
Why Your Body Needs Collagen?
Imagine your body as a beautiful structure held together by an important building block – collagen. Collagen is the most abundant protein in the human body, accounting for approximately 30% of all its proteins. This amazing protein is the most common in your body. It works like glue, keeping everything in place. From your skin’s healthy glow to your strong bones, collagen is key to your body’s health and energy.
It helps keep various tissues strong and stretchy. It creates a supportive base for your skin, helping it stay firm and soft. In your joints, collagen acts as a cushion and allows easy movement. It also makes bones stronger, supports hair and nail growth, and is important for wound healing.
How Collagen is Synthesized in the Body
Collagen production is a complex, ongoing process in our bodies, akin to building a sophisticated structure that requires the right materials and tools. It begins with amino acids—primarily glycine, proline, and lysine—from protein-rich foods. These amino acids are assembled into procollagen within fibroblasts, with vitamin C playing a crucial role; insufficient vitamin C halts this assembly.
Once formed, procollagen exits the cell and, with enzymes dependent on minerals like zinc and copper, is bundled into strong collagen fibrils. These fibrils organize into fibers that provide structure and resilience to skin, bones, joints, and other tissues.
Several factors influence this synthesis process:
Age: After age 25, fibroblast activity declines, slowing collagen production while increasing breakdown.
Nutrition: A diet lacking essential amino acids, vitamin C, zinc, or copper hampers synthesis.
Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, excessive sun exposure (UV radiation), high sugar intake, and stress damage existing collagen and impede new production.
A holistic approach—combining a nutrient-rich diet with a healthy lifestyle—is crucial for maintaining collagen levels long-term.
Collagen for Skin: Elasticity, Hydration & Anti-Aging Benefits
Many people want to keep their skin young and glowing. As we get older, our bodies produce less collagen. This decrease can make our skin dry, less firm, and more likely to get wrinkles. Collagen is very important for keeping skin elastic and hydrated. These are key factors for healthy, youthful skin.
Collagen helps support the skin, making it firm and strong. This support improves skin elasticity, so the skin can stretch and bounce back. This action can lessen fine lines and wrinkles. Collagen also works well with hyaluronic acid, another important part of skin health. Together, they help pull in and hold moisture, ensuring the skin stays hydrated. This leads to plumper, smoother, and more youthful skin.
To boost collagen levels, you can use supplements or eat foods that help increase collagen. Doing this can help your skin keep its elasticity, hydration, and overall health. This way, you can maintain a radiant and youthful look.
Collagen for Joint Health, Flexibility & Ligament Support
Healthy joints are important for an active and enjoyable life. As we get older, our collagen levels decrease. This can hurt the cushioning and structure of our joints, causing pain and stiffness. Collagen is key for keeping our joints healthy and flexible. It helps support the strength of our connective tissues.
Collagen is a main part of cartilage, which is the smooth, rubber-like tissue that cushions our bones at the joints. It helps absorb shocks, leading to smooth and pain-free movement. Plus, collagen helps make ligaments strong. Ligaments connect bones and give stability and support to our joints.
Keeping good levels of collagen can help keep your joints healthy and flexible for a long time. This can lower the chances of joint pain and stiffness, helping you stay active and comfortable.
Collagen for Hair Growth & Nail Strength
Who doesn’t want strong, shiny hair and healthy nails? Collagen is good not just for skin and joints but also for these important parts of our look.
Collagen helps make keratin, the protein in our hair and nails. It gives strength, support, and flexibility, which help hair grow healthy and keep nails strong and less breakable. Having enough collagen is key to keeping hair follicles and nail beds strong. This leads to healthier growth and less chance of breakage.
Adding collagen-rich foods or supplements to your daily routine can help your body take care of and boost your hair and nails. This can improve their overall health and look.
Collagen for Bone Density & Fracture Prevention
Strong bones are important for a healthy and active life. Collagen has many benefits for bone health. It helps keep bone density and strength, especially as we grow older. Collagen makes up a large part of the organic matrix in bones. This serves as a base for minerals like calcium and phosphate, which help make bones strong and dense.
Collagen supports bone density, which reduces the risk of fractures and helps maintain overall bone health. This is especially important as we age since bone loss is a common issue, especially for postmenopausal women. Eating foods high in collagen or taking supplements can help keep bones healthy and prevent the loss that comes with age.
These beneficial effects of collagen on bone health also lead to better overall well-being and a more active lifestyle.
How Collagen Supports Heart Health & Blood Vessels
Keeping your blood vessels healthy is key for your overall health. Collagen is very important because it helps make blood vessels strong and flexible. Strong blood vessels are necessary for good blood flow. Collagen gives support to the walls of blood vessels, helping them stretch and bounce back. This support is important for maintaining good blood pressure and circulation in your body.
If you produce enough collagen, your blood vessels can open and close properly, which helps control blood flow and keeps your heart healthy. If collagen levels drop, blood vessel walls may weaken, which can raise the risk of heart problems.
You can support collagen production by eating a balanced diet and taking supplements. This helps keep your blood vessels working well, supports healthy blood pressure, and enhances your overall heart health.
Types of Collagen (I–V): Roles & Benefits Explained

Now that we have talked about the amazing benefits of collagen, let’s look at the different types of this important protein and what they do in the body. There are at least 28 types of collagen, but some are more common and have been studied more than others.
