
Introduction
In the world of nutritional supplements, fish oil stands out as a source of fatty acid supplements. It is rich in important fatty acids like eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). Fish oil is well-known for its possible health benefits, especially in supplement use. It may help with heart health and brain function. There are many reasons to add a fish oil supplement to your daily routine. This guide will look at these benefits. It will also cover the different types of fish oil, how much to take, and any possible side effects.
Understanding Fish Oil: Composition and Essential Functions
Fish oil comes from the fatty parts of fish like salmon, tuna, mackerel, and sardines. These fish get omega-3 fatty acids, which contribute to better health, by eating microalgae or smaller fish that have these important nutrients. Why are omega-3 fatty acids, especially EPA and DHA, so vital? They play a key role in many body functions. They help with cell growth, development, and decreasing inflammation.
What Is Fish Oil? Main Nutrients and Active Components
Fish oil mainly contains two important omega-3 fatty acids: EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid). These fatty acids, along with flaxseed oil, help make fish oil a great source of nutrition. Both provide various health benefits, but they work a bit differently in the body.
EPA is known for its strong anti-inflammatory effects. It’s very useful for conditions like heart disease and arthritis. DHA is important for the brain and the retina, which ties it to brain health and cognitive function.
Learning about EPA and DHA helps us understand the different health benefits of fish oil. They help reduce inflammation and support heart and brain health. This is why fish oil is highly regarded in the nutrition world.
How Fish Oil Supports Your Overall Health
The great thing about fish oil as a dietary supplement is that it may offer many health benefits. Taking fish oil daily, in the right amounts, can lead to good health outcomes.
One main way fish oil helps your health is by lowering the risk of cardiovascular issues. Research shows that omega-3 fatty acids, especially EPA and DHA, can lower triglyceride levels and blood pressure. These are two important risk factors for heart disease.
Also, over-the-counter fish oil’s anti-inflammatory effects go beyond just heart health. By reducing inflammation in the body, fish oil pills might help lower the risk of long-term diseases like arthritis, some cancers, and even mental health issues like depression. Although more studies are needed in some areas, the current evidence clearly points to the fact that adding fish oil to your daily routine can help you stay healthy.
Proven Health Benefits of Fish Oil: For Heart, Brain, Joints & More
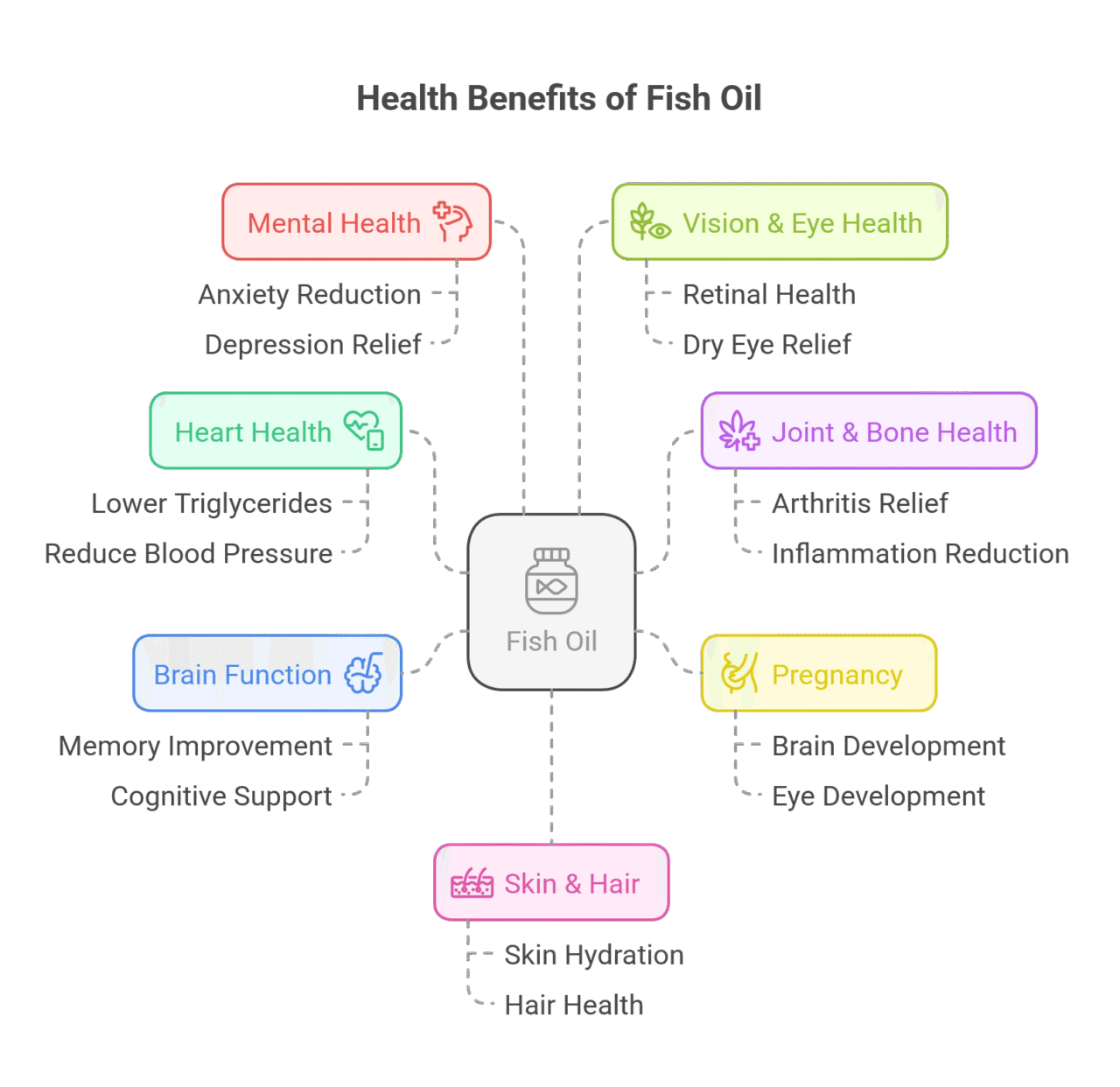
Many scientific studies have looked into the possible benefits of taking fish oil. Although we may still need more research to fully confirm all the claimed benefits, a lot of evidence shows that fish oil can help with different health areas. This includes heart health, mental health, and cognitive function. Let’s take a closer look at some of these benefits.
Fish Oil for Heart and Cardiovascular Health
Fish oil is known for having a lot of omega-3 fatty acids, which can be good for heart health. Research shows that EPA and DHA in fish oil may help lower triglyceride levels, reduce blood pressure, and might prevent plaque from forming in the arteries, contributing to better prescription drugs administration outcomes.
A review published in the Journal of the American Medical Association looked at several studies. It found that taking omega-3 fatty acids, including fish oil, could lower the risk of major cardiovascular disease events, including heart attack, according to the American Heart Association.
