
Introduction
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is a natural compound found in the human body. Recently, it has gained a lot of interest in health care, particularly among researchers at the National Institutes of Health. This important nutrient works as a strong antioxidant and is vital for energy production in our cells. Many people are looking at CoQ10 as a dietary supplement because it is associated with several potential health benefits. This has led many to think about adding it to their wellness routines.
How Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) Works: Function & Mechanism in the Body
CoQ10 is found in every cell of the human body. It is mostly in organs that need a lot of energy, like the heart, liver, and kidneys, where the highest levels of CoQ10 in human tissues are present. Inside cells, CoQ10 is mainly found in mitochondria, which are known as the “powerhouses” of cells. Here, CoQ10 helps make adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the main form of energy for cells.
Besides helping make energy, CoQ10 is also a strong antioxidant. It neutralizes harmful free radicals that can hurt cells and lead to age-related problems. Free radicals are unstable molecules created by normal body processes. CoQ10 protects cells from oxidative stress, aiding in overall health and well-being.
CoQ10 and Cellular Energy Production: ATP & Mitochondrial Health
At the center of how we produce energy in our cells is the electron transport chain. This is a series of complicated chemical reactions that happen inside the mitochondria. This important process changes energy from our food into ATP, which is the main fuel for our cells. CoQ10 is very important in this process. It acts as a carrier for electrons, helping to move them along for ATP creation.
When mitochondria don’t work well, we often see less ATP made. This problem, known as mitochondrial dysfunction, is linked to several health issues like heart disease, brain disorders, and metabolic syndrome. It’s very important to keep our mitochondria working well for good health. CoQ10 is a key player in making energy, so researchers are focusing on it to find ways to support mitochondrial health.
More research is still needed, but keeping CoQ10 levels up through a good diet and, if needed, supplements could be a smart way to help energy production in our cells and promote overall health.
CoQ10 Antioxidant Benefits & Oxidative Stress Protection
Oxidative stress happens when there is an imbalance between harmful free radicals and the body’s ability to fight them with antioxidants. Free radicals are very reactive molecules. They can harm cells through a process called oxidation, which may lead to health problems.
One major target of free radicals is lipids, especially in cell membranes. This harm to lipids is known as lipid peroxidation. It can interfere with how cells work and may cause inflammation and the worsening of diseases.
CoQ10 is a strong antioxidant that can grab free radicals, stopping them from harming cells and causing oxidative stress. Also, CoQ10 can help regenerate other antioxidants, like vitamin E, making it even more protective.
Age-Related Decline: CoQ10 Levels, Aging & Health Impact
As we get older, our body makes less CoQ10. This natural decrease can lead to more oxidative damage and health problems that come with age. Keeping enough CoQ10 in our system throughout life may help reduce these age-related issues.
Lower levels of CoQ10 have been linked to health problems such as heart disease, neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s, and metabolic disorders. While we need more research to understand the full link, it seems that keeping our CoQ10 levels healthy could be important for aging well.
Also, some medications, especially statins that lower cholesterol, can reduce CoQ10 production. This might add to the decline we see with aging. So, people taking statin medications may want to talk to their doctor about taking CoQ10 supplements to help with any low levels.
Types & Forms of Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) Supplements: Ubiquinone vs Ubiquinol
When looking at CoQ10 supplements, it’s important to know there are two main forms: ubiquinone and ubiquinol. Ubiquinone is the oxidized version of CoQ10. This is the form that is found in dietary sources. Ubiquinol is the reduced version. It acts as a strong antioxidant in the body.
Deciding between ubiquinone and ubiquinol often depends on what you need and how well your body absorbs it. Both forms can be helpful, but ubiquinol might be easier for older people to absorb. It’s a good idea to talk to a healthcare professional. They can help you choose the right form and amount for your health goals.
Ubiquinone (Oxidized CoQ10): Benefits & Best Use Cases
Ubiquinone, which is the oxidized form of Coenzyme Q10, is very important for the electron transport chain found in mitochondria. It helps with the production of ATP, which gives us energy. Studies show it may help fight oxidative stress and improve energy production. As a dietary supplement, ubiquinone could be beneficial for heart health, exercise capacity, and even neurodegenerative diseases. Knowing the differences between ubiquinone and ubiquinol can help you choose the right supplement for your specific health needs. This way, you can make smart choices for your wellness and performance.
Ubiquinol (Active CoQ10): Benefits & Who Should Take It
Ubiquinol is the active form of Coenzyme Q10. It is important for making energy in cells. It also works as a strong antioxidant. This helps to fight oxidative stress and support good health. Research shows that ubiquinol may help people with metabolic disorders like diabetes. It can assist in controlling blood sugar levels and improving how mitochondria work. When thinking about taking CoQ10, it is important to look for a version that improves absorption. Depending on your health needs, choosing between ubiquinone and ubiquinol can help you get the best results for your health.
