
Introduction
Vitamin D is known as the “sunshine vitamin.” It is important for our bodies to work well. We can get some vitamin D from the sun, but things like less sunlight, what we eat, and our choices in life can make us lack it. This is why supplements can help. In this blog, we will talk about the importance of vitamin D, especially vitamin D3, and why it is essential for good health and well-being.
What Is Vitamin D3 and Why Is It Important?
Vitamin D3, also called cholecalciferol, is a vitamin that our bodies need for good health. It is fat-soluble, meaning it dissolves in fat. We usually get vitamins from our food, but we can make vitamin D3 when our skin soaks up sunlight.
This important vitamin helps keep our bones strong. It does this by helping our bodies absorb calcium and managing calcium and phosphorus levels in the blood. If we don’t get enough vitamin D, our bones may become weak. This can lead to fractures and diseases like osteoporosis.
Besides bone health, vitamin D also boosts our immune system, helps cell growth, and supports muscle function.
A Brief History of Its Discovery
The discovery of vitamin D in the early 1900s changed how we see nutrition and its effects on health. It started when people noticed that kids who got more sunlight had fewer cases of rickets. This disease makes bones soft and weak.
Scientists found out that sunlight helps the skin make a substance called vitamin D. This discovery showed why rickets was more common in places with little sunlight or among those who didn’t get enough sun exposure.
Recognizing the connection between vitamin D and sun exposure led to efforts to improve public health. One major step was adding vitamin D to foods. This move helped reduce rickets and boosted overall bone health.
Biological Functions of Vitamin D3
Vitamin D3 works like a hormone and affects many processes in our body. It is important for calcium absorption. This helps our bodies use calcium well for strong bones and teeth. Also, vitamin D3 connects with our cells. It affects cell growth, how our immune system responds, and the control of inflammation.
These different roles show why it is important to keep vitamin D3 levels good for our health. It helps not only our bones but also our immune system, heart health, and mental well-being.
How It Regulates Calcium and Phosphorus
Vitamin D3 is very important for balancing calcium and phosphorus. These minerals are key for good bone health. It helps our bodies absorb calcium from the foods we eat. When we consume calcium-rich foods, vitamin D3 makes sure our bodies can use this mineral well.
Also, vitamin D3 controls the levels of calcium and phosphorus in our blood. It works with other hormones, like parathyroid hormone, to keep these minerals ready for building and maintaining bones. It also stops too much of these minerals from staying in the blood.
If our calcium and phosphorus levels are off, it can cause weak bones, muscle weakness, and other health issues. This is why vitamin D3 is essential for strong bones, healthy teeth, and good muscle function.
What Are Vitamin D Receptors and How Do They Work?
Vitamin D works in the body by connecting to special proteins known as vitamin D receptors (VDRs). These receptors let vitamin D enter the cells to do its jobs.
You can find VDRs in many parts of the body, such as the intestines, bones, kidneys, and immune system cells. This shows how important vitamin D is for our health.
When vitamin D connects to VDRs, it starts a series of changes, including the way genes are expressed. This means that vitamin D can switch certain genes on or off, affecting how cells act and work. Because of this, vitamin D helps with calcium absorption, cell growth, immune responses, and many other functions that are important for our health.
How Vitamin D3 Is Synthesized and Activated
The making of vitamin D3 starts in our skin when it gets sunlight. Ultraviolet B (UVB) rays from the sun change a molecule in our skin called 7-dehydrocholesterol into vitamin D3.
The vitamin D3 made in our skin or found in food is not active yet. It needs to change in the body two times to become active. The first change occurs in the liver, and the second change happens in the kidneys.
Issues with the liver or kidneys, like liver disease or kidney disease, can hurt this change. This could make someone have vitamin D deficiency, even if they get enough sunlight or eat enough vitamin D in their meals.
Health Benefits of Vitamin D3
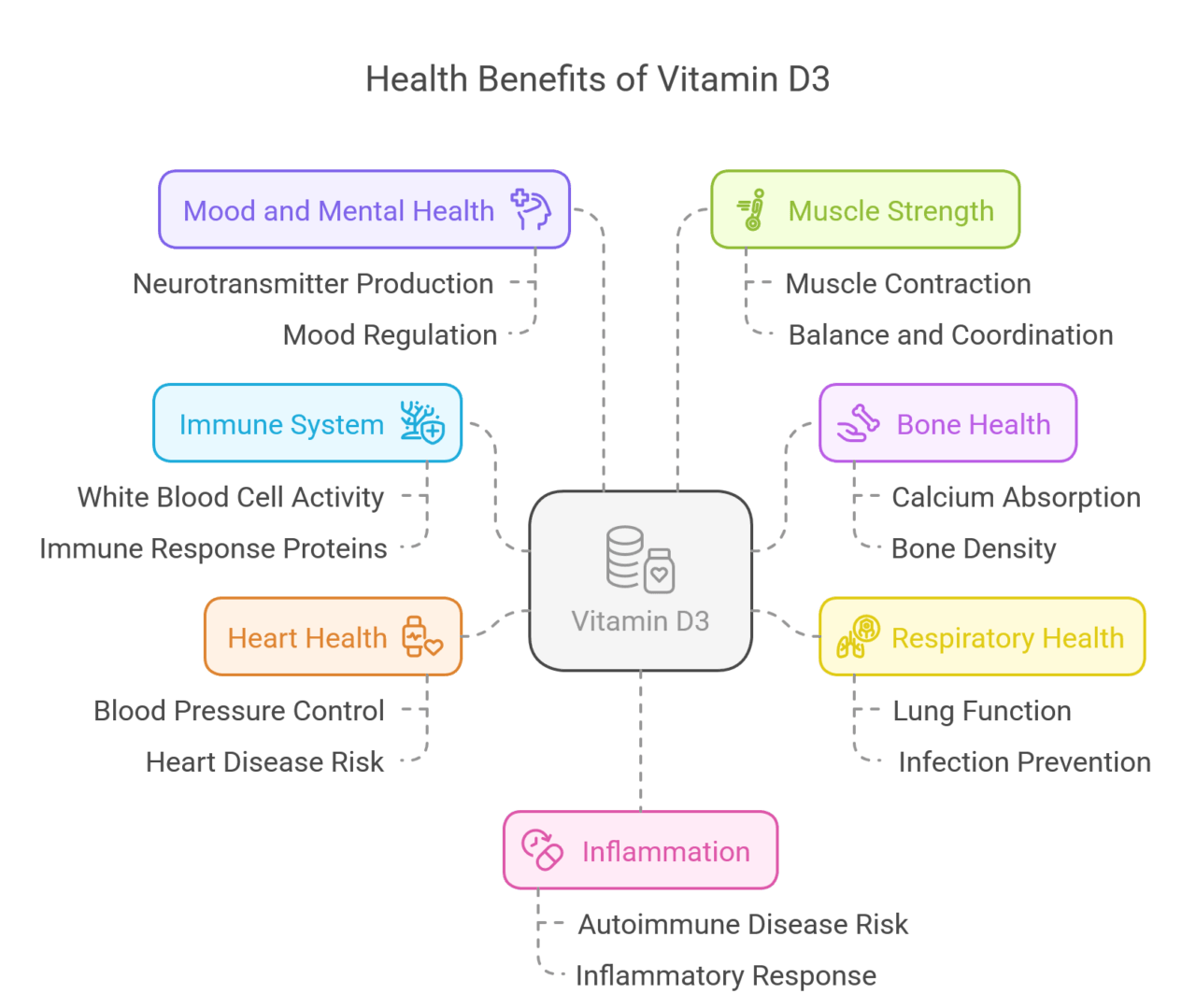
Vitamin D3 is well-known for helping bone health, but it also offers many other benefits for our well-being. It works well with the immune system. It helps strengthen our defenses against infections and sickness.
Studies show that having enough vitamin D3 can lower the risk of long-term health issues like heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and some cancers. This shows just how important vitamin D3 is for our overall health.
How Vitamin D3 Boosts Immune Defense
