell metabolism. This B vitamin helps our body create red blood cells. It supports heart health and keeps nerves working well. Folic acid is especially important during pregnancy to help avoid birth defects. You can boost your folate intake by eating foods like leafy green vegetables, whole grains, and cereals that are enriched. This can help prevent folate deficiency and keep you healthy.
Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin): Benefits, Sources & Deficiency Risks
Cyanocobalamin, or vitamin B12, is very important for making red blood cells and keeping our nervous system healthy. This B vitamin helps us produce energy and makes DNA. Getting enough cyanocobalamin can stop anemia and help our brain function well, which is good for our health. Not having enough vitamin B12 can cause serious problems, like pernicious anemia. Eating foods like meat, fish, dairy, and fortified products can help make sure we get enough of this important nutrient.
Recognizing Vitamin B Deficiency Symptoms
The signs of B-group vitamin deficiency can change a lot based on which vitamin is missing. However, there are some common signs to watch for. People may feel very tired and weak with low energy, even after resting enough. Nerve problems can show up as numbness, tingling, or burning in the hands and feet. These may mean there is a lack of B12. Also, mood swings like irritability or sadness may happen due to low levels of some B vitamins. Skin issues, like rashes, can come up too, especially with a lack of riboflavin or niacin. In addition, digestive problems might occur if there are not enough of these vitamins, which can lower nutrient absorption. If you think you have a deficiency, it’s important to talk to a healthcare provider about these signs and check for the right tests and solutions.
Learn the key signs of Vitamin B deficiencies with this simple chart. It will help you see symptoms early and improve your health.
| Vitamin B Type | Common Symptoms of Deficiency | Who’s at Risk | Key Food Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin B1 (Thiamine) | Fatigue, irritability, reduced reflexes, nerve damage, muscle weakness, confusion | Alcoholics, elderly, those with poor diet | Whole grains, pork, legumes, seeds |
| Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) | Cracks at mouth corners, sore throat, red lips, inflammation of the tongue, skin disorders | Vegetarians, pregnant women, alcoholics | Dairy, eggs, green leafy vegetables |
| Vitamin B3 (Niacin) | Pellagra (diarrhea, dermatitis, dementia), fatigue, depression | Poor diet, alcohol abuse, Hartnup disease | Poultry, tuna, mushrooms, peanuts |
| Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid) | Fatigue, irritability, numbness, muscle cramps | Rare, malnourished individuals | Chicken, beef, whole grains, avocados |
| Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) | Irritability, depression, confusion, mouth sores, weakened immune function | Pregnant women, those with kidney issues | Chickpeas, bananas, potatoes, tuna |
| Vitamin B7 (Biotin) | Hair thinning, skin rashes, brittle nails, depression, hallucinations | People on long-term antibiotics, raw egg white diet | Eggs, nuts, seeds, sweet potatoes |
| Vitamin B9 (Folate/Folic Acid) | Fatigue, gray hair, mouth sores, poor growth, anemia | Pregnant women, alcoholics, people with celiac disease | Leafy greens, legumes, fortified cereals |
| Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) | Fatigue, weakness, constipation, nerve problems, memory issues, megaloblastic anemia | Vegans, elderly, people with pernicious anemia | Meat, dairy, eggs, fortified foods |
Vitamin B Complex for Cognitive Health & Mental Clarity
Vitamin B plays a crucial role in promoting mental clarity and enhancing cognitive function. Essential for the synthesis of neurotransmitters, vitamins B6, B9, and B12 are particularly important, as they work together to support brain health. These vitamins help to reduce homocysteine levels, an amino acid linked to cognitive decline, thus playing a protective role against memory loss. Additionally, B vitamins contribute to energy metabolism, ensuring that the brain has a steady supply of energy to function optimally. Incorporating vitamin B-rich foods such as leafy greens, whole grains, and lean meats into your diet can help bolster your mental acuity and overall cognitive performance, making them key players in maintaining a sharp mind as you age.
Vitamin B Sources: Foods vs. Supplements

Vitamin B is a crucial group of nutrients that play a vital role in maintaining overall health and well-being. It consists of eight different vitamins, each with its own specific functions and benefits for the body. Incorporating a variety of foods rich in vitamin B into your nutritious diet is essential for ensuring you meet your daily requirements.
