
Introduction
Vitamin K may not get as much attention as vitamin D, but it is very important. Vitamin K2, in particular, is a strong nutrient with many health benefits. Many people forget this, but eating enough vitamin K is crucial. It helps with blood clotting, supports bone health, and may lower the risk of heart disease.
How Vitamin K2 Works: Calcium Metabolism & Body Functions
To really understand why vitamin K2 is important, we need to look at how it helps with calcium use in the body. Think of calcium like a team of builders. Vitamin K2 is the guide who tells them what to do. Without guidance, calcium can gather in unwanted places, like your arteries.
That’s where vitamin K2 comes in. It helps turn on proteins such as osteocalcin, which is needed for building bones, and matrix GLA protein, which helps stop calcium from building up in blood vessels. So, vitamin K2 works like a traffic manager, directing calcium to your bones where it’s needed, and keeping it away from sensitive areas like your arteries.
This smart control of calcium is key to keeping your bones healthy and your vascular system in good shape. It plays a big role in how well you feel and stay healthy.
Vitamin K2 and Calcium Absorption: Vascular & Bone Health
Think of your arteries as the plumbing in your body. Just like how mineral buildup can block pipes, vascular calcification—when calcium builds up in your blood vessels—can disrupt blood flow.
This is where vitamin K2 comes in. It works by activating matrix GLA protein (MGP), a special protein that requires vitamin K. This activated MGP prevents calcium from sticking to the inside of your arteries.
By keeping your arteries free from calcium, vitamin K2 helps promote healthy blood pressure. It supports good circulation and lowers the risk of heart disease linked to vascular calcification. This makes vitamin K2 very important for maintaining cardiovascular health as we get older.
Vitamin K2 for Bones, Arteries & Whole-Body Support
Maintaining enough vitamin K is like having a good boss for your body’s building team. This becomes even more important as you get older because the chances of heart disease and weak bones increase.
Besides helping bones and blood vessels, vitamin K2 may also benefit other parts of the body. New studies show it might help protect against insulin problems, some cancers, and even support brain health. However, we need more studies to confirm these benefits.
With its many possible benefits, vitamin K2 is getting more attention from scientists. It is seen as a key part of good health and a long life.
Vitamin K2 MK-4 vs MK-7: Differences, Benefits & Sources

When picking a vitamin K2 supplement, you will find two main types: MK-4 and MK-7. Both types can offer important health benefits. However, they differ in how well your body absorbs them, how long they last, and where they come from in food.
Knowing these differences can help you choose the form of vitamin K2 that fits your health needs and what you eat. Let’s look at these two forms to understand them better.
Vitamin K2 Forms: Menaquinones (MK-4, MK-7) Explained
Vitamin K2 is not just one type of nutrient. It has a group of molecules called menaquinones, or MKs. The most important ones for our health are MK-4 and MK-7. You can think of them like siblings who act a little differently.
MK-4 is a shorter version that the body absorbs easily but doesn’t stay long. You can find it in animal products like butter, egg yolks, and meat. MK-7 is a longer version that lasts longer in the body. It’s mainly found in fermented foods, especially natto, which is a dish made from fermented soybeans in Japan.
Both MK-4 and MK-7 are important for calcium management and bone health. They help protect against vascular calcification, keeping you healthy overall. However, their unique traits change how they work in the body.
MK-4 vs MK-7: How Each Form Works in Your Body
MK-4 has a shorter half-life. This means the liver quickly uses it for blood clotting. This is a key role of vitamin K, but it leaves less MK-4 to go to other tissues, such as bones and arteries.
On the other hand, MK-7 lasts longer and is better absorbed. It easily activates osteocalcin, which helps build bones. It also prevents arterial calcification and may protect against heart disease.
Research is still ongoing to understand the exact details. However, the differences in how MK-4 and MK-7 work and how long they last help shape their unique profiles.
MK-4 or MK-7: Pros, Cons & Which is Best for You?
When you look at vitamin K2 from fermented foods and animal products, each type has good and bad points. Fermented foods give you natural sources, while animal products contain more vitamin K2 that your body can use easily. To get the most health benefits, it’s important to balance both types.