Vitamin D3 is very important for a healthy immune system. It helps different immune cells work together properly, like a conductor leading an orchestra.
One way vitamin D3 boosts immune health is by increasing the activity of white blood cells. These cells are the body’s first protection against infections. They spot and kill harmful germs, stopping you from getting sick.
Additionally, vitamin D3 helps control the production of certain proteins that are part of the immune response. This balance leads to a stronger and more effective immune reaction. Overall, the immune-boosting effects of vitamin D3 support our health and make us more resistant to infections.
Preventing Bone Loss and Fractures
Having enough vitamin D is very important for strong and healthy bones, especially as we grow older. One main way vitamin D helps our bones is by improving how our body absorbs calcium. You probably know that calcium is key for building and keeping bone strength.
When we make sure our bodies can absorb calcium well from our food, vitamin D helps keep our bones strong. This lowers the chance of fractures and problems like osteoporosis, which is when bones become weak and fragile.
If vitamin D levels drop too low, our bodies might take calcium from our bones to keep blood calcium levels normal. This can weaken our bones over time. So, it is very important to have enough vitamin D to support lasting bone health and to avoid fractures.
Respiratory Health and Lung Support
Recent research shows that vitamin D may help support our breathing health. Studies found a link between vitamin D deficiency and a higher risk of respiratory infections, like the common cold and flu.
Moreover, having enough vitamin D can lead to better lung function, especially for people with asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
While we need more studies to really understand how these links work, keeping good levels of vitamin D through a balanced diet, getting enough sun exposure, or taking supplements might help improve respiratory health.
Heart Health and Blood Pressure Regulation
Vitamin D is often known for supporting bone health. But studies show it may also help with heart health. Research links having low vitamin D to a higher risk of heart disease. This includes issues like heart attacks and strokes.
One way vitamin D can help the heart is by helping to control blood pressure. Studies suggest that people with enough vitamin D often have lower blood pressure. In contrast, those lacking this vitamin may have higher blood pressure.
Still, more studies are needed to show the clear link between taking vitamin D and reducing heart disease risk. However, eating foods rich in vitamin D or thinking about taking supplements could be good for heart health. It’s best to talk to a healthcare professional first.
Mood, Brain Function, and Mental Health
Vitamin D is good for more than just our physical health. It also affects our mood, brain function, and overall mental well-being. Many studies show that not having enough vitamin D may lead to a higher chance of mood disorders, like depression.
Scientists are still exploring how this works. They think vitamin D may help with making and using important brain chemicals, called neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine. These chemicals are key to keeping our mood steady.
Some research suggests that taking vitamin D can help boost mood and lessen symptoms of depression. This is especially true for people who have a vitamin D deficiency. Keeping your vitamin D levels up with food, getting sun exposure, or taking supplements could help you feel happier and improve your mental well-being.
Improving Muscle Strength and Mobility
Vitamin D is important not just for strong bones. It also helps with muscle function, strength, and movement. It does this by affecting how our muscles use calcium. Calcium is necessary for muscles to contract.
When our brain tells the muscles to contract, calcium flows into the muscle cells. This starts the contraction. Vitamin D makes sure there is enough calcium in the muscle cells for the best contractions.
Research shows a link between vitamin D deficiency and weaker muscles. This is especially true for older adults. Keeping enough vitamin D levels can help muscle function. This can lead to better strength, balance, and movement.
Reducing Inflammation and Autoimmune Risks
Chronic inflammation is a big cause of many health issues. Studies show that vitamin D can help control inflammation by affecting how immune cells work.
Also, not getting enough vitamin D can raise the chance of getting autoimmune diseases. These are conditions where the immune system attacks the body’s own tissues by mistake.
More studies are needed to really understand how vitamin D relates to autoimmune diseases. However, keeping good vitamin D levels could help. You can do this by eating a balanced diet, getting sun exposure, or taking supplements, as suggested by a healthcare provider. This may support a strong immune system and lower the risk of some autoimmune problems.