Whole grains and fortified breakfast cereals are an excellent source of B vitamins, particularly B1 (thiamine), B2 (riboflavin), and B3 (niacin). Leafy green vegetables like spinach and kale are rich in folate (B9), while lean meats such as chicken and turkey provide ample amounts of B6 (pyridoxine) and B12 (cobalamin). Fish, beans, lentils, and fortified cereals are also great options to consider when aiming to increase your vitamin B intake.
While obtaining these nutrients through diet is ideal, certain groups may benefit from taking B vitamin supplements. Pregnant women often require additional folic acid (a synthetic form of folate) to support fetal development. Older adults may have difficulties absorbing enough vitamin B12 from food alone due to age-related changes in digestion. Individuals with certain health conditions that affect nutrient absorption or metabolism may also need supplementation.
It is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplementation regimen to determine your specific needs and the appropriate dosage for optimal health outcomes. By combining a balanced diet with targeted supplementation when necessary, you can ensure that your body receives an adequate supply of essential vitamin B nutrients to support various bodily functions and promote overall wellness.
Best Foods Rich in Vitamin B Complex
Getting enough B vitamins from your diet is important for staying healthy. Thankfully, there are many tasty and easy-to-find foods that are great for providing these crucial nutrients.
Leafy green vegetables, like spinach, kale, and collard greens, are rich in folate, riboflavin, and vitamin B6. Dairy products, such as milk, yogurt, and cheese, are great sources of riboflavin, vitamin B12, and pantothenic acid.
Make sure to include these foods in your meals, along with:
Whole grains: Choose brown rice, quinoa, oats, and whole-wheat bread for thiamin, niacin, and B6.
Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are good for folate, thiamin, and niacin.
Meat and poultry: Beef, chicken, and turkey provide vitamin B12, niacin, and B6.
Fish: Enjoy salmon, tuna, and mackerel as they are rich in vitamin B12, niacin, and riboflavin.
Who Needs Vitamin B Complex Supplements?
While a balanced diet typically provides sufficient B vitamins, certain circumstances may necessitate the use of dietary supplements. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine if supplementation is right for you.
Consider B vitamin supplements in the following cases:
Dietary restrictions: Vegans and vegetarians may benefit from B12 supplements, as it is primarily found in animal products.
Age: Older adults may have reduced absorption of B12 and may need supplementation.
Health conditions: Certain conditions, such as celiac disease or Crohn’s disease, can impair nutrient absorption, leading to deficiencies.
Pregnancy: Increased demand for folate during pregnancy often necessitates supplementation.
Group | Recommended Supplement |
|---|---|
Vegans and vegetarians | Vitamin B12 |
Older adults | Vitamin B12 |
Pregnant women | Folic acid (B9) |
How to Diagnose Vitamin B Deficiency: Tests & Screening

Diagnosing a vitamin B deficiency usually includes a physical check-up, going over medical history, and tests in a lab. A healthcare provider will look at symptoms, eating habits, and any health issues that might lead to a deficiency.
Blood tests are often done to check the levels of certain B vitamins in the body, including methylmalonic acid levels. For example, a complete blood count (CBC) can help find anemia, which may show a B12 or folate deficiency. Other tests can measure the amounts of specific B vitamins in your blood or urine.
Clinical Trials & Research on Vitamin B Complex
Many research studies and clinical trials have looked into the roles of B vitamins in different health conditions. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) and other research centers around the world are studying the possible benefits and risks of taking B vitamins.
These studies focus on how B vitamins affect heart health, brain function, energy levels, and various long-term illnesses. over a period of time. While some hopeful results have come out, more research is often needed to reach clear conclusions and make recommendations. It’s very important that clinical trials are done in a careful and ethical way to keep participants safe and healthy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, looking into the benefits of Vitamin B shows that it is very important for our health and well-being. It helps boost energy levels and supports cell metabolism. Each type of Vitamin B has a key role in our bodies. You can get enough Vitamin B by eating a balanced diet that includes good sources of it. Sometimes, supplements can help too. Knowing how important these essential nutrients are can help you make better choices for your health. Taking advantage of the benefits of Vitamin B is a smart way to boost your energy and support different body functions.