However, just taking fish oil won’t remove all risk factors. Using it along with a heart-healthy lifestyle, which includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, and managing stress, can really help keep your heart healthy.
Fish Oil for Joint & Bone Health: Arthritis and Inflammation Relief
One of the best-known benefits of fish oil is that it may help with joint pain and lessen inflammation. This is especially true for people with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. The EPA found in fish oil is thought to be important in doing this.
Research has shown that taking fish oil can help reduce joint pain, stiffness, and tenderness for those with rheumatoid arthritis. Some studies even suggest that fish oil might lower the need for nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). This offers a possibly safer and more natural way to manage joint pain.
Fish oil should not replace medicines your doctor prescribes. However, it can be a helpful part of your overall plan to manage arthritis and other joint problems.
Fish Oil During Pregnancy: Benefits for Infant Development
DHA is very important during pregnancy and infancy. It is a key part of the brain and eyes. DHA helps with growth, especially in the brain and sight.
Research shows that getting enough DHA during pregnancy can lead to better thinking skills and eyesight in babies. Some studies suggest that DHA can also help lower the chances of allergies and eczema in infants if taken during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Pregnant women should talk to their healthcare provider before starting any new supplements, like fish oil. The evidence helps show how DHA is important for healthy growth and long-term health benefits for babies.
Fish Oil for Brain Function: Memory and Cognitive Support
The brain is a complex part of the body. It needs the right balance of nutrients to work well. DHA plays an important role in brain health. It is a main part of brain cell membranes. Keeping a good level of DHA is important for thinking and memory throughout life.
Many studies have looked at the benefits of fish oil, which is full of DHA. This oil may help support brain health and potentially benefit individuals with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. It might reduce cognitive decline as people get older. Research shows positive results. Fish oil supplementation could help improve memory, focus, and how well older adults think.
While we need more studies to understand how it works, the evidence says adding fish oil to your meals, especially as you age, can help keep your brain healthy and maintain its function.
Fish Oil and Mental Health: Support for Anxiety and Depression?
The connection between diet and mental health is getting more attention. Omega-3 fatty acids are important because they may help with mood and lower symptoms in the treatment of depression, as well as anxiety and depression.
Research results are not completely certain. Mental health is complicated, and many factors play a role. However, some studies say that people with depression could have less EPA and DHA in their blood.
Because of this, fish oil supplementation has been looked at as a possible extra treatment for depression and anxiety. Some studies show that taking fish oil can slightly lower symptoms, especially those related to depression.
Fish Oil for Vision and Eye Health
The eyes need special nutrients to stay healthy, just like the brain does. DHA is very important because it is found a lot in the retina.
Getting enough DHA is thought to help the retina work well. It may also protect against some eye problems, especially age-related macular degeneration (AMD). AMD is a top reason for vision loss in older adults.