Best Sources of Vitamin D3 (Sunlight, Food, Supplements)

It is important to use different sources to keep good Vitamin D3 levels. Sunlight is the main natural source. It helps the body make Vitamin D in the skin. But you can also get Vitamin D from food. Fatty fish, like salmon, fortified foods, and supplements are great options. While sunlight is a good source, you should be careful to limit how much you get. This will help avoid skin damage. Eating foods rich in Vitamin D, such as eggs and fortified dairy products, can support your sunlight exposure. Supplements are helpful for anyone who doesn’t get enough sun or has special dietary needs. They can help make sure you have enough Vitamin D3 for good health.
Sunlight Exposure: Natural Synthesis
Sunlight is the best way to increase vitamin D3 levels naturally. When our skin gets sunlight, especially the UVB rays, it starts to make vitamin D3.
Even a little bit of direct sunlight without sunscreen can help produce vitamin D3 a lot. Still, it’s important to be safe in the sun. This helps avoid sunburn and skin cancer.
How much sunlight you need can change. It depends on your skin type, where you are, and what time of day it is. Too much sun can be dangerous. That’s why it’s wise to talk to a healthcare provider. They can help you find the best amount of sun exposure for making vitamin D while keeping your skin safe.
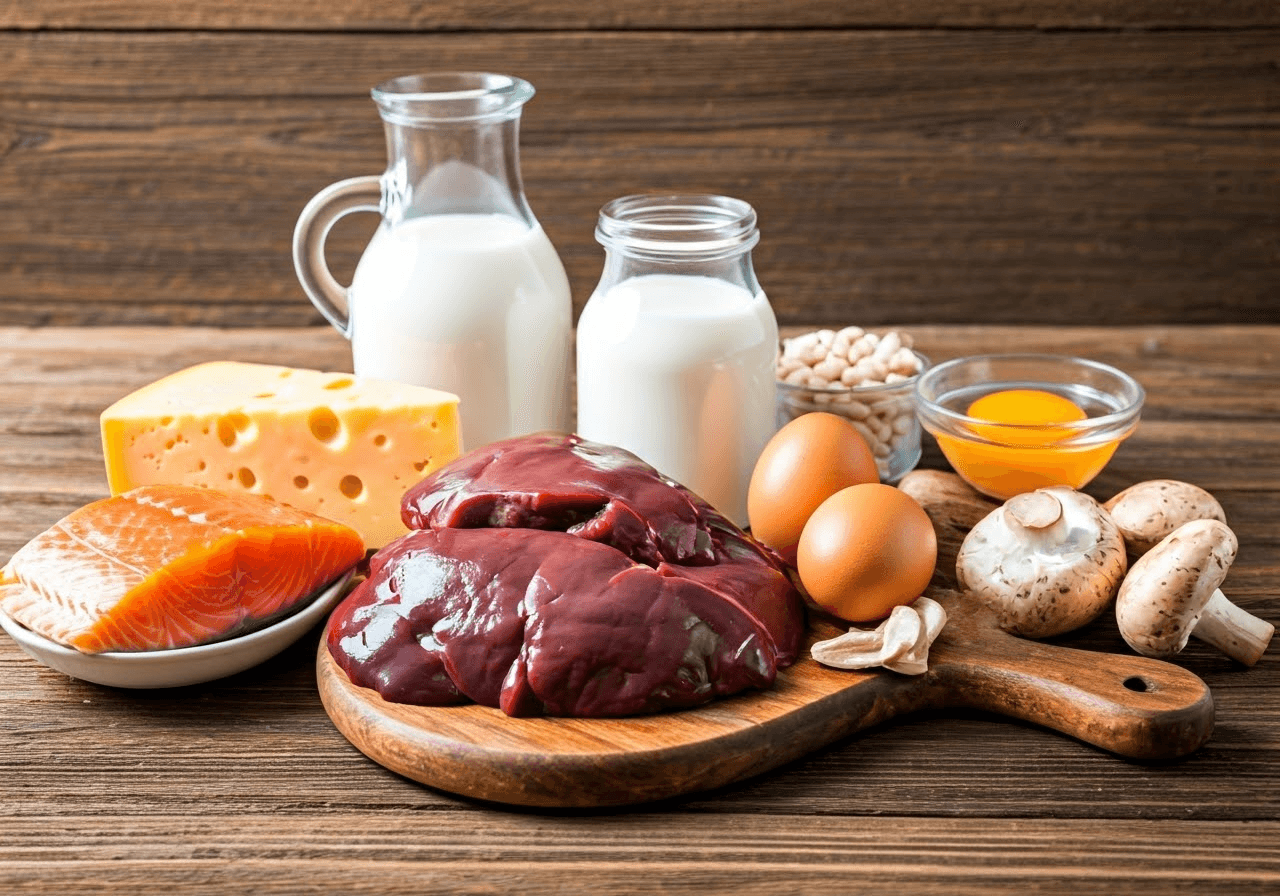
Dietary Sources: Best Foods for Vitamin D3
Sunlight is the main way we get vitamin D3, but certain foods can help us get this important nutrient too. Fatty fish are some of the best sources of vitamin D3.
Here are some great food options to include:
Fatty fish: Salmon, tuna, mackerel, and sardines are full of vitamin D3.
Cod liver oil: This oil has a lot of vitamin D3, but use it carefully because it also has high vitamin A.
Egg yolks: Eggs have less vitamin D3 than fatty fish but are a good and easy source to add to our meals.
Fortified foods: Many items, like milk, orange juice, and cereals, have added vitamin D3. Always check food labels to find these options and use them in your diet.