CoQ10 Comparison: Ubiquinone vs Ubiquinol Supplement Forms
| Feature | Ubiquinone (Oxidized Form) | Ubiquinol (Reduced Form) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The oxidized form of Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) | The reduced (active) form of CoQ10 |
| Bioavailability | Lower; requires conversion to ubiquinol in the body | Higher; more readily absorbed |
| Function in the Body | Plays a role in ATP (energy) production | Acts as a powerful antioxidant and supports cellular energy |
| Conversion in the Body | Must be converted into ubiquinol for optimal use | Already in the active, usable form |
| Best For | General energy production, younger individuals with efficient conversion | Older adults or those with impaired CoQ10 conversion |
| Absorption Rate | Lower compared to ubiquinol | 2-4 times more bioavailable |
| Antioxidant Properties | Minimal | Strong antioxidant, protects cells from oxidative stress |
| Common Supplement Form | Cheaper, widely available | More expensive due to higher bioavailability |
| Who Should Take It? | Younger individuals with good metabolic function | Older adults, those with cardiovascular issues, or those on statins |
| Food Sources | Found in meat, fish, nuts, and whole grains | Converted from ubiquinone in the body |
Ubiquinone or Ubiquinol: Which CoQ10 Supplement Is Best for You?
Deciding whether to use ubiquinone or ubiquinol often means looking at personal factors and getting help from a qualified health care provider. Things like your age, health, lifestyle, and any specific health issues can all play a part in making this choice.
Both forms may have benefits, but some health care practitioners in alternative medicine might suggest ubiquinol for older adults or those with absorption problems. This is because ubiquinol is the active antioxidant form in the body and does not need conversion.
The best way forward is to have a clear and informed talk with a trusted health care provider. They can look at your health needs, check your medical history, and give tailored advice on CoQ10 supplementation, making sure it fits with your overall health goals.
Liquid vs Softgel vs Powder CoQ10: Which Supplement Form Is Most Effective?
Coenzyme Q10 supplements come in different forms. You can find them as capsules, tablets, and liquids. When picking the best form, consider how well your body can absorb it and what you prefer.
Most people take oral supplementation in capsules or tablets. The body’s absorption, known as bioavailability, can change a little depending on how the supplement is made. For example, some brands use lipid-based formulas to help with absorption.
Liquid forms of CoQ10 are also sold, but people often debate how well they work. It is important to talk with a healthcare provider to help you choose the right form and dosage based on your needs and preferences.
| Feature | Liquid CoQ10 | Softgel CoQ10 | Powder CoQ10 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Absorption Rate | Highest, as it bypasses digestion and is quickly absorbed | High, especially when formulated with oil for better bioavailability | Lowest, since it requires digestion and fat for absorption |
| Ease of Use | Easy to take, mix into drinks | Convenient, pre-dosed capsules | Can be mixed into food but may require effort |
| Bioavailability | Best, as it’s pre-dissolved | Good, especially in oil-based formulas | Lower unless taken with fat |
| Stability & Shelf Life | Shorter shelf life, may require refrigeration | Most stable and protected from oxidation | Can degrade if not stored properly |
| Best For | Those needing quick absorption (e.g., elderly, athletes) | General use, those wanting a balanced option | People who prefer customizing their dosage |
| Digestive Sensitivity | May cause stomach discomfort in some | Generally well-tolerated | Can be harsh on digestion if not taken with food |
| Who Should Take It? | Those who struggle with absorption or need fast results | Most users, as it balances effectiveness and convenience | Those looking for a customizable dosing option |
Top Health Benefits of Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) Supplements

CoQ10 supplements have been studied a lot, and many research projects show they might offer several health benefits. Still, it is important to look at these findings with care since research is ongoing. While CoQ10 is usually safe and can be taken well, it should not take the place of regular medical treatment, as highlighted in the health professional version of CoQ10.
Some benefits of taking CoQ10 include helping heart health by improving how the heart works, reducing blood pressure, and possibly lowering the risk of heart disease. CoQ10 may also boost exercise performance by increasing energy production and reducing oxidative stress in athletes. It’s crucial to talk to a healthcare professional before starting any new supplements.
CoQ10 for Heart Health & Cardiovascular Support
The heart is a very active organ. It always needs energy to work well. CoQ10 plays a key role in helping our cells make energy. This is why scientists, including Al Saadi T, have studied CoQ10 for its possible benefits for heart health. Research shows that taking CoQ10 might help heart function, especially in people with heart failure. Heart failure means the heart has trouble pumping blood effectively.
CoQ10 also has antioxidant properties. These can help the heart by fighting oxidative stress. Oxidative stress damages blood vessels and can lead to cardiovascular disease. It can also cause atherosclerosis. This is when plaque builds up in arteries, making blood flow harder.
Some early studies suggest that CoQ10 might help lower blood pressure a little. While more studies are needed, adding CoQ10 to a heart-healthy lifestyle could be a good idea.
CoQ10 for Energy, Endurance & Athletic Performance
Coenzyme Q10 is important for producing energy. This makes it a popular choice for athletes who want to improve endurance and performance. It helps make ATP, which helps the body use energy better during exercise. Studies show that CoQ10 may improve exercise capacity and overall physical performance. Athletes should think about using CoQ10 as a dietary supplement to increase their energy levels and possibly improve their endurance when they work out. It helps with mitochondrial function and lowers oxidative stress, which can lead to better performance in sports. In short, Coenzyme Q10 can be a helpful part of an athlete’s health routine.