Studies on fish oil supplementation and AMD prevention have had mixed results. However, some research shows that fish oil might be helpful. Also, some people take fish oil supplements for dry eyes, which happens when the eyes do not have enough moisture.
Fish Oil for Skin and Hair: Anti-Aging & Hydration
Fish oil provides health benefits not only for your insides but also for your skin and hair. The omega-3 fatty acids in fish oil, especially EPA, can help reduce inflammation, showcasing beneficial effects for skin issues like acne and eczema.
DHA is important too. It helps keep skin cells strong, which can keep your skin hydrated and may help slow down aging. Many people notice that taking fish oil supplements makes their skin feel softer and more moisturized.
There isn’t much scientific proof that fish oil helps with hair growth directly. However, some people say their hair becomes thicker and healthier when they regularly consume fish oil. This could be due to healthier skin and the role of essential fatty acids in helping cells grow and repair.
Summary Table: Health Benefits of Fish Oil
| Health Benefit | How Fish Oil Helps | Key Omega-3s Involved | Scientific Support |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heart Health & Cardiovascular Support | Lowers triglycerides, reduces blood pressure, may prevent artery plaque | EPA & DHA | Strong evidence; supported by JAMA review |
| Joint & Bone Health | Reduces joint pain, stiffness, and inflammation (especially for arthritis) | EPA | Well-supported; may reduce NSAID use |
| Pregnancy & Infant Development | Supports brain and eye development in babies, may reduce allergy risk | DHA | Strong evidence for cognitive benefits |
| Brain Function & Cognitive Enhancement | Supports memory, focus, and cognitive function, may reduce cognitive decline | DHA | Some evidence, needs more research |
| Mental Health Support | May reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression | EPA & DHA | Mixed evidence but promising results |
| Vision & Eye Protection | Supports retinal health, may reduce risk of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) | DHA | Mixed research results but potential benefits |
| Skin & Hair Health | Reduces inflammation (acne, eczema), improves hydration, may slow aging | EPA & DHA | Some evidence for skin benefits, limited for hair growth |
Types of Fish Oil Supplements: Cod Liver, Krill, Algal, and Fish Body Oil

To navigate the world of fish oil supplements, it is important to know about the different types. Each type has its own makeup and possible benefits. For example, cod liver oil, krill oil, and algal oil are popular options. Exploring these choices helps you make the best decision based on your own needs and likes.
Cod Liver Oil: Nutrient Profile and Safety Considerations
Cod liver oil is a special fish oil that many remember as a supplement for children from the past. It’s made from the liver of codfish and has a lot of omega-3 fatty acids along with vitamins A and D.
Even though vitamins A and D are important for health, having too much can be bad. This is a concern with cod liver oil because it has high levels of vitamin A. Taking too much cod liver oil might lead to vitamin A toxicity. This can cause problems for the body.
Therefore, it is important to take cod liver oil in moderation. Also, it’s good to pick well-known brands that follow the safe limits for vitamin A. If you are thinking about using cod liver oil, it is a good idea to talk to your healthcare provider. They can help you decide if it is right for your needs.
Fish Body Oil – Standard Omega-3 Source
Fish body oil is what we often think about when we hear about fish oil supplements. It comes from the flesh of fatty fish like salmon, tuna, mackerel, herring, and anchovies, unlike cod liver oil, which is made from the liver.
Fish body oil offers good amounts of EPA and DHA, making it beneficial for the treatment of dry eye disease. These are the two main omega-3 fatty acids linked to many health benefits. The amount of EPA to DHA can change based on the type of fish used. For example, salmon oil usually has more DHA, while oils from herring, mackerel, and anchovies may have more EPA.
Fish body oil is typically safe to take when you stick to the recommended amounts. It’s wise to choose well-known brands that ensure purity and quality.
Krill Oil vs Fish Oil: Which Supplement to Choose?
Krill oil is becoming popular as a different source of omega-3 fatty acids. It comes from krill, which are small sea animals. Krill oil has EPA and DHA, but these fatty acids are linked to phospholipids. In fish oil, they are linked to triglycerides.
This difference may help the body absorb omega-3s from krill oil better. Plus, krill oil has a strong antioxidant called astaxanthin. This antioxidant gives krill oil its red color. Astaxanthin may have extra health benefits. It might help protect against oxidative stress and support eye health.
Even though krill oil looks promising for omega-3s, we need more studies. We must find out if it truly has better benefits than regular fish oil.
Algal Oil: Vegan-Friendly Alternative to Fish Oil
For people who are vegan or vegetarian, finding a good plant-based replacement for fish oil has been important. Algal oil, which comes from microalgae, is a great option. What sets algal oil apart is that it offers DHA, the omega-3 fatty acid linked to brain and eye health.
Many plant sources of omega-3s mainly have ALA (alpha-linolenic acid). The body has to convert ALA into EPA and DHA, but it does this with little success. In contrast, algal oil gives you DHA directly, eliminating that extra step.