Comparison Table: Bioavailability, Benefits, Sources
Here’s a simple breakdown to highlight the key differences between MK-4 and MK-7:
Feature | MK-4 | MK-7 |
|---|---|---|
Source | Found in animal-based foods (butter, egg yolks, liver, meat) | Found in fermented foods (natto, aged cheese) |
Absorption & Half-Life | Short half-life (~1–2 hours), requires frequent dosing | Long half-life (~72 hours), better accumulation in blood |
Primary Benefits | Supports brain function, hormone balance, bone health | More effective for heart health, arterial flexibility, and long-term calcium regulation |
Bioavailability | Quickly absorbed but does not stay in circulation long | Higher bioavailability due to extended half-life |
Recommended Supplement Form | Often taken in high doses (milligrams) | Effective in lower doses (micrograms) |
Best For | Individuals focusing on brain and hormone health | Those looking for cardiovascular and bone health support |
This table provides an at-a-glance comparison, but it’s always best to consult with your healthcare provider or a registered dietitian for personalized advice based on your individual health needs and dietary intake of vitamin K.
By making informed choices, you can harness the power of vitamin K2 to enhance your health and well-being.
Vitamin K2 Health Benefits: Bones, Heart & More
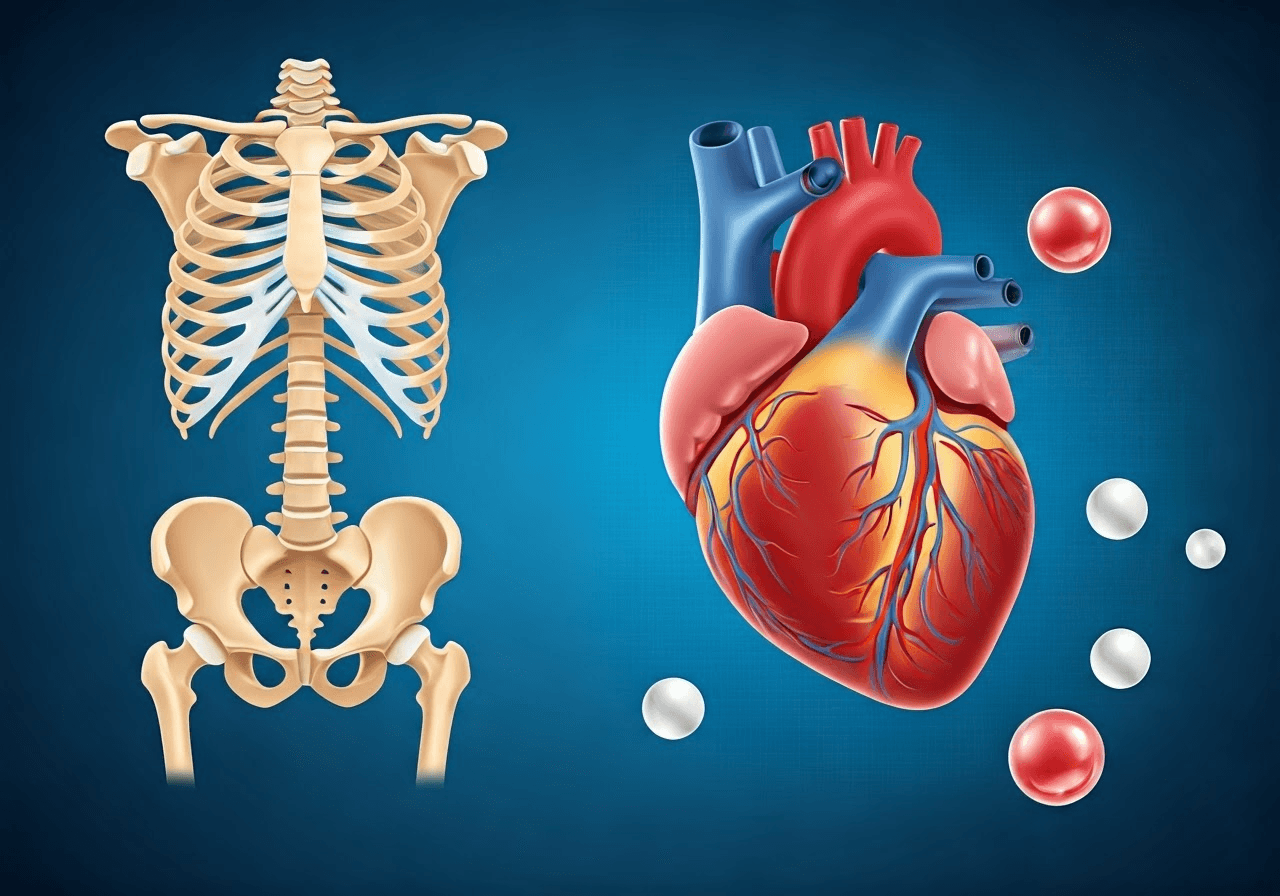
Vitamin K2 is not just important for blood clotting; it also plays a big role in heart and bone health. This vitamin helps guide calcium to the bones, where it is needed, and keeps it away from the arteries, where it can do harm. Because of this, vitamin K2 is a key part of good health.