CoQ10 for Muscle Recovery & Reducing Fatigue
Strenuous exercise can cause muscle damage and tiredness. This can make it hard to perform well in sports and recover overall. CoQ10 might help with muscle recovery and reduce tiredness because it produces energy and protects against damage.
CoQ10 helps make ATP, which supplies energy during exercise. This can help restore energy levels that drop after working out. With enough energy, CoQ10 may lessen muscle aches and help you get back to performing your best quicker.
Additionally, CoQ10 has antioxidant qualities. This means it can help reduce oxidative stress that occurs from exercise, which can hurt muscles and cause fatigue. By fighting free radicals created during tough workouts, CoQ10 can help shield muscle cells from damage, lower inflammation, and speed up recovery.
CoQ10 for Brain Health & Cognitive Function
The brain needs a lot of energy to work well. It depends on mitochondria to stay healthy. CoQ10 is important for making energy in the mitochondria, especially given the brain’s high fatty acid requirements. That’s why it has caught interest for its possible role in keeping the brain and mind healthy.
As we age, CoQ10 levels can drop. This often happens along with a higher chance of brain problems and neurodegenerative diseases. Keeping enough CoQ10 in our bodies may help protect our thinking skills as we get older.
We need more studies to find out all the details. Still, CoQ10 looks promising for brain health and cognitive function. Eating foods high in CoQ10 and talking about supplements with a doctor can be good ways to help keep our brains healthy.
CoQ10 for Skin Health & Anti-Aging Benefits
CoQ10 has many benefits, not just for the body but also for the skin. It helps fight signs of aging. Environmental things like UV rays and pollution can cause oxidative stress. This stress can harm skin cells and cause wrinkles, fine lines, and age spots.
CoQ10 is a strong antioxidant. It can fight against free radicals that hurt skin cells. This helps protect the skin from oxidative stress and keeps it looking youthful. When CoQ10 is put directly on the skin, it can help reduce the depth of wrinkles and make the skin more elastic.
Eating foods rich in CoQ10 is good for overall health, including skin health. However, using creams or serums with CoQ10 gives strong protection to the skin.
CoQ10 for Immune System Support & Protection
A strong immune system needs cells to work well, which includes making energy effectively. CoQ10 is important in producing energy in mitochondria. It helps support the immune system. When CoQ10 levels are good, immune cells have the energy they need to work well. This helps them fight off germs and keep watch for problems.
CoQ10 is also a powerful antioxidant that helps the immune system. Free radicals can harm cells, including immune cells. Though they are normal byproducts of our body’s processes, they can still affect how well immune cells function. CoQ10 helps by neutralizing these free radicals, which protects immune cells from oxidative stress. This support helps the body defend against threats.
To keep CoQ10 levels at their best, it is good to focus on a healthy diet and supplements, as suggested by a health care professional. This can help overall health, including the immune system.
CoQ10 for Blood Sugar Control & Diabetes Management
Diabetes mellitus is a long-term health issue that raises blood sugar levels. It impacts millions of people around the world. Scientists are still learning how it works, but some research suggests that CoQ10 could help manage blood sugar.
Some studies show that taking CoQ10 might make insulin work better. Insulin is a hormone from the pancreas. It helps cells take in glucose from the blood. When insulin works well, cells can use glucose more effectively. This can help control blood sugar levels better.
CoQ10 also has antioxidant qualities. This can help protect against oxidative stress. Oxidative stress is a problem that can make diabetes worse. Though more studies are needed, talking to a healthcare professional about adding CoQ10 to your diabetes care may be a good idea.
CoQ10 for Fertility & Reproductive Health
Fertility and reproductive health depend on a careful balance of hormones, cell function, and overall health. CoQ10 is important for energy production and helps fight oxidative damage. This has led researchers to look into its possible benefits for both men and women in reproductive health.
In men, CoQ10 is essential for sperm movement and performance. Research suggests that taking CoQ10 could improve sperm quality, especially in men who have trouble due to low sperm movement related to male infertility. CoQ10’s ability to fight oxidative damage might also help protect sperm from harm, which can support male fertility.
For women, more research is needed to fully understand CoQ10’s effects on fertility. However, some studies show that CoQ10 might help improve the quality of eggs and increase the chances of getting pregnant, especially in older women.