This makes algal oil easy to use and friendly for vegans who want the benefits of DHA. It is also better for the environment than fish oil since it doesn’t rely on harming fish populations.
Comparison Table: Types of Fish Oil Supplements
| Factor | Cod Liver Oil | Fish Body Oil | Krill Oil | Algal Oil |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Liver of cod fish | Flesh of fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines) | Small crustaceans (krill) | Marine algae |
| Omega-3 Content | Moderate to high EPA & DHA; rich in vitamins A & D | High EPA & DHA; minimal vitamins | Lower total EPA & DHA than fish oil, but in phospholipid form; contains astaxanthin | High DHA, very low or no EPA |
| Typical EPA:DHA Ratio | Usually more DHA than EPA | Balanced or more EPA than DHA | EPA:DHA ratio often around 2:1 | Mostly DHA; EPA usually very low or absent |
| Absorption | Good (triglyceride form) | Variable (triglyceride form is best; ethyl ester is less bioavailable) | Very high (phospholipid form enhances absorption) | Good (triglyceride form) |
| Antioxidants | Natural vitamins A & D | Minimal | Contains astaxanthin (potent antioxidant) | May be fortified with antioxidants (not always included) |
| Taste/Aftertaste | Strong fishy taste; often in liquid form | Mild to strong; some deodorized; fishy burps possible | Mild, fewer “fish burps” | Neutral or mild; no fishy aftertaste |
| Allergen Concerns | Fish allergy risk | Fish allergy risk | Shellfish allergy risk | Allergen-free (vegan-friendly) |
| Dietary Suitability | Not suitable for vegans/vegetarians | Not suitable for vegans/vegetarians | Not suitable for vegans/vegetarians | Vegan, vegetarian |
| Risks | Excess vitamin A can be toxic; caution in pregnancy | Risk of oxidation/rancidity; possible heavy metals or pollutants (if unpurified) | Shellfish allergy risk; more expensive; limited long-term data | Low risk; very low EPA content; may not meet all needs |
| Best Uses | Bone/joint health, immune support (short-term use) | General heart & brain health; most common supplement | Superior absorption, brain & heart health; antioxidant boost | Vegan/vegetarian DHA source; brain health; pregnancy support |
Best Food Sources of Fish Oil

As helpful as fish oil supplements might be, getting omega-3 fatty acids from whole foods is the best way to go. Nature has many fatty fish that are rich in EPA and DHA, which are the key omega-3s.
Adding these fish to your meals gives you important fatty acids along with other nutrients that are essential for good health. Let’s look at the best natural sources of fish oil and see how you can make them tasty in your dishes.
Fatty Fish – The Best Source of EPA & DHA
If you want to increase your intake of EPA and DHA, which are important omega-3 fatty acids, also known as polyunsaturated fatty acids, in fish oil, look to fatty fish. These fish are called “fatty” because they are full of omega-3, making them great for heart health, brain function, and overall well-being.
Here are some of the best fatty fish you can eat:
- Salmon: Known for its great taste and versatility, salmon is a fantastic source of both EPA and DHA.
- Mackerel: Enjoy mackerel fresh, smoked, or even canned. This oily fish is also rich in omega-3s.
- Sardines: Don’t ignore these small fish! Sardines provide a lot of omega-3s and are packed with calcium and vitamin D too.
Plant-Based Alternatives: Can ALA Replace Fish Oil?
Plant-based omega-3 (ALA) has some benefits, but it might not be enough to replace fish oil completely. ALA is a solid source, but fish oil provides important EPA and DHA that plant-based choices do not. These nutrients are essential for your health. For the best results, think about using both ALA and fish oil.
Fish Oil Supplements: Dosage, Forms & Quality Standards

Fish oil supplements are a simple way to boost your omega-3 intake. This is great if you do not like eating fish often. However, picking the right fish oil supplement can be confusing. There are many brands, types, and doses to choose from.
It’s important to know the difference between liquid fish oil and capsules. You also need to find the right dosage for your needs. Lastly, make sure to focus on quality when selecting a fish oil supplement that fits your health goals.
Fish Oil: Liquid vs Capsules – Which Form to Choose?
When you want to choose the best fish oil products supplement, you might wonder whether to pick liquid fish oil or capsules. Both give you omega-3 fatty acids, but they are different when it comes to how well you can absorb them and how easy they are to use.
Liquid fish oil usually has more omega-3s in each serving than capsules. But the taste can be very strong and “fishy,” which some people do not like.
Fish Oil capsules are easier to take and help hide the fishy taste. They are also better for traveling. However, some capsules may have extra ingredients, like fillers and coatings, which may not work for everyone.
In the end, the best fish oil for you depends on what you like and your way of life. If you do not like strong tastes, capsules could be better. But if getting a higher amount of omega-3s is important to you, then liquid fish oil might be the way to go.