Food | Serving Size | Vitamin D3 Content (IU) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Salmon (sockeye) | 3 oz (85 g) | 570–715 IU | Natural source, varies by wild/farmed |
| Mackerel | 3 oz (85 g) | 360 IU | Natural source |
| Sardines (canned) | 2 sardines (46 g) | 46 IU | Natural source |
| Tuna (canned in oil) | 3 oz (85 g) | 154 IU | Natural source, watch for mercury levels |
| Cod liver oil | 1 tsp (4.9 ml) | 1,360 IU | Very high in D3 and vitamin A |
| Egg yolk | 1 large | 37 IU | Natural source |
| Fortified milk | 1 cup (240 ml) | 115–130 IU | Fortified source |
| Fortified orange juice | 1 cup (240 ml) | 100 IU | Fortified source |
| Fortified cereal | 1 serving (~30 g) | 40–100 IU | Fortified source, varies by brand |
| Mushrooms (UV-exposed) | ½ cup (cooked) | 400 IU | Plant-based, fortified with UV light |
Supplements: When Diet and Sunlight Aren’t Enough
We can get vitamin D3 from the sun and our food. However, things like having little sun exposure, where we live, and what we like to eat can make it hard to get enough. In these cases, dietary supplements can help.
Vitamin D supplements are easy to find at stores, and they provide a simple way to increase your vitamin D3 levels. They usually come in two types: D2 (ergocalciferol) and D3 (cholecalciferol).
When picking a vitamin D supplement, people often recommend D3. This is the type our bodies naturally create and absorb better. Still, it’s important to talk to a healthcare professional to find the right dosage for you.
How to Take Vitamin D3: Dosage and Supplementation Guide
Taking vitamin D3 supplements can help you keep enough levels in your body. However, knowing the right dose and when to take it is important. This way, you will get the benefits without risks. The daily intake of vitamin D3 may change based on age, health status, and sun exposure.
Always talk to your healthcare provider to find the best dosage for you. They can arrange a blood test to check your vitamin D3 levels. Then, they will suggest a plan that fits your needs.
When Should You Take Supplements?
The best time to take your vitamin D3 supplement can vary. It depends on your daily routine and any medications you are taking. While there isn’t a “best” time for everyone, some tips can help you absorb it better.
Vitamin D3 is a fat-soluble vitamin. This means it works well when taken with food that has fat. Try taking your supplement with breakfast, lunch, or dinner—whichever meal has healthy fats.
Being consistent is important. Pick a time that is best for you and stick to it for regular vitamin D3 intake. Your healthcare provider can give you advice based on your personal needs and health.
Recommended Dosage by Age and Condition
The recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for vitamin D varies depending on age, with infants, children, and older adults requiring different amounts than adults. It’s essential to ensure you’re getting enough vitamin D through a combination of diet, sun exposure, and supplementation, if needed, for optimal health.
Here’s a general guide for recommended vitamin D intake:
| Age Group | Recommended Daily Intake (IU) |
|---|---|
| Infants (0-12 months) | 400 IU |
| Children (1-18 years) | 600 IU |
| Adults (19-70 years) | 600 IU |
| Older Adults (71 years and older) | 800 IU |
It’s important to note that these are general guidelines, and your healthcare provider might recommend different dosages based on your individual needs, health status, and blood vitamin D levels.
Best Ways to Take Vitamin D3 Supplements
When you take vitamin D3 supplements, it’s important to be consistent. Adding them to your daily routine helps keep your levels good. Taking them with a meal that has healthy fats can help your body absorb them better. Also, if you spread out the dose during the day, you can use it more effectively. Always talk to a healthcare provider for personal advice, especially if you have health issues or take medication. Make sure to follow the directions on the supplements and do not take more than the recommended dose to get the best benefits.
Special Guidelines for Pregnancy and Infants
During pregnancy, getting enough vitamin D is very important for the mother’s health and the baby’s growth. Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium, which is needed for the baby’s bones and overall development.
Babies, especially those who only drink breast milk, may need vitamin D supplements. This is because breast milk might not give enough vitamin D. The American Academy of Pediatrics says that all breastfed and partially breastfed babies should get 400 IU of vitamin D each day.
Talk to your healthcare provider or pediatrician to find the right amount of vitamin D supplements for pregnant women and babies. They can check your needs and help you follow the safest ways to keep adequate vitamin D levels during these important times.
Vitamin D3 Side Effects and Safety Considerations

Vitamin D3 is very important for our health. However, taking too much of it can cause side effects. Vitamin D toxicity is uncommon, but it can lead to too much calcium in the body, which can create health problems.
It’s important to follow the recommended dose. Always talk to your healthcare provider before starting any new supplements. This is especially true if you have health issues or take medications, to avoid drug interactions.
Signs and Risks of Taking Too Much
Vitamin D toxicity is also called hypervitaminosis D. It happens when there is too much vitamin D in the body. This situation is rare but can happen if you take too many vitamin D supplements. This often occurs when people do not follow the suggested dosages.
Some signs of vitamin D toxicity include nausea, vomiting, constipation, weakness, and urinating often. In serious cases, it can cause high calcium levels in the blood (hypercalcemia). This can harm kidney function and lead to more health issues.
To avoid vitamin D toxicity, do not go over the daily intake of vitamin D unless your healthcare provider tells you to. If you notice any strange symptoms after taking vitamin D supplements, stop using them and talk to your healthcare provider.
Medication Interactions You Should Know
Vitamin D can work with some prescription drugs. This can change how effective the drugs are or raise the chance of side effects. It is important to know about these interactions to keep yourself safe.
For example, vitamin D supplements might affect how thiazide diuretics work. These drugs help treat high blood pressure. Also, taking vitamin D with corticosteroids, like prednisone, could lead to more calcium in the blood.