Best Natural Food Sources of Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10)
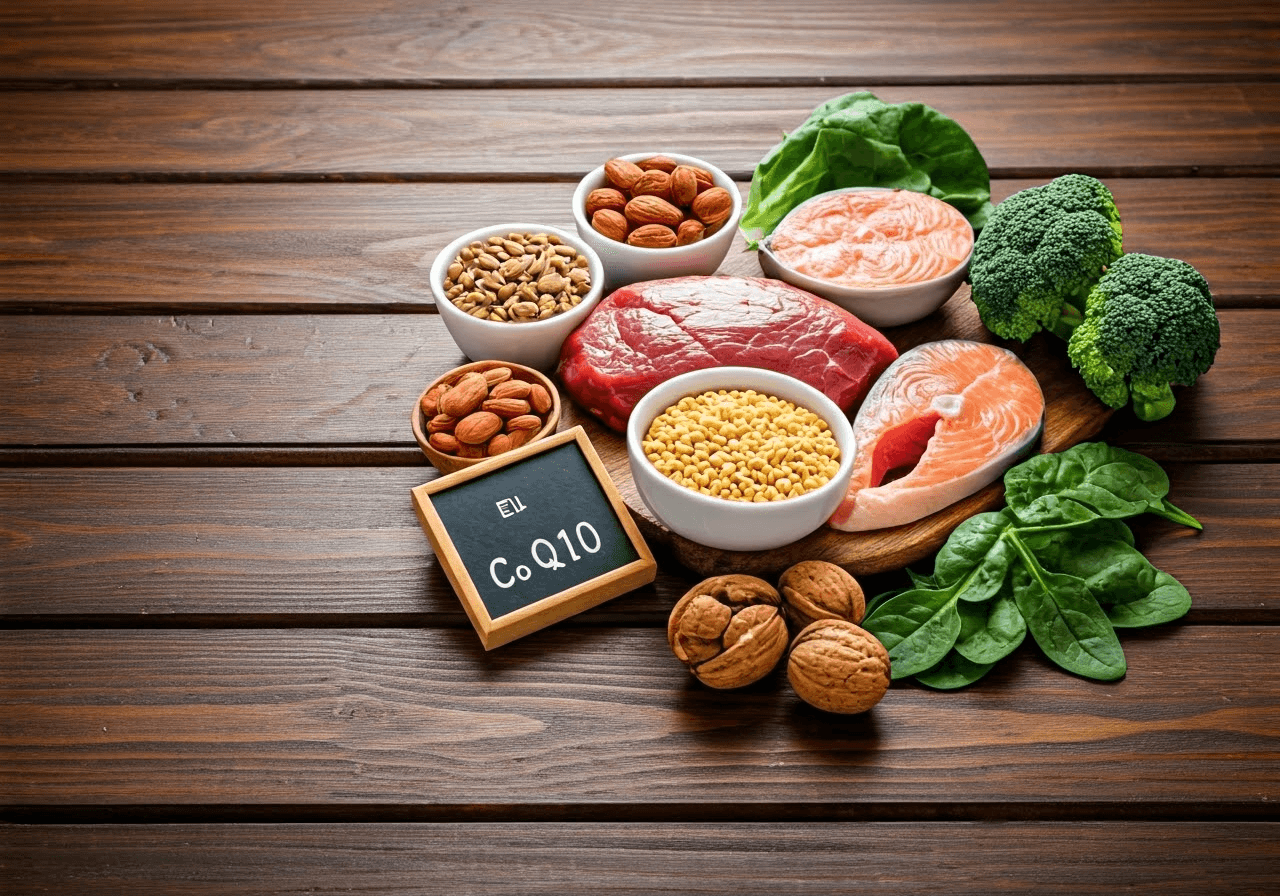

CoQ10 supplements are an easy way to get more of this nutrient, but it’s better to get nutrients from natural foods. Luckily, some foods are high in CoQ10. Eating these foods can help keep CoQ10 levels healthy and support overall health.
Organ meats such as heart and liver have a lot of CoQ10. Fatty fish like salmon, tuna, and sardines are also great sources. Additionally, dairy products are important to consider alongside plant-based foods like spinach, broccoli, and cauliflower, which are good options as well. Adding a mix of these foods to your balanced diet can naturally increase this important nutrient.
Here’s a comparison table of the best natural sources of Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) from both animal-based and plant-based sources:
| Category | Animal-Based Sources | Plant-Based Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Highest CoQ10 Content | Organ meats (heart, liver, kidney) | Peanuts, soybeans |
| Moderate CoQ10 Content | Fatty fish (salmon, tuna, sardines, mackerel) | Spinach, broccoli, cauliflower |
| Lower CoQ10 Content | Beef, chicken, pork | Oranges, strawberries |
| Bioavailability | High – better absorption due to fat content | Lower – but absorption improves with healthy fats |
| Additional Benefits | Rich in protein, iron, B vitamins | Contains fiber, antioxidants, vitamins |
| Best for Vegetarians/Vegans? | No | Yes |
| Best for Keto/Paleo? | Yes | Limited but possible |
Animal-Based CoQ10 Food Sources: Meat, Fish & Organ Meats
Animal-based foods that contain coenzyme Q, or CoQ10, are usually more concentrated and easier for the body to absorb than plant-based ones. This is because animal tissues have CoQ10 in its active form, which is called ubiquinone. It is simpler for people to use.
Animal studies show a link between eating CoQ10 from these sources and better heart health, improved exercise performance, and better brain function. However, we should remember that what we learn from animal studies doesn’t always apply to humans, even though they give helpful information for further studies.
Among animal sources, organ meats like beef heart and liver have the highest CoQ10 levels. Other great sources are fatty fish like salmon, tuna, mackerel, and sardines. Eating these healthy foods, along with a balanced diet of other important nutrients, can help keep good levels of CoQ10 in the body.