The benefits of vitamin K2 go even further. Let’s look at how this powerful nutrient supports many health benefits, helping you stay healthy from your bones to your brain.
Bone Health: Vitamin K2 for Osteoporosis Prevention
Strong bones need more than just calcium. Calcium helps build your bones, but vitamin K2 plays a key role. It ensures that calcium is used properly in your body.
Vitamin K2 activates a protein called osteocalcin, which comes from special cells called osteoblasts that build bones. Once activated, osteocalcin pulls calcium from your blood. This helps make bones denser and stronger.
This is especially important for postmenopausal women. They often lose bone mass faster because of hormone changes. Getting enough vitamin K2 can slow this process down. It may lower the risk of fractures and help maintain good bone health.
Heart Health: Vitamin K2 for Cardiovascular Protection
Heart disease is still one of the top causes of death around the world. This makes it very important to use preventive measures. While diet and exercise are vital, vitamin K2 is becoming more recognized for its role in heart health.
Vitamin K2 helps prevent arterial calcification. It activates a protein called matrix GLA protein (MGP), which stops calcium from building up on the walls of arteries. This keeps the arteries flexible and helps blood flow easily.
When arteries are less stiff, there is a lower chance of cardiovascular events like heart attacks and strokes. More research is needed, but the potential of vitamin K2 for heart health looks very promising.
Dental Health: Vitamin K2 Benefits for Teeth & Gums
Vitamin K2 is very important for dental health, just like it is for bones. It helps teeth stay strong by promoting the mineralization of dentin, the tough tissue under tooth enamel.
Osteocalcin, which gets activated by vitamin K2, is key in this process. It helps put minerals into teeth, making them denser and stronger. This mineralization helps prevent cavities, reduces tooth sensitivity, and keeps your mouth healthy overall.
While it’s important to keep up good oral hygiene, having enough vitamin K2 in your diet or through supplements can help you have strong and healthy teeth.
Brain Function: Vitamin K2 for Cognitive & Brain Health
Emerging research shows that vitamin K2 might help with brain health and cognitive impairment, although scientists are still looking into how it works. Some studies suggest that K2 could protect against memory loss as we get older and may support healthy brain function.
One idea is that vitamin K2 affects sphingolipids, which are fats found in the brain. These fats are important for how brain cells communicate and for overall brain health.
While more research is needed to clearly understand how vitamin K2 links to brain function, the current evidence points to a possible connection between having enough K2 and keeping our cognitive health as we age.
Skin & Anti-Aging: Vitamin K2 for Youthful Skin
The exact role of vitamin K2 in skin health is still a topic of discussion. However, there are some interesting signs that it could help keep skin looking young and support healthy aging.
Some people think that vitamin K2 helps make collagen. Collagen is a protein that keeps skin firm and stretchy. Unfortunately, we produce less collagen as we get older, which can lead to wrinkles and droopy skin.
More studies are needed to see if vitamin K2 really helps skin health. Still, getting enough vitamin K2 from what you eat or from supplements might be good for your overall health and could include benefits for your skin.
Top Food Sources of Vitamin K2: Animal, Plant & Fermented

Are you ready to increase your vitamin K2 levels? Good news! You can add this important nutrient to your diet without making big changes. Many tasty and easy-to-find foods are full of vitamin K2.
The trick is to mix different foods in your meals to get the best amount and enjoy all the benefits this nutrient offers. Let’s look at the best food sources of vitamin K2, organized into categories for you.
Fermented Foods Rich in Vitamin K2 (Natto, Cheese & More)
Fermented foods are great sources of Vitamin K2. Foods like natto, sauerkraut, and some cheeses provide a lot of this important vitamin. Adding fermented foods to your meals can really help your overall health, especially for your bones and heart health. By choosing these tasty and healthy foods, you can naturally raise your vitamin K2 levels and enjoy the benefits it brings.