The table below compares liquid fish oil and capsules side by side, helping you decide which form best fits your needs and lifestyle.
| Feature | Liquid Fish Oil | Fish Oil Capsules (Softgels) |
|---|---|---|
| Dosage & Flexibility | Highly flexible; easy to measure by milliliter/teaspoon. Ideal for high or titrated doses (e.g., therapeutic use, children). | Fixed dose per capsule. Increasing dose requires more capsules, which can be inconvenient. |
| Convenience & Portability | Less convenient: requires spoon or dropper, can be messy, needs refrigeration after opening. Not ideal for travel or on-the-go use. | Very convenient: easy to carry, store, and take anywhere. No measuring needed. |
| Taste & Aftertaste | Strong fishy taste for many; premium brands may add lemon/orange flavors. May be unpleasant for some users. | Tasteless when swallowed; some may experience “fish burps.” Enteric-coated capsules can help prevent this. |
| Absorption | Slightly faster—absorbed directly (no capsule to break down). | Excellent absorption; slightly delayed due to capsule shell, but difference is minimal for most people. |
| Freshness & Stability | More prone to oxidation/rancidity after opening; exposed to air. Requires refrigeration and should be used within a few months. | More stable and long-lasting: capsules protect oil from air and light, preserving freshness. |
| Cost Per Serving | Generally more cost-effective—higher EPA/DHA per dollar. | Usually more expensive per gram of omega-3 due to encapsulation process. |
| Dosing Accuracy | Can be highly accurate if measured with proper tool; risk of dosing error if not measured carefully. | Always precise—each capsule contains a standard, labeled amount. |
| Best For | People who need high or therapeutic doses, children or adults who can’t swallow pills, and those looking for a budget-friendly option. | People who prioritize convenience or travel, are sensitive to the taste of fish oil, or want standard maintenance dosing. |
| Downsides | Unpleasant taste for some, risk of spills, refrigeration needed, less portable, shorter shelf life after opening. | Dose not easily adjustable, may cause “fish burps” in sensitive individuals. |
How to Take Fish Oil: Dosage, Timing & Tips
To get the most out of fish oil supplements, you need to take them the right way. Knowing the right doses, the best times to take them, and any possible side effects can help you absorb them better and boost your health.
Most health experts suggest taking about 250-500 milligrams (mg) of EPA and DHA together each day for good health, especially for those managing health concerns like high blood pressure or high triglyceride levels. This amount can change based on your needs. For people with specific health issues, a healthcare provider may suggest a higher dose.
It’s usually a good idea to take fish oil with a meal that has some fat in it. Fish oil dissolves in fat, so having it with healthy fats can help your body absorb it better.
| Category | Details / Recommendations |
|---|---|
| Typical Dosage | 250–500 mg combined EPA + DHA daily for general health (adults).1000 mg or more daily may be recommended for specific conditions (e.g., high triglycerides) under healthcare supervision. |
| How to Take | With food, preferably a meal containing fat, to improve absorption. |
| Best Time to Take | Any time of day; consistency is key.Morning is preferred by some to avoid possible “fish burps” at night. |
| Liquid vs Capsule | Liquid allows flexible dosing; capsules provide convenience and accurate, pre-measured doses. |
| Divided Doses | Splitting the total daily dose (e.g., morning and evening) may reduce side effects and support better absorption. |
| Tips to Reduce Aftertaste | Store in refrigerator; choose enteric-coated capsules or flavored liquids; always take with meals. |
| Who Should Consult a Doctor | Pregnant or breastfeeding women, people taking blood thinners, or those with chronic health conditions should consult a healthcare professional before use. |
| Maximum Safe Dose | Up to 3000 mg EPA + DHA per day is generally considered safe for most adults (NIH/EFSA).Higher doses only under medical supervision. |
| What to Check on Labels | Check EPA/DHA amounts (not just total fish oil), product purity, third-party testing, freshness, and expiration date. |
When to Take Fish Oil: Morning or Night?
The debate about when to take fish oil is ongoing. There isn’t a clear answer with strong scientific proof, but thinking about things like your body clock, meal times, and possible side effects can help you decide.
Some people like to take fish oil in the morning. They believe it jumps up their metabolism and gives them energy for the day. But taking fish oil on an empty stomach may cause some stomach issues, like burping or indigestion, for some people.
On the other hand, taking fish oil at night might work better with how our bodies naturally function. While we sleep, the body works on repair and healing. Taking fish oil at night might help your body absorb and use omega-3 fatty acids much better for these processes.
How to Choose the Best Fish Oil Supplement
The many fish oil supplements available can be confusing. To help you choose a good product that gives you real benefits, here are some key things to consider:
Quality Standards: Look for supplements that have been tested by a third party. This means they check for purity, strength, and freshness. Organizations like the International Fish Oil Standards (IFOS) and the Council for Responsible Nutrition (CRN) offer certifications for products that meet their strict quality rules.