The content on WellwayHub.com is intended for general informational purposes only and should not be taken as medical advice. Please consult your doctor or a qualified health professional before making any changes to your health routine.
Some links on WellwayHub.com may be affiliate links. This means we may earn a small commission if you make a purchase through these links, at no extra cost to you. This helps support our mission to provide trusted wellness content.
Frequently Asked Questions
Taking vitamin B every day can be beneficial for many people, as it plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. However, it’s important to note that the daily recommended intake of vitamin B can vary depending on factors such as age, sex, and individual health conditions.
Before starting a daily vitamin B regimen, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian to determine your specific nutritional needs and whether taking a vitamin B supplement is appropriate for you. They can help you assess your current diet and lifestyle to see if you may benefit from additional vitamin B supplementation. Remember, moderation is key when it comes to taking any supplements, so always follow the recommended dosage guidelines provided on the supplement packaging or by your healthcare provider.
B vitamins dissolve in water. However, taking high doses from supplements can cause side effects. These side effects can include problems with the stomach, damage to nerves (especially if you take too much B6), and skin flushing (which can happen with high doses of niacin).
Having too much vitamin B in your system can lead to various symptoms and potential health risks. Some possible effects of excessive vitamin B intake include:
1. Nausea and vomiting: Too much vitamin B can cause gastrointestinal issues such as nausea, vomiting, and stomach pain.
2. Skin flushing: High doses of certain B vitamins like niacin can cause skin flushing, redness, and itching.
3. Liver damage: Excessive intake of certain B vitamins over time can lead to liver damage.
4. Nerve damage: In some cases, too much vitamin B6 can result in nerve toxicity and permanent nerve damage.
5. Increased risk of certain diseases: Research suggests that high levels of certain B vitamins may be linked to an increased risk of conditions like cardiovascular disease and cancer.
It’s important to be mindful of your vitamin B intake and consult with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian if you have concerns about your vitamin levels or are considering taking supplements.
To maximize the benefits of Vitamin B complex, it is generally recommended to take it in the morning. This timing aligns with your body's natural energy production cycle, helping to fuel your day and combat fatigue. Taking B vitamins with food can also enhance absorption and minimize any potential stomach upset. However, it's crucial to listen to your body; if you find that taking them at a different time works better for you, feel free to adjust. Consistency is key in reaping their full benefits for energy and overall health.
Vitamin B plays a crucial role in energy production by helping convert the food you eat into energy that your body can use. Specifically, B vitamins are essential for breaking down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins from your diet and turning them into fuel for your body’s cells. They may also help reduce the risk of heart disease by supporting the function of your nervous system and helping maintain healthy skin, eyes, hair, and liver. Inadequate levels of Vitamin B can lead to fatigue, weakness, and other symptoms related to low energy levels. It is important to ensure you are getting enough Vitamin B through your diet or supplements to support optimal energy production in your body.
Vitamin deficiency can show up in different ways. You might feel tired and low on energy. Your mood can change, leading to irritability or depression. You may notice pale skin, mouth sores, or tingling and numbness in your hands and feet. It can also affect how well you think and focus.
B complex vitamins are very important for making energy. They work as helpers in processes that change food into energy. They help break down carbohydrates, fats, and protein. This fuels your physical activity and helps lessen tiredness.
All B vitamins are important, and each has its own special job. This makes it hard to say which one is the most important. However, B12 is very important for nerve function and for making red blood cells. Folate is also vital, especially during pregnancy, because it helps prevent birth defects.
To boost your Vitamin B complex intake, consider incorporating a variety of foods into your diet. Whole grains like brown rice and oats are excellent sources, as well as legumes such as lentils and chickpeas. Leafy greens offer folate, while eggs and dairy products provide B12. Meat, particularly liver, is packed with several B vitamins, making it a powerhouse option. Fish, especially salmon and trout, not only enrich your diet with omega-3 fatty acids but also contribute to your B vitamin levels. Nuts and seeds can be great snacks that enhance your nutrition seamlessly.