Always tell your healthcare provider about all the drugs, supplements, and herbs you take. This helps to avoid any interactions. They can look into the risks and change the doses or suggest different medicines to keep you safe and make your treatment better.
| Medication Class | Common Drugs | Potential Interaction | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diuretics (Thiazide) | Hydrochlorothiazide, Chlorthalidone | May increase calcium levels when taken with vitamin D | Monitor calcium levels; use with caution |
| Corticosteroids | Prednisone, Dexamethasone | May reduce calcium absorption and vitamin D metabolism | May need higher vitamin D intake; monitor bone health |
| Anticonvulsants | Phenytoin, Phenobarbital, Carbamazepine | May increase vitamin D breakdown, lowering blood levels | Consider supplementation; monitor levels regularly |
| Weight-loss medications | Orlistat | Reduces fat absorption, which may decrease vitamin D absorption | Take vitamin D with a separate, fat-containing meal |
| Cholesterol-lowering agents | Cholestyramine, Colestipol | Bind bile acids, may impair vitamin D absorption | Take vitamin D at different times; consider higher dose |
| Antifungals | Ketoconazole | May interfere with vitamin D activation in the liver | Monitor vitamin D status; adjust dose as needed |
| HIV treatment (HAART) | Efavirenz, Ritonavir | May lower vitamin D levels through enzyme induction | Regular vitamin D monitoring recommended |
How to Monitor and Prevent Side Effects
Monitoring potential side effects from any supplement, including vitamin D, is always a smart idea. Serious side effects are rare. However, it is important to stay alert and talk to your healthcare provider if you notice anything unusual.
If you are taking vitamin D supplements, watch for symptoms like nausea, constipation, frequent urination, or muscle weakness. These may mean that you are getting too much vitamin D.
Regular checkups and blood tests, as your healthcare provider suggests, can help you keep track of your vitamin D levels. This is especially important if you are taking high doses of vitamin D or have health issues.
Metabolism and Absorption of Vitamin D3
Our bodies process vitamin D3 in a really interesting way. It gets turned into active forms that can help us in many ways. We can get vitamin D3 from foods, supplements, or by making it in our skin when we get sun exposure. But we don’t use it right away.
First, vitamin D3 goes through different changes in our liver and kidneys. These changes turn it into active forms. This allows vitamin D3 to help regulate calcium absorption, support bone health, and help with other body functions.
What Is 25(OH)D and Calcitriol?
25(OH)D is a form of vitamin D that changes into the active type, called calcitriol. It is the main kind measured in blood tests to check your vitamin D level. Calcitriol helps your body take in calcium and phosphorus from food. This is important for good bone health.
What Affects How Well Vitamin D3 Is Absorbed?
Many things can affect how our bodies take in vitamin D3. One important factor is dietary fat. Since vitamin D3 is a fat-soluble vitamin, it is best to eat it with healthy fats.
Some health conditions can also change how well we absorb vitamin D3. For example, people who have had gastric bypass surgery or suffer from celiac disease or Crohn’s disease may not absorb vitamin D well because of changes in their digestion.
Also, body mass index (BMI) and age can make a difference. People with obesity might need more vitamin D because it’s stored in fat. Older adults may also have more trouble absorbing it.
Causes and Diagnosis of Vitamin D3 Deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency is a common health issue around the world. It happens when the body does not have enough vitamin D. This can be due to not getting enough sunlight, not eating the right foods, or some health problems.
If you think you might have a deficiency, you can take a simple blood test. This test checks the level of 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D] in your blood. To fix vitamin D deficiency, you usually need to increase your intake. This can be done by eating certain foods, being in the sun more, or taking supplements. It’s best to follow the advice of a healthcare provider.
Main Causes and Risk Factors
Vitamin D deficiency can happen for many reasons. These reasons include lifestyle choices, the environment, and certain health conditions. One of the main causes is not getting enough sun. Our bodies need sunlight to create vitamin D. If we do not get enough sun, especially during winter or in places with little sunlight, our risk of deficiency goes up.
Diet also matters a lot. Eating foods low in vitamin D, like fatty fish, eggs, or fortified products, can lead to deficiency. People with darker skin might have a higher risk too. This is because melanin, the pigment that colors our skin, can reduce how much vitamin D we get from sunlight.
Some health issues that affect how we absorb fat, like celiac disease or Crohn’s disease, can also hurt our ability to absorb vitamin D. This can cause deficiencies even when we take in enough vitamin D.
Symptoms and Possible Health Issues
Vitamin D deficiency often goes unnoticed. The signs can be subtle and may seem like other health issues. In children, a serious lack of vitamin D can cause rickets, which makes bones soft and weak.
In adults, the signs may be mild. They can include feeling tired, pain in bones and muscles, a higher chance of getting sick, and changes in mood like depression. A long-term shortage of vitamin D can lead to more serious health problems like osteoporosis, heart disease, and type 2 diabetes.
If you think you may have a vitamin D deficiency, see your healthcare provider. They can check your risk factors, look at your symptoms, and request a blood test to check your vitamin D levels. Finding and treating this deficiency early is important for preventing problems and keeping good health.
| Symptom | Body System Affected | Common in | Severity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bone pain | Skeletal | Adults | Moderate to Severe |
| Muscle weakness | Muscular | Adults, Children | Mild to Moderate |
| Frequent infections | Immune | Adults, Children | Moderate |
| Fatigue | General / Neurological | Adults | Mild to Moderate |
| Slow wound healing | Immune / Skin | Adults | Moderate |
| Mood changes (e.g., depression) | Neurological | Adults, Teens | Moderate |
| Hair loss | Dermatological / Hormonal | Adults | Mild to Moderate |
| Growth delays | Skeletal / Developmental | Children | Severe |
| Rickets (bone deformities) | Skeletal | Children | Severe |
| Osteomalacia (soft bones) | Skeletal | Adults | Severe |
How to Test and Interpret Your Vitamin D Levels
Healthcare providers use a blood test to check a person’s vitamin D level. This test often measures 25-hydroxyvitamin D. It helps see if someone has enough, not enough, or too little vitamin D.
Here’s how the results break down:
- Sufficient: 20 ng/ml or higher
- Insufficient: 12-20 ng/ml
- Deficient: Less than 12 ng/ml
Your healthcare provider will look at your medical history, lifestyle, and personal needs when they check your vitamin D level. They can then suggest steps you can take. This may include changing your diet, getting more sun exposure, or taking vitamin D supplementation. This way, you can reach and keep healthy levels of vitamin D.
Who Is Most at Risk?
Anyone can have a vitamin D deficiency, but some people are at a higher risk. Older people are especially vulnerable. Their skin does not make vitamin D from sunlight as well as it used to with age.