Each type of collagen has its own structure and purpose. They help keep specific tissues healthy and strong. When we know more about the roles of these collagen types, we can make better choices about adding them to our diets to meet our body’s needs.
Type I
Type I collagen is the most common type in the human body. It has a strong, fibrous form that supports many tissues. This type of collagen is found in skin, tendons, ligaments, bones, and teeth.
In the skin, type I collagen creates a network of fibers that helps keep the skin strong and elastic. This keeps the skin looking youthful and glowing. It works well with other types of collagen to help maintain skin health and reduce the signs of aging. Also, type I collagen is important in healing wounds, building bones, and strengthening ligaments and tendons.
Taking in enough type I collagen through diet or supplements is essential. It helps keep tissues strong and healthy, supporting overall well-being and energy.
Type II
When we talk about joint health, type II collagen is very important. It is a major part of cartilage. Cartilage is the soft tissue that cushions and protects our joints. Type II collagen acts like a shock absorber. This helps us move smoothly and without pain.
As we get older, our body makes less type II collagen. This can hurt cartilage and lead to joint pain, stiffness, and less ability to move. Many people look for supplements that support joint health and help with joint pain, especially those with osteoarthritis.
Adding foods or supplements with type II collagen to your diet can help your body keep cartilage healthy. This can reduce joint discomfort and improve overall joint health. It allows you to move more easily and comfortably.
Type III
Type III collagen is an important part of the collagen family. It works together with type I collagen to help keep various tissues strong and in good shape. You can find type III collagen alongside type I in places like the skin, blood vessels, and organs. It is made up of finer and more delicate fibers.
This type of collagen helps with skin elasticity, which makes the skin look youthful and smooth. It also helps to keep blood vessels strong and healthy, which is good for heart health.
In organs, type III collagen is part of the connective tissues. It gives necessary support and strength. Keeping enough type III collagen is important to have healthy tissues and to help them work well.
Type IV
Type IV collagen is important because it creates a light, mesh-like structure known as the basement membrane. This thin layer of tissue rests below epithelial cells. It provides support and helps filter substances in different organs.
Type IV collagen is key to keeping the skin, kidneys, and other organs working well. In the skin, it connects the outer layer, called the epidermis, to the lower layer known as the dermis. This connection helps keep the skin’s structure and function correct.
Additionally, type IV collagen is essential in the filtering parts of the kidneys. It helps the body remove waste. It’s important to keep type IV collagen healthy to support the proper function of these vital organs.
Type V
Type V collagen has a variety of important roles in keeping different tissues and cells healthy in the body. It usually works alongside other types of collagen, helping them do their jobs and keeping tissue strong.
This type of collagen helps form cell surfaces. It affects how cells stick together and how they send signals to one another. You can find type V collagen in the hair, placenta, and cornea, where it helps support their specific structures and functions.
Even though type V collagen is not as common as type I collagen, it is still very important. It helps with the development and function of many different tissues. This shows how connected collagen is to overall health.
Table: Comparing Common Collagen Types
| Collagen Type | Primary Location(s) in the Body | Key Functions & Benefits | Common Sources (Food & Supplements) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type I | Skin, bones, tendons, ligaments, teeth, blood vessels (80–90% of body’s collagen) | Provides tensile strength, skin elasticity, and hydration. Crucial for wound healing and bone structure. | Bovine (beef) collagen, marine (fish) collagen, bone broth, eggshell membranes. |
| Type II | Cartilage (joints), vitreous body of the eye | Main structural component of cartilage, cushions joints, absorbs shock, promotes flexibility and mobility. | Chicken cartilage (sternum), UC-II supplements, chicken bone broth. |
| Type III | Skin, muscles, blood vessels, internal organs (often with Type I) | Supports structure of muscles, organs, and arteries. Essential for skin elasticity and firmness. | Bovine collagen, bone broth (especially from beef), some marine sources. |
| Type IV | Basement membranes (skin, kidneys, blood vessel walls, various organs) | Forms mesh-like sheets supporting epithelial and endothelial cells, filtration barrier in kidneys and skin. | Synthesized by the body. Not available as a supplement; supported by protein-rich foods. |
| Type V | Cell surfaces, hair, cornea, placenta, lungs (co-exists with Type I & III) | Regulates collagen fiber assembly, necessary for eye health, hair, placenta, and some vessel walls. | Present in eggshell membrane; found in small amounts in multi-collagen supplements. |
Best Collagen Supplements: Peptides, UC-II, Gelatin & Vegan Boosters

With a better understanding of collagen’s many roles, you may ask how to support your body’s natural collagen levels. Eating a balanced diet with foods that boost collagen is helpful. However, using supplements is a simple and effective way to increase collagen intake.
There are many types of collagen supplements you can find. Picking the right one for your needs might feel overwhelming. Let’s look at some of the most popular collagen supplements and what makes each one special.
Hydrolyzed Collagen (Collagen Peptides)
Hydrolyzed collagen, or collagen peptides, is a form of collagen that gets broken down into smaller pieces. This change makes it easier for the body to absorb. People like this type of collagen because it works well to help create more collagen in the body. Collagen peptides help with skin elasticity, joint health, and overall support for connective tissue. Adding hydrolyzed collagen to your daily routine can boost collagen production. This can lead to better skin hydration and improved joint function. Try including collagen peptides in your diet. They have many beneficial effects on skin health and overall well-being.