EPA and DHA Content: Check the amounts of EPA and DHA on the supplement label. Don’t just look at the total fish oil amount. The EPA to DHA ratio can be different based on the type of fish, so select a product that matches your health needs.
Sustainability: If you care about the environment, choose brands that focus on sustainable fishing. They should get their fish oil from well-managed fisheries. Look for certifications like the Marine Stewardship Council (MSC) label.
Signs of Omega-3 Deficiency: When You May Need a Supplement

Our bodies need omega-3 fatty acids for many important functions. However, some people are unsure if they are getting enough. Knowing the signs of omega-3 deficiency can help you address any issues and take the right action.
A lack of omega-3 can show up in different ways. It can affect your skin, mood, and brain health. Here are some common signs and symptoms:
- Dry, itchy skin: Omega-3s help keep your skin hydrated. If you don’t get enough, your skin can become dry, flaky, and itchy.
- Dull hair and brittle nails: Omega-3s support healthy hair and nails. When you are deficient, nails can become dry and weak, and hair can look dull and lifeless.
- Difficulty concentrating and memory problems: Omega-3s, especially DHA, are critical for brain health. Without enough, you might face brain fog, problems focusing, and memory issues.
- Mood swings and irritability: Studies show a connection between omega-3 levels and mood. A deficiency might cause mood swings, irritability, and an increase in anxiety or depression.
If you think you may not be getting enough omega-3 fatty acids, it’s important to talk with your healthcare provider for advice that suits you.
| Sign / Symptom | How It May Present | Why It Happens / Notes | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dry or Itchy Skin | Rough, flaky, or irritated skin; slow wound healing | Omega-3s help keep the skin barrier strong and hydrated | Increase omega-3-rich foods (e.g., fatty fish, flaxseed, walnuts) or consider a supplement; use gentle skincare products |
| Brittle Hair and Nails | Hair that breaks easily; soft, splitting nails | Omega-3s support healthy hair and nail growth | Eat more oily fish, walnuts, or flaxseed; consult a healthcare provider if the problem persists |
| Frequent Fatigue | Low energy, feeling tired often | Omega-3s play a role in energy metabolism and cell function | Check your diet for healthy fats; consider omega-3 supplementation; rule out other causes of fatigue |
| Poor Concentration or Memory | Trouble focusing, brain fog, forgetfulness | EPA and DHA are crucial for brain and nerve function | Add more omega-3s to your diet; see your doctor if cognitive issues are ongoing |
| Mood Changes | Depression, irritability, or increased anxiety | Low omega-3 status is linked to mood disorders in research | Boost omega-3 intake; seek support from a mental health or healthcare professional |
| Joint Pain or Stiffness | Achy, stiff, or inflamed joints | Omega-3s help reduce inflammation in joints | Try an omega-3 supplement; talk to your doctor about joint pain |
| Dry Eyes or Vision Problems | Burning, stinging, or blurred vision | DHA is a key component of the eye’s retina | Eat more omega-3-rich foods; consult an eye specialist if symptoms persist |
| Frequent Infections | Getting sick more often | Omega-3s support immune system health | Improve nutrition with omega-3s and other nutrients; see a doctor if infections are frequent |
| High Triglycerides/Heart Issues | Elevated triglycerides, increased cardiovascular risk | Omega-3s help lower triglycerides and support heart health | Adopt a heart-healthy diet, increase omega-3 intake; follow up with your healthcare provider |
| Slow Wound Healing | Cuts or scrapes that heal slowly | Omega-3s aid in cell repair and inflammation control | Eat a balanced diet with omega-3s; consult a doctor if healing is unusually slow |
| Who Is Most at Risk | People with low fish intake, vegans/vegetarians, pregnant/breastfeeding women, those with malabsorption or certain chronic illnesses | These groups are more likely to develop a deficiency | Monitor for deficiency signs; discuss omega-3 supplementation with a healthcare professional |
Fish Oil for Weight Management and Metabolic Health

Nutrition plays a big part in managing weight and keeping metabolic health in check. Fish oil is important because it has special omega-3 fatty acids. These have gained interest for how they might help with weight and health.
Fish oil may affect body makeup and blood sugar levels. By learning more about how eating fish oil connects to metabolic health, we can see its possible benefits. This can help in reaching and staying at a healthy weight.
Fish Oil and Weight Loss: Impact on Fat Burning
Fish oil is not a magic weight-loss cure, but some studies show it may help with weight management. This is mainly because it might affect your metabolism and body makeup.
Omega-3 fatty acids, especially EPA and DHA, play a role in the way our body uses fat. Docosahexaenoic acid supplementation and polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation may help your body burn fat for energy, which could lead to small drops in body fat percentage and waist size.
Also, fish oil might help control your hunger and make you feel full. This means that taking fish oil could help you stay satisfied longer, which may lower how many calories you eat.