The table below highlights the top fermented foods highest in vitamin K2, their key nutrients, and simple tips for adding them to your diet.
| Food Source | Approx. Vitamin K2 Content (per 100g) | Type of K2 | Other Notable Nutrients / Benefits | Tips for Consumption / Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natto (fermented soybeans) | ~900–1100 mcg | MK-7 | Protein, probiotics, iron, calcium | Most concentrated K2 source; strong flavor; traditional Japanese breakfast |
| Hard Cheeses (Gouda, Edam) | ~60–80 mcg | MK-4, MK-7 | Calcium, protein, vitamin B12 | Aged cheeses higher in K2; eat in moderation due to fat/sodium content |
| Soft Cheeses (Brie, Camembert) | ~40–50 mcg | MK-4, MK-7 | Calcium, protein, vitamin B12 | Milder flavor; enjoy with fruit or whole-grain bread |
| Sauerkraut (fermented cabbage) | ~4–5 mcg | MK-7 | Vitamin C, fiber, probiotics | Go for unpasteurized varieties for probiotic benefits |
| Kimchi (fermented vegetables) | ~3–5 mcg | MK-7 | Vitamins A & C, fiber, probiotics, antioxidants | Choose raw/fermented kimchi; use as side dish or topping |
| Fermented Soybean Paste (Miso) | ~2–8 mcg | MK-7 | Protein, manganese, copper, probiotics | Adds umami to soups and dressings; high sodium; use in moderation |
| Yogurt (fermented milk, full-fat) | ~1–4 mcg | MK-4 | Protein, calcium, probiotics | Look for full-fat, traditionally fermented varieties for higher K2 |
| Kefir (fermented milk) | ~1–3 mcg | MK-4 | Protein, calcium, probiotics | Drink plain or use in smoothies; choose live culture versions |
Animal-Based Vitamin K2: Meat, Dairy & Eggs Sources
Animal-based foods like meat, dairy, and eggs are good sources of Vitamin K2. They offer a form of the vitamin that your body can easily absorb. This supports bone health and helps your heart. Eating these foods can help you keep the right Vitamin K2 levels. This is important for stopping arterial calcification and improving your health. But, you should also eat different healthy foods. This will help you have a balanced dietary intake. Including these animal-based sources carefully can really boost your Vitamin K2 levels.
The table below lists the top animal-based sources of vitamin K2, their key nutrients, and simple tips for adding them to your diet.
| Food Source | Approx. Vitamin K2 Content (per 100g) | Type of K2 | Other Notable Nutrients / Benefits | Tips for Consumption / Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Goose Liver | 370–800 mcg | MK-4 | Vitamin A, iron, protein | Very high K2; eat in moderation due to high cholesterol and vitamin A |
| Hard Cheeses (Gouda, Edam) | 60–80 mcg | MK-4, MK-7 | Calcium, protein, vitamin B12 | Aged cheeses are richest; eat in moderation |
| Chicken Liver | 60–90 mcg | MK-4 | Protein, iron, vitamin A, B vitamins | Nutrient-dense; best cooked and eaten occasionally |
| Soft Cheeses (Brie, Camembert) | 40–50 mcg | MK-4, MK-7 | Calcium, protein, vitamin B12 | Milder flavor; great with fruit or whole-grain bread |
| Pork (various cuts, especially organ meats) | 20–40 mcg | MK-4 | Protein, B vitamins, zinc | Most K2 in organ meats; choose lean cuts for less fat |
| Chicken (thigh, leg) | 8–13 mcg | MK-4 | Protein, B vitamins, selenium | Dark meat has more K2 than white; skinless is lower in fat |
| Egg Yolk | 6–32 mcg | MK-4 | Protein, vitamin D, choline, healthy fats | Eat cooked; use in salads, sandwiches, or as breakfast |
| Butter (cow’s milk) | 15 mcg | MK-4 | Vitamin A, saturated fat, vitamin D | Use sparingly; high in fat and calories |
| Whole Milk (cow’s) | 1–4 mcg | MK-4 | Calcium, protein, vitamin D, B vitamins | Choose whole or full-fat for slightly more K2; keep portions moderate |
| Yogurt (full-fat) | 1–4 mcg | MK-4 | Protein, calcium, probiotics | Go for full-fat, traditionally fermented for highest K2 |
Plant-Based Vitamin K2 Sources: Vegan-Friendly Options
Plant-based foods that have Vitamin K2 are natto, fermented soybeans, some cheeses like brie and gouda, sauerkraut, and miso. These foods give you a vegan-friendly way to add Vitamin K2 to your diet.