Practical tip: Most unflavored collagen peptides dissolve almost completely in hot drinks like coffee without altering the taste. When mixing with cold water, more thorough stirring may be needed and some clumping can occur. If you’re sensitive to aftertastes, start by adding the powder to smoothies or yogurt.
Undenatured Collagen (UC-II)
UC-II is a type of undenatured collagen that is very good for joint health. Unlike hydrolyzed collagen, UC-II keeps its original form, which helps it work better in the body. This special collagen helps joint function by supporting the immune system. This way, it keeps joints healthy and reduces discomfort. Research shows that UC-II can help lower joint pain and stiffness. This makes it a great choice for people looking for natural options for joint support. Adding UC-II to your everyday routine might bring you good benefits for joint health and mobility.
Gelatin
Gelatin is a kitchen favorite because it helps make fun desserts and tasty dishes. It is actually a form of collagen. Gelatin comes from collagen hydrolysate and goes through more steps to get its special gelling abilities. Even though it is not a full protein, gelatin has many amino acids that help make collagen.
People usually do not eat gelatin by itself, but we can find it in many meals. It is great for thickening soups and stews. It also helps in making delicious broths and sweet desserts. Gelatin brings good texture and adds nutrition to our food.
Adding gelatin to your recipes is an easy way to get more collagen in your diet. Whether you love cooking or just want to add more protein creatively, gelatin is a tasty and useful choice.
Plant-Based (Vegan) Collagen Boosters
Add plant-based collagen boosters to your daily routine. They can help support collagen production naturally. Look for sources that are rich in vitamin C. Citrus fruits and whole grains are great options. These foods aid in collagen synthesis. Plant sources of hyaluronic acid can improve skin hydration and elasticity. Vegan collagen supplements provide a cruelty-free way to promote skin health. Choose collagen-boosting foods and supplements that suit your values. This will help ensure your balanced diet enhances the beneficial effects of collagen on your skin and overall well-being. Boost your collagen intake with vegan alternatives for the best results.
It’s important to know that vegan collagen boosters do not have real collagen in them. They give your body the nutrients it needs to help make its own collagen. How well they work depends on your health and if your body can take in these nutrients. You might not see results as clearly as you would if you take hydrolyzed collagen from animal sources.
Table: A Comparative Look at Different Collagen Supplement Forms
| Supplement Type | Description / Form | Primary Proposed Benefit(s) / Use Case | Key Characteristics / Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrolyzed Collagen (Peptides) | Collagen broken down into smaller peptides for easier absorption | Supports skin elasticity, joint health, and overall connective tissue | High bioavailability; available in various forms like powders and capsules. Studies indicate improved skin hydration and elasticity with regular intake. |
| Undenatured Collagen (UC-II) | Maintains its native, triple-helix structure | Promotes joint health and modulates immune response for joint comfort | Acts via the immune system; effective in small daily doses (e.g., 40 mg). Derived from chicken sternum cartilage. |
| Gelatin | Partially hydrolyzed form of collagen that gels when cooled | Supports gut health; provides dietary collagen through foods | Common in cooking and baking; not a complete protein on its own. Rich in glycine, which supports the gut lining. |
| Plant-Based (Vegan) Boosters | Nutrient-rich compounds that stimulate collagen production | Enhances natural collagen synthesis; supports skin health | Contains no actual collagen; relies on nutrients like vitamin C, zinc, and amino acids. Effectiveness may vary compared to animal-derived collagen. |
Top Natural Collagen Sources in Food

Boosting your collagen levels does not mean you have to take pills or mix powders. Nature offers many whole foods packed with collagen and the nutrients that help your body make it.
Eating these collagen-rich foods can improve your collagen intake. It also helps you take a natural and healthy route to better overall health. Let’s look at some amazing foods that can help you get glowing skin, strong bones, and healthy joints from within.
Top Foods That Boost Collagen Naturally
The good news is many tasty and easily found foods can help your body make more collagen. Eating these nutrient-rich foods is a tasty and simple way to keep your collagen levels healthy.
Here are some foods that can help boost your collagen production:
Bone broth: This flavorful mix is made from animal bones and tissues. Bone broth is packed with collagen, gelatin, and amino acids that help with collagen synthesis.
Chicken and fish with skin: Don’t throw away the skin! Chicken and fish skin has collagen and other important nutrients that support skin health and overall well-being.
Citrus fruits: Packed with vitamin C, fruits like oranges, lemons, and grapefruits are important for collagen formation. They support healthy skin, hair, and nails.
Berries: Full of antioxidants, berries like strawberries, blueberries, and raspberries help protect against collagen loss and support overall skin health.
By adding these foods to your meals, you can nourish your body from the inside out. This supports healthy collagen levels and lets you enjoy their amazing benefits.