Infants who only get breast milk are at risk, too. This is because breast milk does not have enough vitamin D. Also, people with darker skin might need more sun exposure to produce enough vitamin D. This is due to the extra melanin in their skin.
Certain medical problems, like cystic fibrosis, Crohn’s disease, and celiac disease, can affect how well the body absorbs vitamin D. This means that even if a person eats enough vitamin D, they could still face a deficiency. Knowing about these risks can help people and healthcare providers spot issues early and take steps to prevent them.
Long-Term Health Consequences of Low Levels
Chronic vitamin D deficiency is often ignored, but it can seriously affect long-term health. It can weaken bones and raise the risk of fractures and osteoporosis, especially in older adults.
Research shows that low vitamin D levels are linked to a higher risk of serious health problems like cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and some types of cancer. It may also harm immune function, making people more likely to get infections and autoimmune diseases.
Fixing vitamin D deficiency is important. You can do this by getting more sun exposure and eating foods that are rich in vitamin D. You might also need supplements, but it’s best to talk with a healthcare provider first. This can help reduce risks and support better health in the long run.
Vitamin D3 and Chronic Health Conditions

Research keeps finding possible connections between vitamin D3 levels and different long-term health issues. It is not easy to prove direct links, but studies show that not having enough vitamin D3 might raise the chance of getting some conditions.
These conditions are bone problems, autoimmune diseases, cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, depression, and brain disorders. Keeping good vitamin D3 levels is important. You can do this by eating the right foods, getting sun exposure, and taking supplements if needed. This can help your overall health and might lower the increased risk of some long-term illnesses.
Bone Disorders: Rickets and Osteomalacia
Vitamin D is important for absorbing calcium. This makes it necessary for keeping bones healthy and growing. If someone does not have enough vitamin D, it can cause bone problems. In kids, this can lead to rickets, and in adults, it can cause osteomalacia.
Rickets makes children’s bones soft and weak. This happens when their bodies can’t absorb enough calcium because they have low vitamin D. It can cause problems with growth, changes in the shape of bones, and pain in the bones.
Osteomalacia is when adults suffer from the same issue as rickets. Here, low vitamin D leads to soft bones and a greater chance of breaking them. Getting enough vitamin D through eating, sun exposure, or supplements is very important. This helps prevent and treat bone issues and keeps your bones strong throughout life.
Connection to Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune diseases are conditions where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues. Many people around the world are affected by these diseases. New research shows a possible link between vitamin D and autoimmune diseases.
Studies hint that people who lack vitamin D may have a higher chance of getting autoimmune disorders like rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and type 1 diabetes.
Scientists are still looking into how this link works, but it seems that vitamin D helps control immune function. Keeping good vitamin D levels by eating well, getting sun exposure, or taking supplements might help manage immune responses. This can potentially lower the risk of getting some autoimmune diseases.
Role in Cardiovascular Disease
Cardiovascular disease is a serious condition that impacts the heart and blood vessels. It is one of the main reasons for death around the world. Some research suggests that not having enough vitamin D may raise the risk of developing cardiovascular disease.
Studies reveal that people with low levels of vitamin D often experience higher rates of high blood pressure, heart attacks, strokes, and other heart issues.
Although we need more studies to fully understand this connection, getting enough vitamin D from food, sun exposure, or supplements can help promote a healthy heart. It’s important to follow advice from a healthcare provider about maintaining adequate vitamin D levels.
Impact on Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a condition where blood sugar levels are high, and it affects many people around the world. New studies suggest that not getting enough vitamin D may be linked to type 2 diabetes.
Research shows that vitamin D might help the body use insulin better. Insulin is the hormone that controls blood sugar levels. If vitamin D levels are low, insulin may not work properly. This can cause higher blood sugar levels and increase the chance of getting type 2 diabetes.
While we need more studies to find a clear link, keeping vitamin D levels up can help manage blood sugar. You can do this by eating a healthy diet, getting enough sun exposure, or taking supplements if a healthcare provider recommends them. This could lower the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Links to Depression and Neurological Health
Vitamin D is important not just for physical health but also for our brain and mood. Research shows that not having enough vitamin D is linked to a higher chance of having mood problems, like depression.
The details of how this all works are still being studied. However, vitamin D may help produce and manage brain chemicals, called neurotransmitters, like serotonin and dopamine. These chemicals are important for controlling mood.
Some studies say that taking vitamin D supplements could help lift mood and lessen signs of depression in people who don’t have enough vitamin D. Keeping good levels of vitamin D through food, sun exposure, or supplements can help with mental health and may lower the risk or seriousness of mood issues.
Chronic Kidney Disease Considerations
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) happens when the kidneys slowly lose their ability to work well. This condition affects millions of people around the world. A key part of managing CKD is dealing with vitamin D deficiency, which is common in CKD patients.
Healthy kidneys help change vitamin D into its active form called calcitriol. When the kidneys are damaged, they cannot make this change effectively. This leads to vitamin D deficiency in those with CKD.
Low levels of calcitriol can harm bone health for people with CKD. Because of this, doctors often suggest taking active vitamin D supplements like calcitriol or similar kinds. These supplements help improve vitamin D levels, which can lead to better bone health and well-being for CKD patients.
Vitamin D3 in Obesity and Metabolism
The connection between vitamin D3 and obesity has gained a lot of attention. Studies show that not having enough vitamin D may raise the risk of obesity.
We need more research to fully understand how they are related. Vitamin D3 may help control appetite, affect how fat cells work, or influence hormones that manage energy.
However, just taking vitamin D3 does not promise weight loss. To deal with obesity, people often need to make many changes. This includes adjusting their diet, being active, and changing other parts of their lifestyle.