Here’s a quick look at the top animal-based foods highest in CoQ10. Use this table to find the best dietary sources to naturally boost your Coenzyme Q10 intake.
| Food Source | Approx. CoQ10 Content (per 100g cooked) | Other Notable Nutrients / Benefits | Tips for Consumption / Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pork Heart | ~120 mg | Protein, B vitamins, iron, selenium | Tender if slow-cooked. Enjoy in moderation. |
| Beef Heart | ~113 mg | Protein, B vitamins, zinc, iron, selenium | Very rich source. Cook thoroughly; ideal in stews or roasts. |
| Beef Liver | ~39–50 mg | Vitamin A, protein, iron, B vitamins, selenium | Extremely nutrient-dense. Limit intake due to vitamin A. |
| Beef Kidney | ~26–31 mg | Protein, B12, selenium, iron | Eat in moderation; strong flavor; cook thoroughly. |
| Pork Liver | ~23–26 mg | Protein, vitamin A, iron, B vitamins, selenium | Slightly milder than beef; do not overcook. |
| Chicken Liver | ~11–13 mg | Protein, vitamin A, folate, iron, vitamin B12 | Milder flavor; nutritious; suitable for pâtés. |
| Chicken Heart | ~9 mg | Protein, B vitamins, iron, selenium | Versatile in grilling or stews; nutrient-dense. |
| Mackerel | ~6.8 mg | Omega-3s, vitamin D, selenium, protein | Grill or bake; rich in flavor and healthy fats. |
| Sardines (with bones) | ~6.4 mg | Omega-3s, vitamin D, calcium, protein, B12 | Eat whole for extra calcium and nutrients. |
| Herring | ~3.9 mg | Omega-3s, vitamin D, selenium, protein, B12 | Good smoked, pickled, or grilled. |
| Beef (muscle meat) | ~3.1 mg | Protein, iron, zinc, B vitamins, creatine | Choose lean cuts; CoQ10 varies by cut. |
| Pork (muscle meat) | ~2.4 mg | Protein, thiamine, iron, zinc | Lean cuts are healthier; avoid overcooking. |
| Rainbow Trout | ~2.4 mg | Protein, omega-3s, vitamin D, selenium | Mild flavor; best grilled or baked. |
| Chicken (muscle meat) | ~1.2–1.8 mg | Protein, B vitamins, selenium | White meat has less CoQ10 than organ meats. |
| Tuna | ~1.6 mg | Protein, omega-3s, selenium, vitamin D | Can be eaten grilled, baked, or raw (sashimi). |
| Salmon | ~0.4–1.4 mg | Omega-3s, vitamin D, protein, selenium | Best grilled, baked, or poached. |
| Eggs (whole) | ~0.7 mg | Protein, vitamin B12, selenium, choline | Hard-boiled, scrambled, or poached for variety. |
| Milk | ~0.1–0.4 mg | Calcium, protein, vitamin B12, vitamin D | Good for dairy, but much lower in CoQ10 than meats. |
Plant-Based CoQ10 Food Sources: Vegetables, Nuts & Legumes
For people who follow plant-based diets, getting enough coenzyme Q, or CoQ10, needs careful food choices. You might also think about using dietary supplements if needed. Plant sources of CoQ10 may not have as much as those from animals, but eating a mix of plant foods with CoQ10 can still help keep levels healthy.
Cruciferous vegetables, like broccoli, cauliflower, and Brussels sprouts, are great sources of CoQ10 for plant-based diets. Other good options include spinach, peanuts, sesame seeds, and legumes. Adding these foods to meals and snacks often can help increase CoQ10 naturally.
However, CoQ10 from plants might be harder for the body to absorb than from animals. How you cook the food and what other nutrients are in the meal can affect how well it gets used by the body. If you are worried about your CoQ10 levels on a plant-based diet, it’s a good idea to talk with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian for personal advice.
Here’s a quick reference table of the top plant-based foods containing CoQ10. Use it to help plan meals that naturally support your CoQ10 intake on a plant-based diet.
| Food Source | Approx. CoQ10 Content (per 100g raw/cooked) | Other Notable Nutrients / Benefits | Tips for Consumption / Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Peanuts | ~2.6 mg | Protein, healthy fats, vitamin E, niacin | Eat roasted or raw. Watch portion size due to calories. |
| Soybeans | ~1.9 mg | Protein, iron, calcium, folate, isoflavones | Enjoy as tofu, tempeh, or boiled edamame. |
| Sesame Seeds | ~1.7 mg | Healthy fats, calcium, magnesium, zinc | Use in tahini or sprinkle on salads and grains. |
| Pistachios | ~1.6 mg | Protein, fiber, vitamin B6, potassium | Snack raw or roasted; good in sweet or savory dishes. |
| Spinach | ~0.6–0.9 mg | Iron, vitamin K, folate, antioxidants | Eat raw or cooked; cooking improves absorption. |
| Broccoli | ~0.6–0.7 mg | Vitamin C, fiber, sulforaphane | Steam or roast for best flavor and nutrient retention. |
| Cauliflower | ~0.5–0.7 mg | Vitamin C, fiber, vitamin K | Use in stir-fries, mashes, or roasted. |
| Whole Wheat | ~0.4–0.6 mg | Fiber, B vitamins, iron, magnesium | Eat as whole grain bread, pasta, or cereals. |
| Avocado | ~0.5 mg | Healthy fats, fiber, potassium, vitamin E | Spread on toast, add to salads, or use in smoothies. |
| Strawberries | ~0.2 mg | Vitamin C, antioxidants, fiber | Enjoy fresh or in smoothies. |
| Oranges | ~0.2 mg | Vitamin C, fiber, folate | Eat whole or drink freshly squeezed. |
| Potatoes | ~0.1–0.2 mg | Potassium, vitamin C, fiber | Best boiled or baked with skin for more nutrients. |
| Legumes (beans/lentils) | ~0.2 mg | Protein, fiber, B vitamins, iron | Use in soups, stews, and salads. |
Who Should Take Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) Supplements?