You don’t need supplements to support collagen—many everyday foods naturally boost, protect, or supply it. Here are the top collagen-friendly foods and how they help.
| Food Source | How It Supports Collagen | Key Nutrients & Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Bone Broth | Direct source of collagen (Types I & III) and amino acids | Glycine, proline, gelatin – supports skin, joints, gut |
| Chicken Skin & Cartilage | Direct source of Type II collagen | Collagen, chondroitin – aids cartilage health |
| Fish (with skin) | Direct source of Type I collagen | Collagen, omega-3s – hydrates skin, reduces inflammation |
| Egg Whites | Supplies amino acids necessary for collagen production | Proline, glycine – builds structural proteins |
| Citrus Fruits | Stimulates collagen synthesis | Vitamin C – essential for collagen production |
| Berries | Protects existing collagen from breakdown | Vitamin C, antioxidants – anti-aging effects |
| Leafy Greens | Promotes collagen production and protects existing stores | Chlorophyll, vitamin C – supports connective tissues |
| Nuts and Seeds | Supports collagen structure and enzymatic activity | Zinc, copper, amino acids – repair and regeneration |
| Garlic | Supports collagen cross-linking and tissue strength | Sulfur, taurine – reinforces collagen bonds |
| Tomatoes | Protects against collagen degradation | Lycopene, vitamin C – antioxidant skin protection |
| Avocados | Helps maintain collagen-rich skin with healthy fats | Vitamin E, omega-9 – moisturizes and reduces inflammation |
| Beans | Provides amino acids and minerals for collagen synthesis | Lysine, zinc – supports production and tissue health |
| Papaya | Stimulates collagen synthesis and provides antioxidant support | Vitamin C, enzymes – boosts collagen and repairs skin |
| Bell Peppers | Enhances collagen production | Vitamin C – vital co-factor in collagen formation |
| Pumpkin | Protects collagen with antioxidants | Beta-carotene, vitamin C – supports skin structure |
| Carrots | Preserves collagen structure | Beta-carotene – supports skin and tissue health |
| Sunflower Seeds | Stabilizes collagen and supports skin repair | Vitamin E, selenium – antioxidant protection for skin matrix |
Important note: While these foods are very good for you, it is not easy and takes a lot of calories to get the amount of collagen you need (5–10 grams) by eating food alone. For example, you have to drink a very big bowl of bone broth to get 10 grams of collagen. That is why food is a good base to help keep your collagen levels up, and supplements give you a sure way to add more when you need it.
How to Increase Collagen Naturally: Quick Tips
Besides eating certain foods, you can help your body keep and build collagen by following a few easy habits every day. Here is a simple list that can help you take care of the collagen you have and help your body make more. You do not need to use supplements for this.
Eat a Complete Diet: Try to eat foods with plenty of protein. The protein will give your body amino acids like glycine and proline. Add lots of colorful fruits and veggies, because they are full of vitamin C and other antioxidants. Include foods with zinc and copper too. Nuts, seeds, and whole grains have these minerals.
Protect Your Skin from the Sun: The sun’s UV rays are very harmful to your skin’s collagen. You should use sunscreen with at least SPF 30 every day. Put it on even when it’s cloudy. Make this a daily habit for your skin.
Limit Sugar and Refined Carbs: Eating too much sugar helps make AGEs, which hurt and break down your collagen fibers. This makes skin feel looser. Try to have less sugar and few refined carbs.
Stay Well-Hydrated: Your body needs water to help your skin stay firm and healthy. Drink water often during the day to help your skin. This will keep your tissues looking good and feeling full.
Manage Stress: Stress can raise the cortisol level in your body. Too much cortisol will harm your collagen. To feel better, add stress-busters to your day. Try yoga, walking, or fun hobbies.
Avoid Smoking: Smoking limits blood flow to your skin. This keeps out oxygen and good nutrients. Smoking also sends bad chemicals into your body. These damage both collagen and elastin. Smoking is bad for your skin’s
How Diet & Key Nutrients Influence Collagen Production
The saying, “You are what you eat,” is important for understanding collagen levels. Genetics matter, but what we eat really affects how our body makes and keeps collagen. A balanced diet full of protein, vitamins, and minerals gives us what we need for collagen synthesis.
Eating enough protein is key. This means we need the amino acids glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline to help make collagen. Vitamin C is also very important for collagen formation. You can find it in citrus fruits, berries, and leafy greens. It helps protect collagen from breaking down.
Eating different colorful fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats makes sure we get the right nutrients to support good collagen production. By focusing on a balanced and healthy diet, you can help your body keep healthy collagen levels. This is good for your skin, joints, bones, and more. Remember that dietary supplements may help, but they work best with a healthy and balanced diet.