Fish Oil for Blood Sugar and Diabetes Risk
The rise in type 2 diabetes around the world has made people pay more attention to prevention and lifestyle changes. It is important to keep blood sugar levels steady to lower the chances of getting this condition.
Research shows that fish oil may help with blood sugar control. Omega-3 fatty acids in fish oil could make the body better at using insulin to manage blood sugar.
Studies suggest that taking fish oil supplements might help people who are at risk or already have type 2 diabetes. This could lead to some improvement in blood sugar levels.
Fish Oil for Athletic Performance and Recovery

Athletes always look for ways to improve their nutrition. They want strategies that help them perform better and recover quicker. Fish oil is popular because it has many omega-3 fatty acids. This makes it a possible aid for athletes. It could help improve their performance and support recovery after workouts.
Now, let’s take a closer look at how fish oil may benefit athletes. It might help lessen muscle soreness and improve stamina and endurance.
Fish Oil for Muscle Soreness and Recovery
Intense exercise often causes muscle pain and swelling. This can disrupt an athlete’s training plan and overall performance. Delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS) is a common issue for athletes. It comes with muscle pain, stiffness, and sensitivity. These feelings usually get worse 24 to 72 hours after hard workouts.
Omega-3 fatty acids, especially EPA, are known for their ability to reduce inflammation. They may help decrease the muscle damage and inflammation linked to DOMS.
Research on fish oil supplementation and its effects on muscle soreness and recovery has shown different results. Some studies found that athletes who took fish oil supplements had less muscle pain and lower levels of muscle damage compared to those who did not take these supplements.
Fish Oil for Stamina and Endurance
Endurance athletes like marathon runners, cyclists, and swimmers often push their bodies to the limit. They need a lot of energy and good heart health. While carbohydrates are the main fuel for endurance sports, getting enough omega-3 might help improve performance. This is because omega-3 can influence energy use and reduce inflammation.
Some studies show that omega-3 fatty acids may help the body use oxygen better during exercise. This can let athletes work harder for longer. This benefit comes from fish oil, which can improve blood flow and deliver more oxygen to muscles that are working.
Also, by lowering inflammation caused by exercise, fish oil may help reduce muscle damage and tiredness. This can help athletes recover more quickly and keep up with their training plans.
Potential Risks and Side Effects of Fish Oil

Fish oil is usually safe to take in recommended amounts. However, it is important to know about possible risks and side effects. By understanding these points, you can make better choices about fish oil supplementation. This will help you take steps to reduce the chance of any bad reactions.
Common Fish Oil Side Effects and How to Reduce Them
Fish oil is usually safe for most people when taken in the right amounts. Some may feel mild side effects, mainly in the stomach area. These side effects tend to happen more when a higher dose of fish oil is used.
The most common side effects of fish oil are:
- Fishy Burps: Many people find that they have fishy burps after taking fish oil supplements. This can be an annoying aftertaste for some.
- Indigestion: Some might feel indigestion, heartburn, or a bloated feeling after using fish oil.
- Diarrhea: Fish oil can act as a mild laxative, and for some, it may lead to diarrhea, especially at high doses.
Luckily, there are ways to lessen these side effects. This can make adding fish oil to your daily routine more enjoyable. The best way is to start with a small dose and slowly increase it if needed.
| Side Effect / Concern | Severity / Frequency | Why It Happens / Description | How to Avoid or Minimize It |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nausea, Stomach Upset, Diarrhea | Common / Mild to Moderate | Most frequent side effects, especially at higher doses. Fish oil can irritate the gastrointestinal tract in some individuals. | • Start with a lower dose and gradually increase• Take with food• Split the daily dose into 2–3 servings |
| “Fishy” Aftertaste or Burps | Common / Mild | Fish oil may “repeat” on you (“fish burps”), especially with uncoated capsules or large doses. | • Choose enteric-coated capsules• Take with meals• Try flavored liquids• Store capsules in the refrigerator |
| “Fishy” Body Odor (Breath, Sweat) | Occasional / Mild | Caused by breakdown of certain fish oil compounds (trimethylamine). More likely at very high doses (>3,000 mg/day). | • Lower the dose• Maintain good hydration and hygiene• Try different brands or purified fish oil products |
| Increased Bleeding Risk | Rare / Dose-dependent | Large doses of fish oil (>3,000 mg/day) may reduce blood clotting slightly; caution if taking blood thinners or before surgery. | • Stay within recommended dose unless advised by a healthcare provider• Consult your doctor if taking blood thinners |
| Allergic Reactions | Rare / Mild to Severe | Most likely in people with fish or shellfish allergies; can cause rash, itching, or swelling. | • Use algal oil (plant-based omega-3) if allergic to fish/shellfish• Seek medical help if symptoms occur |
| Elevated Blood Sugar (in Diabetes) | Rare / Mild to Moderate | Some studies suggest large doses may slightly raise blood sugar in people with diabetes. | • Monitor blood sugar levels• Stay within recommended dose• Consult your healthcare provider if you have diabetes |
Who Should Avoid Fish Oil Supplements?