Including foods rich in CoQ10 in your diet is good for you. However, some people may need more CoQ10 or may struggle to make or absorb enough of it. In these cases, taking CoQ10 supplements might help, but it should be done with guidance from a healthcare professional.
People who might benefit from these supplements include those with heart issues, those on statin drugs, older adults feeling tired, those with metabolic problems, and those who have low CoQ10 levels. Yet, it’s not a good idea to self-treat with CoQ10. It’s very important to work with a healthcare professional when making decisions about this to ensure it is safe and effective.
CoQ10 Supplementation for Cardiovascular Disease & Heart Issues
Cardiovascular disease includes different conditions that affect the heart and blood vessels. It is still a major health issue around the world. People with cardiovascular disease may have issues with heart function and less blood flow, which can lower their quality of life.
CoQ10 helps in making energy for cells, especially in the heart. It has been studied as a possible added treatment for cardiovascular disease. Some studies say that taking CoQ10 might help improve heart function in people with chronic heart failure, a problem where the heart has trouble pumping blood properly.
CoQ10 also has antioxidant qualities. This means it might help protect the heart by fighting oxidative stress, which is a big factor in how heart damage and heart disease gets worse. Oxidative stress can harm blood vessels and lead to atherosclerosis. More research is necessary, but adding CoQ10, with advice from a healthcare professional, could be a helpful part of a complete plan for heart health.
CoQ10 for Athletes & Physically Active People
Athletes and active people always want to improve their physical performance, recover faster, and push their limits. CoQ10 is important for energy production and helps fight oxidative damage. This has made it popular as a possible aid for enhancing athletic performance.
Research shows that CoQ10 supplements may help trained athletes improve their exercise capacity, especially in those with mitochondrial disorders. It might boost endurance and help delay fatigue. This could be due to CoQ10 improving mitochondrial function, which leads to more ATP production. ATP is the main energy source for cells.
CoQ10 also works well as an antioxidant. It can protect the body from oxidative stress caused by exercise. Intense workouts create free radicals that can harm muscle cells and slow down recovery. CoQ10 can help reduce this oxidative damage, which supports muscle recovery and helps lessen fatigue after exercise.
CoQ10 for Statin Users: Reducing Muscle Pain & Side Effects
Statin drugs are often given to manage cholesterol and lower the risk of heart disease. They do this by blocking an enzyme that makes cholesterol. However, this also reduces the production of CoQ10, which is important for energy production in cells.
These statin medications are usually safe and effective, but some people experience muscle pain, weakness, and cramps when taking them. These muscle-related side effects can be common.
Some studies show that taking CoQ10 supplements might help with muscle pain caused by statins. This is because CoQ10 can restore energy production in muscle cells. If you have muscle pain while using statin drugs, it might be a good idea to talk to your doctor about taking CoQ10.
CoQ10 for Fatigue in Older Adults & Aging Population
Fatigue is a constant feeling of tiredness or low energy. It is often seen in older people. As we get older, our body makes less CoQ10. This drop in CoQ10 can lead to lower energy and more fatigue.
When CoQ10 levels go down with age, it affects how our cells work. It reduces the production of ATP, which is the main energy source for our cells. Without enough ATP, cells find it hard to work properly. This can cause fatigue and make it difficult to exercise.
In addition, older age can increase oxidative stress. This happens when there are more free radicals than the body can defend against. CoQ10 has strong antioxidant qualities, as reported by various researchers and studies, et al. It can help reduce oxidative stress, possibly boosting energy levels and decreasing tiredness in older adults.
CoQ10 for Metabolic Disorders: Diabetes & Blood Sugar Support
Supplementing with Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) greatly helps people with metabolic issues, especially diabetes. Research shows that CoQ10 can aid in controlling blood sugar levels and improving endothelial dysfunction in diabetic patients. Since diabetes increases the risk of heart problems, the antioxidant features of CoQ10 can help lower oxidative stress and promote heart health for these individuals. It is a good idea to talk to a healthcare provider to decide on the right dose and check for any interactions with diabetes medications.
How to Take Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) for Best Results

To take CoQ10 effectively, it’s important to help your body absorb it well. The dose you should take can change based on your age, health, and specific concerns. A usual guideline for adults is to take between 100-200 mg each day. It’s best to split this into two doses.
Choosing a good quality CoQ10 supplement is key to getting its benefits. Selecting well-known brands that focus on quality ingredients and carry out third-party testing can ensure it is pure and effective. Since CoQ10 dissolves in fat, taking it with a meal that has healthy fats can improve how your body absorbs it.
Recommended CoQ10 Dosage: How Much Should You Take?