Table: Key Nutrients Essential for Your Body’s Collagen Synthesis
| Nutrient | Role in Collagen Production/Maintenance | Common Food Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Amino Acids (Glycine, Proline, Hydroxyproline) | Serve as the primary building blocks of collagen protein | Bone broth, meat, fish, dairy, eggs, spinach, soy products |
| Vitamin C | Acts as a critical co-factor for collagen synthesis and functions as an antioxidant | Citrus fruits, strawberries, bell peppers, broccoli, kale |
| Zinc | Functions as a co-factor in collagen formation and supports tissue repair | Beef, oysters, chickpeas, pumpkin seeds, cashews |
| Copper | Assists in cross-linking collagen fibers to strengthen connective tissues | Liver, oysters, sesame seeds, sunflower seeds, whole grains |
| Antioxidants (e.g., flavonoids, carotenoids) | Neutralize free radicals that degrade collagen and support skin repair | Berries, tomatoes, carrots, sweet potatoes, green tea |
| Vitamin A (Retinol and Beta-Carotene) | Supports skin health and may enhance collagen production | Liver, sweet potatoes, carrots, spinach, kale |
| Sulfur-Containing Compounds | Necessary for collagen synthesis and stability | Garlic, onions, cruciferous vegetables (e.g., broccoli, Brussels sprouts) |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Reduce inflammation and may protect collagen from degradation | Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts |
| Silicon | Plays a supportive role in collagen matrix formation and skin elasticity | Whole grains, oats, bananas, green beans, beer |
| Lysine | Essential amino acid that contributes to collagen cross-linking | Meat, dairy products, legumes, quinoa, nuts |
Top Health Benefits of Collagen Supplements
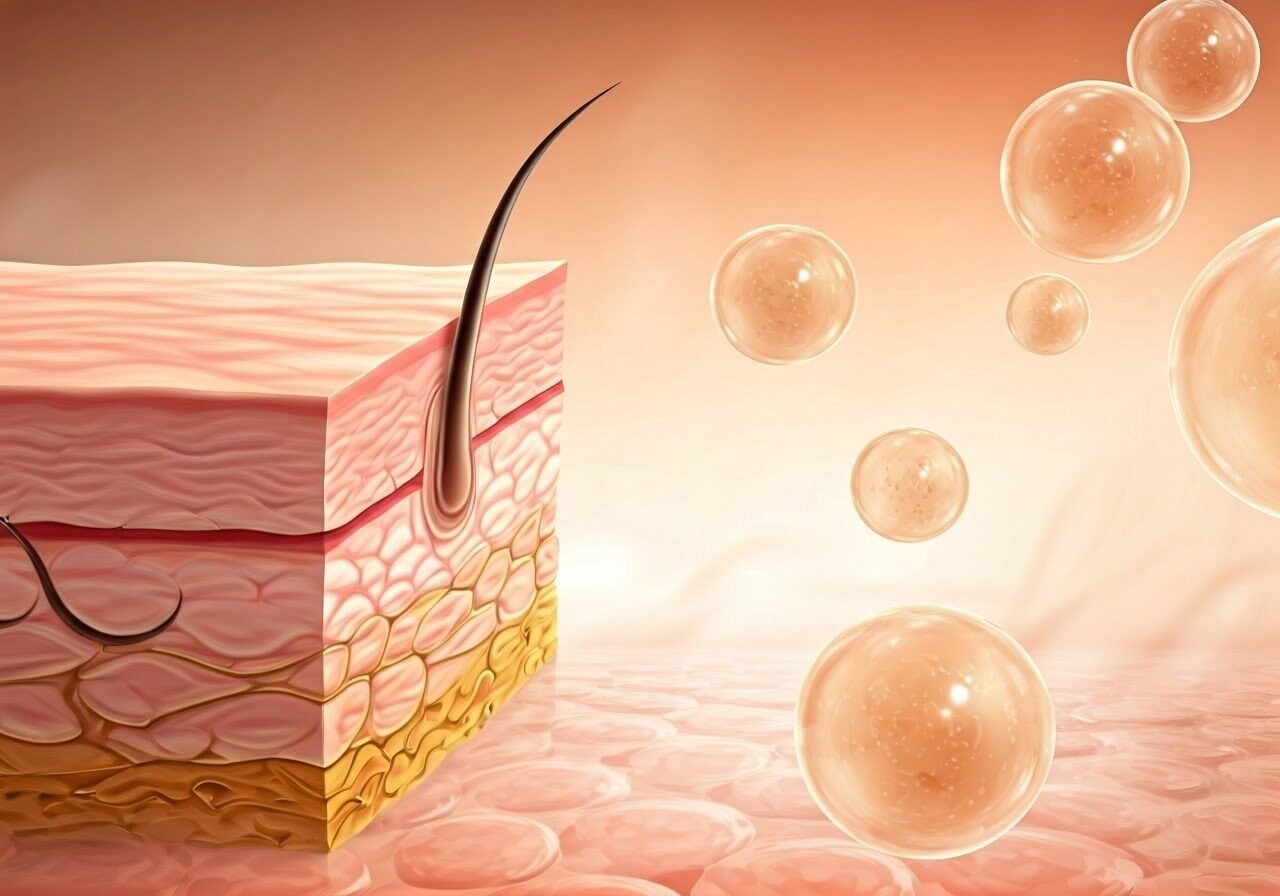
A healthy diet is important, but collagen supplements can also help. They give you an easy way to get this important protein. This might make the benefits of collagen even better and help with certain health issues.
Collagen has many benefits. It can improve skin elasticity, reduce wrinkles, support bone density, and help joint health. If you want to boost skin hydration, lessen joint pain, or promote hair and nail growth, collagen supplementation can be a good choice in a healthy lifestyle. Still, remember that collagen supplements aren’t a quick fix. They are most effective when you also follow a balanced diet and exercise regularly.
Collagen for Skin Elasticity & Wrinkle Reduction
One of the most popular benefits of collagen supplements is that they can improve skin health and help reduce signs of aging. As we get older, our body produces less collagen. This drop can make our skin less elastic, causing wrinkles, fine lines, and less firmness.
Collagen supplements, especially hydrolyzed collagen peptides, can help boost skin elasticity and lessen the look of wrinkles. Research shows these supplements may encourage collagen synthesis in the skin. This can lead to a plumper, smoother, and younger-looking skin. By increasing collagen levels, these supplements can also enhance skin moisture and reduce fine lines and wrinkles, helping to tackle common aging issues.