While fish oil has many possible health benefits, some people should be careful or avoid taking fish oil supplements. This is because it might interact with their health issues or medications.
- Individuals with Bleeding Disorders: Fish oil can thin the blood. This may raise the risk of bleeding for people who have bleeding disorders or who take blood-thinning medications like warfarin.
- Individuals with Fish or Shellfish Allergies: Since fish oil comes from fish, those with fish or shellfish allergies should stay away from fish oil supplements to prevent allergic reactions.
- Pregnant and Breastfeeding Women: Omega-3 fatty acids are important during pregnancy and breastfeeding, especially DHA for developing fetal brains and eyes. However, it is crucial to talk with a healthcare provider before taking fish oil supplements. Some fish oil, like cod liver oil, might have high levels of vitamin A, which can be harmful during pregnancy.
The table below shows which groups should be cautious with fish oil supplements and what steps to take for safety.
| Group | Why Caution Is Needed | Recommended Precaution |
|---|---|---|
| Pregnant Women | High doses of fish oil may increase bleeding risk or affect fetal development; cod liver oil may have excessive vitamin A | Avoid high-dose supplements; avoid cod liver oil; consult your obstetrician or healthcare provider |
| Breastfeeding Women | Some contaminants (e.g., mercury, PCBs) may pass into breast milk if fish oil is not purified | Use only high-quality, purified fish oil; do not exceed recommended amounts |
| Infants & Young Children | Sensitive to impurities and excessive doses; risk of choking on capsules | Use only pediatric formulations under medical supervision |
| People with Bleeding Disorders or on Blood Thinners | Fish oil may increase bleeding risk, especially at high doses | Consult your healthcare provider before use; avoid high doses |
| People with Fish or Shellfish Allergies | Risk of allergic reaction | Choose algal oil (plant-based omega-3) or avoid fish oil; consult an allergist |
| People with Diabetes | Large doses may slightly raise blood sugar or interact with medications | Monitor blood sugar closely; consult your healthcare provider |
| People with Upcoming Surgery | Fish oil may increase bleeding risk during and after surgery | Stop taking fish oil at least 1–2 weeks before surgery, as advised by your provider |
Conclusion
Fish oil has many health benefits. It helps your heart, joints, brain function, and mental health. The omega-3 fatty acids in fish oil are very important for your overall well-being. You can take fish oil supplements or add natural sources of fish oil to your meals. It is essential to get enough to improve your health. Always talk to a healthcare provider before you start a new supplement, especially if you have health issues. Make your health a priority by thinking about adding fish oil to your daily routine.
The content on WellwayHub.com is intended for general informational purposes only and should not be taken as medical advice. Please consult your doctor or a qualified health professional before making any changes to your health routine.
Some links on WellwayHub.com may be affiliate links. This means we may earn a small commission if you make a purchase through these links, at no extra cost to you. This helps support our mission to provide trusted wellness content.
Frequently Asked Questions
Fish oil supplements provide omega-3 fatty acids (EPA and DHA) that support heart, brain, eye, and joint health. They may help lower triglycerides, support cognitive function, and reduce inflammation.
Fish oil supplementation can give you helpful EPA and DHA, but it shouldn’t fully replace the good nutrition from eating fish. Whole fish provide more nutrients like protein, vitamins, and minerals. These all help with your overall health.
For many people, taking fish oil supplements every day is usually safe when you follow the directions and stick to the recommended amounts. Still, it’s best to consult your health care provider before you begin any new supplement routine, including fish oil.
Fish oil supplements are usually safe. However, some people may experience mild side effects. These can include fishy burps, indigestion, or diarrhea. To reduce these effects, you can start with a lower dose and slowly increase it as your body gets used to it.
People who have fish or shellfish allergies, bleeding problems, or take blood thinners need to talk to a doctor before they use this. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should also check with a doctor before they use it. If you have surgery planned soon, you should ask your healthcare provider about this before you use it.
The best time to take fish oil supplements can be different for everyone. You can take them at any time of the day that works for you. Some people like to take fish oil with a meal. This can help your body use the oil better and can also stop you from feeling sick. You should make taking your fish oil a habit. Pick the time that is easy for you to remember every day.
To keep fish oil supplements fresh and stop them from going bad, store them in a cool, dark spot. It’s best to place them in the refrigerator after you open the bottle. Heat, light, and air can make fish oil lose its quality.
To pick a good fish oil supplement, you need to read the label and check what’s in it. The best ones have high amounts of EPA and DHA, which are the main types of omega-3 fats. They should not have a lot of fillers or fake stuff added. Get products that are pure and tested for things like heavy metals. A good supplement will say it is tested by a trusted third party. If you want, you can ask your doctor which brands they think are good. Do this to help find a safe choice that works for you.