Table: Vitamin D3 impact on chronic conditions
| Condition | Vitamin D3 Role | Supporting Evidence | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Osteoporosis | Enhances calcium absorption, supports bone mineralization | Strong evidence; widely recommended in clinical guidelines | Supplement with calcium; ensure adequate intake through diet and sun exposure |
| Rickets / Osteomalacia | Prevents bone softening in children and adults | Historic evidence; near elimination in fortified populations | Ensure early childhood supplementation; consider routine screening |
| Autoimmune Diseases | Modulates immune response; may lower inflammation | Growing evidence from observational and interventional studies | Monitor levels in high-risk groups; supplementation may reduce flare-ups |
| Cardiovascular Disease | May help regulate blood pressure and reduce vascular inflammation | Observational studies show correlations; causality still under review | Maintain optimal vitamin D levels, especially in at-risk individuals |
| Type 2 Diabetes | May improve insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism | Some studies support improved glycemic control with adequate vitamin D | Monitor vitamin D in diabetic or prediabetic patients |
| Depression and Mood Disorders | Supports serotonin and dopamine production; may reduce inflammation in the brain | Several studies show improvement in mood with supplementation | Consider checking vitamin D levels in patients with mood disorders |
| Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) | Kidneys activate vitamin D; deficiency worsens mineral metabolism in CKD | Strong evidence in nephrology; vitamin D analogs often prescribed | Use active forms of vitamin D; regular monitoring required |
| Obesity | Vitamin D stored in fat tissue; low bioavailability in overweight individuals | Inverse correlation between vitamin D levels and BMI | Higher doses may be required; weight management also important |
Vitamin D3 Needs Across the Lifespan
Our need for vitamin D3 changes as we go through life. It helps with growth, development, and our well-being. Infants and
Requirements for Children and Teens
For kids and teenagers, getting enough Vitamin D3 is very important for their growth and development. This vitamin helps with strong bones, good muscle function, and overall health. During times of fast growth, it is even more important to maintain the right levels of Vitamin D. This helps support bone health and calcium absorption. If children and teens don’t get enough Vitamin D, they might face risks like bone fractures and muscle weakness. To make sure they get their daily Vitamin D, it’s good to add foods like fatty fish, dairy products, and supplements to their meals.
Maintaining Levels in Adulthood
To keep good levels of Vitamin D3 as you grow up, try to get enough sun, eat foods like fatty fish, and take vitamin D supplements. As you get older, your skin can produce less Vitamin D3, so taking supplements can be important. Having enough Vitamin D3 helps with bone health, immune function, and muscle strength, which are all needed for good health. Talk to your healthcare provider to find the best dosage and how often to take it for your needs. It’s important to find the right balance; avoid low levels to prevent health issues, but don’t take too much, either. Stay active in managing your Vitamin D3 levels for a healthier adult life.
Supporting Seniors’ Health and Stability
Keeping good levels of Vitamin D3 is important for the health and stability of older adults. Many seniors do not get enough sun exposure, which can lead to Vitamin D deficiency. This deficiency can harm bone health, muscle function, and the immune system. It can also affect overall well-being. To help older adults keep healthy levels of this vital nutrient, they can include Vitamin D-rich foods, take supplements, or practice safe sun exposure. This will support their health and stability as they grow older.
Environment and Vitamin D3 Levels

Seasons and sunlight are important for vitamin D levels. Where you live affects how much sunlight you get, impacting how your skin makes vitamin D. People in sunny areas may need less vitamin D supplements than those in places with less sunlight. Knowing these factors can help you change how much vitamin D3 you take. Being aware of your location can help you improve your vitamin D levels naturally. Always remember that your environment affects how well your body produces this important nutrient.
How Season and Sunlight Affect Vitamin D Levels
Seasonal changes have a big effect on vitamin D levels because there is less sunlight in winter. Sunlight helps the skin make vitamin D, which is important for good health. In places with long winters and little sunlight, the risk of deficiency increases. On the other hand, summer sunlight helps produce enough vitamin D. Knowing about these changes can help you adjust what you eat or how much you use supplements to keep the right levels all year. Checking vitamin D levels during different seasons ensures you have enough support for your immune health, bone strength, and overall well-being. Adding sunlight exposure to your daily routine can help with vitamin D production.
Adjusting Intake Based on Where You Live
When thinking about where you live, it’s important to adjust your vitamin D3 intake. People who live in places with little sunlight may need to take more supplements. On the other hand, those in sunny spots might need less. Things like air pollution that affect UVB rays and cultural habits can also change your vitamin D3 levels. It’s a good idea to talk to a healthcare provider for advice that fits your needs. Knowing how your surroundings affect vitamin D3 can help you keep your levels good and support your health. It’s key to find the right balance based on where you are for proper supplementation.
Comparing Vitamin D2 and D3
Vitamin D2 and D3 are different, and they can affect your health in various ways. Vitamin D2 usually comes from plants and is common in supplements. On the other hand, D3 mainly comes from animal sources and sunlight. Studies show that D3 might work better at boosting vitamin D levels in the body than D2. Still, both types can raise your vitamin D levels. Knowing these differences can help you choose the right supplements for better health. Be sure to talk to your healthcare provider before starting any new supplements.
| Feature | Vitamin D2 (Ergocalciferol) | Vitamin D3 (Cholecalciferol) |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Plant-based (e.g., UV-exposed mushrooms) | Animal-based (e.g., fatty fish, egg yolks, lanolin) |
| Potency / Effectiveness | Less potent, shorter acting | More potent, longer lasting |
| Absorption Rate | Lower bioavailability | Higher bioavailability |
| Duration in the Body | Shorter half-life | Longer half-life |
| Common Supplement Use | Used in vegan-friendly supplements | Most commonly used in general supplements |
| Food Sources | Fortified foods, mushrooms exposed to UV light | Salmon, mackerel, sardines, cod liver oil, egg yolks |
| Prescription Availability | Available in some prescription vitamin D treatments | Widely available over the counter and by prescription |
Chemical Differences and Dietary Sources
Vitamin D3 and D2 are two types of vitamin D. D3 is more active and better at increasing vitamin D levels in the blood. You can find D3 in animal foods like fatty fish, liver, and egg yolks. D2 mainly comes from plants, especially mushrooms exposed to ultraviolet light. When taking supplements, people usually choose D3 because it is stronger. Still, D2 works for vegetarians. Eating a well-balanced diet that has foods rich in vitamin D and thinking about supplements can help keep your levels good.