It’s important to remember that while collagen supplementation can help the skin’s natural ability to renew itself and promote a youthful look, the results can be different for each person. To get the most out of collagen, it’s best to combine it with a healthy lifestyle. This includes eating a balanced diet, protecting your skin from the sun, and using good skincare products.
Collagen for Bone Density & Joint Support
Collagen is very important for keeping our bones strong and healthy. As we get older, our bone density tends to go down. This can lead to fractures and problems like osteoporosis. Collagen supplements, especially those with type I collagen, may help support bone health. They can promote better bone density and strength.
Research suggests that taking collagen might help increase bone-building cells. This may raise bone mineral density and slow down bone loss, which happens naturally. This is good news for older adults and those at risk of osteoporosis since having enough collagen is essential for healthy bones.
Additionally, collagen supplements, especially those with type II collagen, may help joint health. They provide support for cartilage repair and might reduce joint inflammation. This can ease joint pain, stiffness, and discomfort, which is especially helpful for people with osteoarthritis.
Collagen for Muscle Mass & Heart Health
Adding collagen to your daily routine can help more than just your skin, bones, and joints. It may also be good for muscle mass and heart health. Collagen is a key part of muscle tissue. Keeping the right levels of collagen is said to help with muscle growth and repair.
Some studies, while still in the early stages, show that collagen peptides can boost muscle protein synthesis when paired with resistance training. This could lead to more muscle mass and strength. This is especially important for athletes and older people who may lose muscle as they age.
There is also some early research suggesting that collagen could help heart health. It might do this by promoting healthy blood pressure and flexible arteries. Collagen products, especially those with type III collagen, may help keep blood vessels strong and support heart health. However, more studies are needed to fully understand how collagen affects heart health.
Is Collagen Safe? Side Effects & Medication Interactions

Before starting collagen supplementation, it’s important to think about safety. You should also know about any warnings or interactions. Chatting with your doctor is a good idea before you begin. Collagen is usually safe for most adults if taken as directed. However, like any supplement, being informed is essential.
Let’s look at the safety of collagen supplements and some key precautions to remember when you add them to your health routine.
Understanding the Safety Profile of Collagen Supplements
Collagen supplements are generally safe to use, with only a few side effects when you follow the instructions. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) sees collagen mostly as a food ingredient, not a drug, and lists it as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS). Still, you should keep in mind that there are some risks and the need to be careful.
It’s important to choose good brands that focus on quality in how they make their products. While most people handle collagen well, some might feel mild digestive issues, like bloating, gas, or heartburn. You can start with a low dose and increase it slowly to reduce these problems.
| Side Effect / Concern | Severity / Frequency | Why It Happens / Description | How to Avoid or Minimize It |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bloating, Gas, Mild Heartburn | Common / Mild | Collagen peptides and gelatin can sometimes cause mild digestive discomfort, especially in higher doses or when first starting. | Start with a low dose and gradually increase; take with food; split the daily dose into smaller servings. |
| Unpleasant Aftertaste or Odor | Common / Mild | Some marine or porcine collagen may have a natural taste or smell. | Choose flavored or odor-neutral products; mix in smoothies or flavored drinks. |
| Nausea, Stomach Upset | Uncommon / Mild | Sensitivity to collagen or added ingredients may irritate the stomach. | Try a different collagen source (e.g., switch from bovine to marine); take with a full glass of water or a meal. |
| Headache | Rare / Mild | Some users have reported mild headaches, possibly due to sensitivity to additives or dehydration. | Drink plenty of water; try a different product without additives. |
| Constipation | Rare / Mild | Increased protein intake from collagen may occasionally contribute to constipation in sensitive individuals. | Increase fiber and water intake; adjust dosage if needed. |
| Hyperactivity or Insomnia (with added ingredients) | Rare / Mild | Some flavored or fortified collagen supplements may contain caffeine or other stimulants; not typical for pure collagen. | Check product labels for added stimulants; choose pure collagen if sensitive to these ingredients. |
| Allergic Reaction (rash, itching, swelling) | Rare / Mild to Severe | Possible if allergic to the source (e.g., fish, eggs, or other animal proteins). | Check the ingredient list for allergens; discontinue use and consult a doctor if symptoms appear. |
| Elevated Calcium Levels (with bone-derived collagen) | Very Rare / Mild to Moderate | May occur if supplement contains bone-derived collagen with calcium impurities, potentially raising blood calcium (very rare). | Choose products tested for purity; avoid unregulated or low-quality supplements. |
Also, it’s very important to speak with your healthcare provider before taking any new supplements. This is especially true if you have health issues, are pregnant, breastfeeding, or taking medicine. They can give you the best medical advice based on your situation, which will help you use supplements safely and effectively.
Precautionary Measures When Taking Collagen
Collagen supplements are usually safe for most adults. However, it’s always a good idea to take precautions. Focusing on a healthy lifestyle and using supplements carefully can make your wellness routine safer and more effective.
It’s important to follow the recommended dosage on the product label or as told by your healthcare professional. Taking more than the suggested amount does not mean you will get more benefits. It could also raise the chances of negative effects.
Also, keep in mind that collagen supplements should add to a healthy lifestyle, not replace it. Adding them to a routine that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management, and enough sleep can help improve your overall health.