The table below highlights the main plant-based sources of vitamin K2, their nutritional benefits, and easy ways to include them in your diet.
| Food Source | Approx. Vitamin K2 Content (per 100g) | Type of K2 | Other Notable Nutrients / Benefits | Tips for Consumption / Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natto (fermented soybeans) | 900–1100 mcg | MK-7 | Protein, probiotics, iron, calcium | Most concentrated K2 source; strong flavor; traditional in Japan |
| Sauerkraut (fermented cabbage) | 4–5 mcg | MK-7 | Vitamin C, fiber, probiotics | Choose unpasteurized for maximum benefit |
| Kimchi (fermented vegetables) | 3–5 mcg | MK-7 | Vitamins A & C, fiber, probiotics | Use as a side dish or topping |
| Fermented Soybean Paste (Miso) | 2–8 mcg | MK-7 | Protein, manganese, copper, probiotics | Adds umami to soups; high in sodium; use in moderation |
| Tempeh (fermented soybeans) | 1–4 mcg | MK-7 | Protein, iron, probiotics, fiber | Great in stir-fries and salads; choose traditionally fermented |
Vitamin K2 Deficiency: Symptoms & How to Restore Levels

Severe vitamin K2 deficiency is not very common, but many people have low levels, mainly because today’s Western diet lacks foods high in K2. It is important to recognize the signs of this deficiency and to find ways to raise your levels.
The good news is that fixing vitamin K2 deficiency can be easy. You can often do it with some smart changes in your diet or by taking a good-quality supplement. Let’s look at the symptoms of deficiency and some helpful ways to bring your levels back to normal.
Vitamin K2 Deficiency Symptoms: What to Watch For
Vitamin K2 deficiency often doesn’t show clear signs. But it is important for blood clotting and calcium processes, so some signs could suggest low levels.
Easy bruising or bleeding can be a sign of trouble with blood clotting and might hint at low vitamin K2. This symptom can come from different causes, but it is good to think about vitamin K2 levels, especially if there are other risk factors.
When there is not enough vitamin K2, you might see poor bone quality. This can raise the risk of fractures. Also, calcium getting stuck in soft tissues might happen if vitamin K2 can’t help with calcium use, even if it is not a direct symptom of the deficiency.
How to Increase Vitamin K2: Diet & Supplement Tips
Luckily, you can boost your vitamin K2 levels with changes to your diet and supplements. Starting with foods rich in K2 is a great idea.
Include fermented foods such as natto, sauerkraut, and kefir in your daily meals. If you are not used to their flavor, start with a little bit and slowly add more as you get used to it.
Also, make sure to eat enough vitamin K1-rich foods, like leafy green vegetables. Your body can change some of this into K2. If you find that changing your diet is not enough, vitamin K supplementation can help fill that gap.
Vitamin K2 Deficiency: Signs & Effective Restoration Strategies
Deficiency Symptoms | Description | Strategies to Boost Vitamin K2 |
|---|---|---|
Weak Bones & Osteoporosis Risk | Increased risk of fractures, reduced bone density | Consume fermented foods (natto, cheese) and animal-based sources (egg yolks, liver, butter) |
Arterial Calcification | Hardening of arteries due to improper calcium use | Take MK-7 supplements for long-term heart health and combine K2 with Vitamin D3 |
Tooth Decay & Poor Dental Health | Weak enamel, increased cavities | Eat high-K2 cheeses (Gouda, Brie) and fermented dairy |
Easy Bruising & Bleeding | Impaired blood clotting, frequent bruises | Include leafy greens (for K1) along with K2-rich animal foods |
Joint Pain & Stiffness | Calcium buildup in joints causing pain | Supplement with MK-7 K2 to support calcium metabolism |
Wrinkles & Premature Aging | Reduced skin elasticity due to collagen loss | Increase collagen synthesis by eating Vitamin K2-rich foods |
Brain Fog & Cognitive Issues | Memory problems, difficulty focusing | Include MK-4-rich meats and fatty foods to support brain health |
Vitamin K2 Supplements: How to Choose & Dosage Guide

Vitamin K2 supplements are an easy and helpful way to get more of this vitamin. This is great for those who struggle to get enough from food. Still, it can be hard to choose the right supplement because there are so many options out there.