If you want to find the right daily amount of CoQ10, it’s best to talk to a good health care provider. They can help you decide the proper dosage based on your age, health, any specific health problems, and if you are using CoQ10 for general wellness or to help with a certain health issue.
Usually, adults are recommended to take between 100-200 mg each day. However, people with heart issues or those on statin medications may need a higher amount to manage their migraine frequency. It’s very important to listen to your health care provider, who can give you advice based on your personal needs.
You should start with a lower dose and slowly increase it if you can handle it, always under the guidance of a health care provider. CoQ10 is usually easy for people to handle, but in some cases, taking high doses can cause mild side effects, like upset stomach.
Ubiquinone vs Ubiquinol: Which CoQ10 Supplement Form Is Better?
Ubiquinone and ubiquinol are two main forms of CoQ10 supplements. There is often debate about which one is better based on how well they work in the body. Ubiquinone is the oxidized form. The body turns it into ubiquinol, the active antioxidant form. Some people think ubiquinol is better because it does not need to change.
However, the discussion about which form is best is tricky. While ubiquinol gives the body ready-to-use CoQ10, some believe that the change from ubiquinone can be helpful. It might help release CoQ10 over time.
In the end, picking the right form depends on what each person needs. People worried about absorption or those with specific health issues may find that ubiquinol works better for them. Others might be fine with ubiquinone. It’s a good idea to talk to a health expert who knows about CoQ10 supplements for the best advice.
Best Time to Take CoQ10: Morning vs Night?
The best time to take CoQ10, whether in the morning or at night, is still a topic of debate. Some people say that taking it in the morning helps it work better because the body makes the most energy during the day.
On the other hand, there are those who prefer to take it in the evening. They believe that taking CoQ10 too close to bedtime might disrupt sleep. However, no solid research backs up these ideas.
In the end, when to take CoQ10 depends on your personal choices, daily habits, and any side effects you may notice. What matters most is taking it regularly each day, no matter what time you choose.
How Long Does CoQ10 Take to Work & Show Results?
The time it takes to see the effects of CoQ10 can be very different from person to person. It depends on things like the health issue being treated and how much of CoQ10 is used. Studies on CoQ10 usually take weeks or months to see how well it works for those taking it.
Some people notice they feel more energetic or can exercise better within a few weeks after starting CoQ10. But bigger improvements, like better heart health or blood sugar management, can take a longer time to show.
It’s important to have realistic expectations about using CoQ10. It is not a quick fix. To get the best results, you should take it regularly each day and maintain a healthy lifestyle. This way, you might see slow but steady improvements over time.
CoQ10 Side Effects, Safety & Potential Risks

Coenzyme Q10 is usually safe and well-tolerated when used in the recommended amounts. However, like all supplements or medications, there can be some risks and side effects. It’s good to know that side effects are generally rare. Most people can take CoQ10 without issues.
When side effects do happen, they are often mild and temporary. Some people might face stomach problems, such as nausea, diarrhea, or discomfort in the belly, especially if they take high doses. Other less common side effects might include headaches, dizziness, or skin rashes. It’s a good idea to start with a lower dose and slowly increase it as you adjust. If you have any worries, consult with a healthcare professional.
Common & Mild CoQ10 Side Effects
Side effects from taking CoQ10 are not very common. When they do happen, they are usually mild and go away quickly. Most people can take CoQ10 without issues, even in larger doses. Still, it is important to know about potential adverse effects to use it safely.
The most reported side effects are stomach problems. These can include nausea, discomfort in the stomach, diarrhea, or a lower appetite. These issues often come from using higher doses but can be lessened by taking CoQ10 with food or splitting the daily dose into smaller parts.
Other side effects are less common. These can be headaches, dizziness, trouble sleeping, or rashes on the skin. It can be tough to say if these issues are caused only by CoQ10, as there may be other causes. If you notice any strange or bothersome side effects, it is best to speak with a healthcare professional.
CoQ10 Drug Interactions: Medications to Watch For
CoQ10 is usually safe, but it can interact with some medications. This could change how well the medications work or increase the chance of side effects. It is very important to tell your health care provider about all the medicines, supplements, and herbal products you are using before starting CoQ10. This helps to avoid possible drug interactions.
A key interaction to note is with blood thinners like warfarin (Coumadin). CoQ10 might alter how well warfarin works, which may raise the risk of blood clots. If you are using warfarin, any use of CoQ10 should only happen under close medical care and monitoring of blood clotting, especially in regard to drug administration.
Other drug interactions could happen with medications broken down by the liver, blood pressure drugs, or chemotherapy treatments. Always keep an open discussion with your healthcare provider. Let them know if you start or stop any new supplements or medications, including over-the-counter products or herbal remedies.
Who Should Avoid CoQ10? When to Consult a Doctor
It is very important to get medical advice from a qualified healthcare professional before you start taking CoQ10, especially if you have existing health conditions or take other medications. This helps to ensure that you get personalized care, reduces possible risks, and offers recommendations that fit your health needs.
People with long-term health issues like heart disease, diabetes, liver or kidney problems, bleeding issues, or those who have had cancer should talk to their doctor before using CoQ10. Existing conditions might require changes in dosage or careful checking for any adverse effects.