Possible Interactions with Medications and Conditions
While collagen supplements are often safe, it’s important to know how they may interact with medications and existing health conditions.
Collagen supplements can affect some medications. For instance, if you take blood thinners or medicine that influences blood clotting, be sure to talk to your doctor before starting collagen supplements.
Furthermore, people with certain health issues, like kidney or liver disease, food allergies, or sensitivities, should be careful. It’s crucial to speak with your healthcare provider in these situations. They can help check for risks, change dosages, or suggest other options based on your health needs. By looking into these interactions early, you can make your supplementation safer and more effective.
Some health conditions and medications may affect how your body responds to collagen. See key interactions below.
| Interacting Agent / Condition | Potential Interaction with Collagen Supplements | Recommendation / Precaution |
|---|---|---|
| Blood Thinners (Anticoagulants) | Collagen is typically safe, but supplements containing additional ingredients (like garlic or fish oil) may have mild blood-thinning effects. Could enhance the effects of medications like warfarin or aspirin. | Consult your healthcare provider before starting collagen supplements, especially if they contain added ingredients known to affect clotting. |
| Kidney Disease | High protein intake from supplements can stress the kidneys and may worsen chronic kidney disease. | Consult your doctor regarding appropriate protein intake and the safety of collagen supplementation. |
| Liver Disease | Protein metabolism and collagen accumulation may be altered in liver disease. Excess collagen is linked to liver fibrosis. | Consult your healthcare provider before use. |
| Food Allergies/Sensitivities | Collagen may be sourced from allergens like fish, eggs, or bovine products. | Check product labels carefully and select allergen-free options if needed. |
| Autoimmune Conditions | Certain collagen types, like UC-II, influence immune system behavior, which may affect autoimmune conditions. | Speak with your doctor before use, especially if taking immunosuppressants or managing autoimmune disorders. |
| Pregnancy and Breastfeeding | Limited research exists on the safety of collagen during pregnancy and lactation. | Use only under medical supervision. |
How to Choose the Best Collagen Supplement for Your Needs

Selecting collagen supplements can be overwhelming due to the numerous options available. However, by gathering the right information, you can identify the ideal collagen product that meets your wellness needs. When making your choice, consider the type of collagen, its source, any additional components, the format it comes in, and the dosage. These elements will assist you in finding a supplement that aligns with your health objectives. Before incorporating any dietary supplement into your routine, it is vital to conduct thorough research and reflect carefully. This approach ensures a safe and effective experience. Keep the following crucial factors in mind when selecting a collagen supplement.
Type of Collagen: Different types cater to specific health objectives. For instance, types I and III are beneficial for skin, hair, and nails, whereas type II is geared towards joint support. Opt for a supplement that contains the collagen type(s) relevant to your health goals.
Before you buy, use this easy checklist. It will help you pick the best collagen supplement for what you need:
Collagen Supplement Shopping Checklist
Define your goal: Think about why you want the collagen. If you want it for skin, hair, and nails, choose Type I & III. If you use it for joint support, pick Type II or UC-II.
Check the form: Peptides (hydrolyzed collagen) are the best because they are easy to take in and can be used in many ways.
Consider the source: The collagen can come from cows, fish, or chicken. If you have a fish allergy, you should not use fish collagen.
Review the ingredients: The best supplements have only collagen. But it is fine if there is vitamin C or hyaluronic acid. Do not choose products with extra sugar, fake flavors, or fillers.
Look for certification: A product that has been checked by a third party (like NSF) is better. This shows it is clean and safe to use.
Sourcing and Quality: Select collagen supplements from reputable suppliers who follow ethical and sustainable practices. It is advisable to seek out products that have undergone rigorous testing to verify quality and purity, ensuring they are devoid of harmful substances. Additionally, third-party certifications from organizations like NSF International or USP can offer added peace of mind.
Table: Main Collagen Sources in Supplements
| Collagen Source | Collagen Types | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bovine (from cow hides and bones) | I and III | Affordable; widely available; great for skin and bone health | Not suitable for vegetarians/vegans; risk of impurities if sourced poorly |
| Marine (fish) | Type I only | High bioavailability (smaller peptides); ideal for skin/wrinkle support | More expensive; possible aftertaste; allergies in people sensitive to fish; only type I |
| Chicken | Mainly type II (often UC-II) | Effective for joint support (cartilage collagen); common in UC-II | Less common; not suitable for those avoiding poultry; usually in specialized formulas |
| Porcine (pig) | I and III | Structurally close to human collagen; relatively affordable | Religious restrictions (not kosher/halal); slightly less common than bovine |
| Plant-based sources | No collagen; only nutrients | Suitable for vegans; provides vitamin C, amino acids to support collagen synthesis | Do not contain actual collagen; less effective than animal-derived collagen |
Added Ingredients: Review the label for any additional ingredients. Some collagen supplements may include nutrients like vitamin C or hyaluronic acid, which can enhance absorption or improve collagen’s effectiveness. While these components can be beneficial, they might not be suitable for everyone, so consider any allergies, sensitivities, or potential interactions you may have.
Form and Dosage: Collagen supplements are available in various formats, including powders, capsules, liquids, and gummies. Choose a form that complements your lifestyle and preferences. Recommended dosages may vary depending on your age, health status, and individual needs, so it’s essential to adhere to the manufacturer’s guidelines.