Which Is More Effective and Why?
Vitamin D3 works better than D2 because it is easier for the body to use and can increase blood levels more efficiently. D3 is similar to the form our skin makes, and it remains active in the body for a longer time. This makes D3 a better choice for keeping vitamin D levels healthy.
Daily Vitamin D3 Habits for Optimal Health

Getting enough vitamin D3 is important for your health. Start by getting safe sun exposure, especially in the morning or late afternoon. Include foods that are rich in vitamin D3, like fatty fish, eggs, and milk that has been fortified. If needed, you can think about vitamin D3 supplements, but talk to your healthcare provider first. Create daily habits to keep your vitamin D3 levels good, such as exercising outside. Remember to use moderation; too much vitamin D3 can be harmful. By following these daily habits, you can help your immune system, keep strong bones, and improve your overall health.
Getting Safe Sun Exposure
When you want to enjoy the sun safely, finding the right balance is important. Sunlight is a key source of Vitamin D, but too much can harm your skin. To get the most benefits and lower risks, pay attention to the time of day. Early morning or late afternoon sun is usually the safest. Also, wearing protective clothes and using sunscreen can protect your skin. Gentle exposure, rather than a lot, is vital for getting Vitamin D from the sun. Remember, moderation helps you enjoy the sunlight in a responsible way.
Building a Vitamin D3-Rich Diet
When you want to create a diet that is rich in vitamin D3, adding foods like fatty fish (such as salmon and mackerel), egg yolks, and fortified dairy products can help. Mushrooms that have been exposed to ultraviolet light are also a good choice. Eating a variety of these foods can help you keep the right levels of vitamin D. You can include fortified orange juice or cereals in your daily intake to help meet the recommended levels too. Overall, taking a balanced approach by adding these sources to your diet can support your body’s need for vitamin D3, which is good for your health and well-being.
Daily Habits to Maintain Optimal Levels
To keep good Vitamin D3 levels, it’s important to develop daily habits that help your body. Aim for safe sun exposure. This means you should get enough sunlight without hurting your skin. Eat foods high in Vitamin D3, like fatty fish or foods that are fortified. Being consistent is crucial, so try to have a balance of these foods and, if needed, supplements. Regular exercise can also help your body absorb Vitamin D better. By adding these habits to your daily routine, you can maintain healthy Vitamin D3 levels and support your overall well-being.
Managing Long-Term Vitamin D3 Deficiency
If you have a long-term vitamin D3 deficiency, it’s important to check your levels often. Retesting helps you see any progress and change treatment plans if needed. Working with your healthcare providers can lead to recovery plans that fit your needs. Getting enough sun exposure, thinking about dietary supplements, and living a healthy lifestyle are important for managing this deficiency over time. Remember, being consistent is essential in bringing back and keeping good vitamin D levels. It’s important for your overall health and well-being.
When to Retest and Monitor
It’s important to check your vitamin D levels often. This is especially true if you have been low on vitamin D or if you have made big changes to how you take supplements. You should check your levels after beginning or changing your supplement routine to see how well it works. It’s also a good idea to retest if you feel symptoms of deficiency, have health issues that affect how your body absorbs vitamin D, or if you are getting treatments that might change your levels. You should talk to a healthcare provider to decide how often to test based on your health situation. Regular checks ensure your vitamin D levels stay good for your overall health and wellness.
Creating a Sustainable Recovery Plan
After finding out you have a vitamin D deficiency, it’s important to create a recovery plan that works for you. Your healthcare provider may suggest ways to get sunlight, change your diet, and take vitamin D supplements. These suggestions will fit your individual needs. You should also have regular blood tests. They will help check your progress to make sure your vitamin D levels are in the right range. Stay well-hydrated and eat a balanced diet with foods high in vitamin D. You may need to make some lifestyle changes too. Working closely with your healthcare team and following their advice will help you effectively manage your vitamin D deficiency and improve your overall health and well-being.
The content on WellwayHub.com is intended for general informational purposes only and should not be taken as medical advice. Please consult your doctor or a qualified health professional before making any changes to your health routine.
Some links on WellwayHub.com may be affiliate links. This means we may earn a small commission if you make a purchase through these links, at no extra cost to you. This helps support our mission to provide trusted wellness content.
Frequently Asked Questions
To keep enough vitamin D, try to get 10-30 minutes of sunlight at midday. Make sure the sunlight hits your skin directly. Things like your skin type, where you live, and the time of year can affect how much you need. Balance is important so you do not get hurt by the sun.
To stay healthy, adults usually need 600-800 IU of vitamin D3 every day. Still, what each person needs can differ because of age, where they live, and how much sun exposure they get. It’s a good idea to talk to a healthcare provider for tailored advice.
Taking vitamin D3 every day is a good idea because it doesn’t last long in the body. Some people choose to take higher doses once a week instead, as it is easier for them. It’s best to talk to a healthcare provider to find the right plan that fits your needs and way of life.
Taking too much vitamin D3 can be harmful. It may cause symptoms like feeling sick and weak. It’s important to stick to the suggested amounts. Always check with a healthcare provider for advice. Having too much vitamin D3 can negatively affect your health.
Getting enough vitamin D3 from food can be hard. You can find it in fatty fish, egg yolks, and some fortified foods. However, sunlight is the main source of this vitamin. Sometimes, you may need supplements to make sure you get enough each day.
Vitamin D3 is important for keeping our mood stable. It may help reduce feelings of depression. You can get Vitamin D3 through sunlight and supplements. Having enough of it is connected to better mental health and overall wellbeing.
Signs that you may not have enough vitamin D3 include feeling tired, having muscle weakness, experiencing bone pain, and getting sick often. You might also notice changes in your mood, hair loss, and that cuts take longer to heal. It is important to recognize these signs to address the deficiency properly.
Vitamin D3 is very important for the immune system. It helps to control immune responses and lowers inflammation. This vitamin helps fight off infections and boosts the body’s defenses. Having enough vitamin D3 is key for good immune health.