Moreover, women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should be careful and ask a doctor before starting any supplements, including CoQ10. Although CoQ10 is usually seen as safe, there isn’t enough research to confirm its safety during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
How to Choose the Best CoQ10 Supplement: Quality & Purity Guide

Choosing dietary supplements can be overwhelming because there are many brands and types available. When picking a CoQ10 supplement, it is important to focus on quality. This ensures the product is pure, strong, and really works.
Start by selecting well-known brands. These brands should focus on good manufacturing practices. It is also helpful to choose supplements that have been tested by an independent party. This testing checks that the ingredients and strength of the product match what is said on the label.
Best CoQ10 Brands & Third-Party Tested Supplements
The market for dietary supplements is large and often lacks regulation. Not all supplements are the same. It’s important to pick trustworthy brands when looking for a CoQ10 supplement. Good brands focus on quality, transparency, and safety for consumers. They follow strict manufacturing rules.
A good sign of a trustworthy brand in the United States is their use of third-party testing. This is a process where they send their products to independent labs to check them. This testing makes sure that the ingredients on the label are right and that the strength is as claimed. You can find third-party testing certifications on product labels. These certifications give you extra confidence about the quality and purity of the product.
When you pick a CoQ10 supplement, look for brands that
Best Absorption: CoQ10 Formulation & Supplement Tips
Look for Coenzyme Q10 products that increase absorption for the best benefits. Choosing a product with better absorption can boost the effects of CoQ10 supplements. Pay attention to the type of CoQ10 in the product. Ubiquinol can be easier for the body to use than ubiquinone in some cases. Focusing on these details can help improve the absorption of Coenzyme Q10. This way, your body can make good use of this strong antioxidant to enhance your health and athletic performance. Keep this in mind when picking your CoQ10 supplement.
Ubiquinone vs Ubiquinol: How to Choose the Right CoQ10
When choosing between ubiquinone and ubiquinol, think about what you need. Ubiquinone is the oxidized form found in many supplements. Ubiquinol is the reduced form that your body can use better. If you want a general boost in energy production and overall wellness, ubiquinone may work well for you. But if you want to address specific problems like oxidative stress or if you want better absorption, ubiquinol might be a better choice. Knowing your needs can help you pick the right form of Coenzyme Q10 for the best results.
CoQ10 Storage & Stability: How to Keep Supplements Effective
Coenzyme Q10 needs proper storage to stay effective. Keep CoQ10 in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight. Make sure the container is tightly sealed. This helps keep out air, moisture, and light that can break it down. If you want to store it for a long time, you may want to put it in the fridge. Always check the expiration date. Expired CoQ10 may not work as well as it should. By following these tips, you can keep your Coenzyme Q10 supplements strong and stable.
Conclusion
Coenzyme Q10, which can be either ubiquinone or ubiquinol, is very important for making energy and maintaining health. People who have metabolic issues like diabetes may find it helpful to use CoQ10. It’s important to look at how well the body absorbs it and to consider personal needs. Choosing between ubiquinone and ubiquinol depends on what works best for you. Knowing how CoQ10 is stored and how stable it is really matters for it to work well. In summary, Coenzyme Q10 is a good dietary supplement that may help boost energy production and improve overall health and athletic ability.
The content on WellwayHub.com is intended for general informational purposes only and should not be taken as medical advice. Please consult your doctor or a qualified health professional before making any changes to your health routine.
Some links on WellwayHub.com may be affiliate links. This means we may earn a small commission if you make a purchase through these links, at no extra cost to you. This helps support our mission to provide trusted wellness content.
Frequently Asked Questions
Taking Coenzyme Q10 every day is usually safe for most people. If you have health issues or take medications that could interact with CoQ10, talk to your healthcare provider first. Always stick to the recommended doses and think about your personal needs.
Coenzyme Q10 can work differently for each person. You may start to feel its effects in a few weeks or months of regular use. Things like how much you take, the type of product, and your health can affect how long it takes to see results.
Taking Coenzyme Q10 along with other medications can affect how some drugs work, especially blood thinners or cancer treatments in integrative health. It’s a good idea to talk to a healthcare provider before mixing them. This helps avoid any adverse effects and ensures a safe way to take your medications.
Coenzyme Q10 is usually safe for women who are pregnant or breastfeeding. However, it’s a good idea to talk to a healthcare provider first. There isn’t much research on how it affects pregnancy and breastfeeding, so it’s best to be careful. This way, both the mother and baby stay safe.
Signs that you may not have enough CoQ10 include feeling tired, muscle weakness, high blood pressure, and problems with thinking. Watching for these signs can help you catch any issues early and get the help you need in time.
You can take Coenzyme Q10 in the morning to help with energy production. You can also take it at night, which may help with better absorption while you rest. Think about your individual needs and goals when choosing the best time to take it.
Avoid taking Coenzyme Q10 together with vitamin K if you are using blood thinners. It can affect how your medicine works. Also, talk to your healthcare provider before mixing CoQ10 with other supplements. This can help prevent any potential problems.
Coenzyme Q10, which people also call ubiquinone or ubiquinol, is an important substance for energy production in our cells. Knowing these different names can help when you choose the best form for your needs.