By being informed about the options available, you can select a collagen supplement that aligns with both your health goals and personal preferences.
Latest Research & Scientific Studies on Collagen Benefits

The field of nutrition is always changing, and collagen study is a part of that. Scientists are always looking into collagen’s possible benefits. They are examining how it affects different areas of health and long life.
This commitment to learning more about how collagen works leads to new treatments and creates better ways to help people in the future.
Cutting-edge Studies on Collagen’s Efficacy
The effectiveness of collagen in boosting human health is an exciting field of study. Researchers are running human studies to understand how collagen works and to measure its benefits for different groups of people.
Recent research has looked at how collagen can help with wound healing. The results are good and show that collagen may speed up tissue healing and help close wounds. Studies about collagen and skin health are also growing. They focus on how collagen affects skin aging, elasticity, hydration, and even certain skin problems like eczema and psoriasis.
Researchers are also looking into the long-term benefits of collagen supplements for bone health, especially for people at risk for osteoporosis. This research is important to create evidence-based recommendations and to make the best use of collagen for health goals.
The Future of Collagen in Medical Treatments
Research is looking into collagen and its possible uses in medical treatments, and the results are looking good. Studies are showing how collagen may help in areas like managing joint pain from osteoarthritis, healing wounds, and even in sports medicine.
Scientists are testing collagen injections for treating joint pain in osteoarthritis. They want to see if these injections can help regenerate cartilage and ease pain in the joints. There are also investigations into collagen-based dressings for wound healing. These products take advantage of collagen’s ability to support tissue regeneration and help wounds heal faster.
These new uses show how collagen is becoming more important in today’s medicine. As research goes on, we may see new treatments that use this amazing protein to help patients.
Conclusion
Collagen is an important protein in our bodies. It helps keep our skin elastic, supports our joints, and improves our overall health. Learning about the different types of collagen, where to find it naturally, and the benefits of supplements can help you in your health journey. You might pick hydrolyzed collagen to improve your skin or use gelatin to support your joints. Taking collagen can really increase your vitality. Also, make sure to check safety tips and new research on collagen products. With its many benefits and different forms, think about adding collagen to your routine for better health results.
The content on WellwayHub.com is intended for general informational purposes only and should not be taken as medical advice. Please consult your doctor or a qualified health professional before making any changes to your health routine.
Some links on WellwayHub.com may be affiliate links. This means we may earn a small commission if you make a purchase through these links, at no extra cost to you. This helps support our mission to provide trusted wellness content.
Frequently Asked Questions
Collagen is the most common protein in the human body. It gives support to your skin, bones, joints, muscles, and other tissues. It helps keep your skin firm, hydrated, and strong in several areas. This makes collagen important for staying healthy as you age and for your overall health.
There are at least 28 types of collagen. However, Types I, II, and III are the most common ones.
Type I: Located in skin, bones, and tendons. It helps keep skin stretchy and bones strong.
Type II: Found in cartilage. It is important for making joints feel cushioned.
Type III: Present in skin and blood vessels. It helps support the shape of organs and keeps skin firm.
Sure. Collagen helps both men and women. It supports muscle mass, joint health, skin health, and the gut. It works well for everyone, no matter the gender.
Clinical studies show that collagen peptides can help with skin flexibility, joint movement, and bone strength. How well it works depends on the amount taken, where it comes from, and personal factors like age and diet.
Yes. Taking collagen every day has been shown in studies to boost skin hydration. It also helps to make skin firmer and lessens the look of fine lines and wrinkles as time goes on.
Yes. Type II collagen and broken-down peptides can help reduce joint pain, improve flexibility, and support cartilage repair in people with osteoarthritis or active lives.
Recommended dosages vary:
Skin & hair: Take 2.5 to 5 grams each day.
Joints & bones: Use 10 grams or more each day.
Always read product instructions. Talk to a doctor if you are unsure.
Yes, taking collagen every day is safe and good for you. Using it regularly helps keep your skin hydrated, supports your joints, and helps repair tissues. Pick a hydrolyzed collagen or collagen peptides for better use in your body.
Most people notice improvements in skin texture and hydration within 4 to 8 weeks. The benefits for joints and muscles may take 8 to 12 weeks of regular use.
All forms are good if they have hydrolyzed collagen peptides. However, powders and liquids usually let you take more and get it into your body more quickly than capsules.
Collagen can be taken at any time of day. Many people like to take it in the morning on an empty stomach or in the evening with a meal that has a lot of protein. The key is to be consistent, not focus too much on when to take it.
Yes. In fact, using collagen with vitamin C helps make more collagen. Pairing it with biotin, zinc, or hyaluronic helps skin, hair, and nails stay healthy together.
Collagen is usually safe to use. However, talk to your doctor if you take blood thinners, have allergies, or problems with your kidneys. Some types of collagen have calcium, and this may change how your medicine is absorbed.
There is no real vegan collagen. However, plant-based supplements can help your body make collagen. They use ingredients like vitamin C, silica, zinc, and amino acids. Some items have "vegan collagen" made through fermentation and genetic engineering.
Collagen is mostly safe, but some people might feel mild stomach problems like bloating or an odd taste. In rare cases, allergies can happen, especially from sea or egg sources.