You need to pick the right type, decide how much to take, and know how it might interact with other things. This way, you can use the supplement safely and effectively. Let’s look at the key points to think about when taking vitamin K2.
Best Time & How to Take Vitamin K2 Supplements
Vitamin K2 supplements come in different forms. You can find them as capsules, soft gels, or liquid drops. The best form for you depends on what you like and how well your body absorbs it.
For dosage, it’s best to ask a healthcare professional. The right amount can change based on your age, health, and vitamin K intake from your diet.
It is usually a good idea to take vitamin K2 supplements with a meal that has fat. This helps your body absorb it better. Also, staying consistent is important for supplementation. Try to have your daily intake as your healthcare provider recommends.
Vitamin K2 Dosage: Recommendations by Age & Health
It’s a good idea to talk to your healthcare provider about the best dosage for you. They can look at your health, any risks, and the medicines you take to find the right amount.
For older adults, a higher dose may help with bone health and lower the risk of fractures. If you have a family history of heart disease or want to improve your heart health, a moderate to high dose of vitamin K2 might be good for your arteries.
Keep in mind that taking more supplements does not always mean better results. It’s important to follow your healthcare provider’s advice and the recommended dose on the label.
Choosing the Best Vitamin K2 Supplement: MK-4 vs MK-7
When choosing the best Vitamin K2 supplement, it is important to know the differences between MK-4 and MK-7. MK-4 has a shorter half-life but might work better in staying in the bloodstream. On the other hand, MK-7 works longer and is used better by the body for bone and heart health. Knowing your health needs and talking to a healthcare provider can help you pick the right form. This will improve your well-being. Being aware of these differences helps you get the most from your Vitamin K2 intake.
Vitamin K2 and D3: Benefits of Combining for Absorption
Vitamins D3 and K2 are like best friends for your health. They work together to help your body absorb and use calcium properly. Vitamin D3 helps you take in calcium from your gut. Then, vitamin K2 makes sure this calcium goes to the right places, like your bones, and away from places where it could be harmful, like your arteries.
This teamwork is very important for bone health. Vitamin D3 pulls in the calcium, while K2 makes sure it becomes part of your bones. This helps increase bone density and can lower the risk of fractures.
Many good-quality supplements have both vitamins D3 and K2 to take full advantage of their combined benefits. It’s a good idea to talk to your healthcare provider. They can help you decide if taking both vitamins is right for your health needs and can improve your well-being.
Who Should Not Take Vitamin K2? Precautions & Contraindications

Vitamin K2 is usually safe and good for most people. However, some folks should be careful or skip it altogether. If you have existing health issues or take certain medications, you should talk to your doctor before starting vitamin K2 supplements.
Doing this can help reduce the chance of any problems. It also makes sure that adding vitamin K2 fits into your health plan. Now, let’s find out which people should be careful with K2 supplementation.
Vitamin K2 Cautions: Health Conditions Requiring Care
People with certain health issues, especially those that affect blood clotting or are using blood-thinning medications, should be careful with vitamin K2.
If you have had kidney disease, heart disease, or if you are likely to get blood clots, it is important to check with your doctor before taking vitamin K2 supplements.
Your healthcare provider can look at your risk factors. They can help you decide if K2 supplements are right for you based on your health and the medicines you take.
Vitamin K2 and Blood Thinners: Medication Interactions
If you are on blood thinners like warfarin (Coumadin), it is very important to talk to your doctor before taking vitamin K2 supplements. Vitamin K helps with blood clotting, and changing how much you take could affect how well your medications work.
Your doctor can check your blood clotting time (INR) and change your medication dose if needed. It’s also important to tell your doctor if you take other medications for things like high blood pressure or high cholesterol before starting vitamin K2 supplements.
Being open with your healthcare provider will help make sure your medicines and supplements work well together. This will reduce the risk of problems and help you meet your health goals.
Comparison Table: Who Should Avoid Vitamin K2 and Why?
Who Should Avoid K2? | Reason for Avoidance | Alternative Approach |
|---|---|---|
People on Blood Thinners (e.g., Warfarin) | Vitamin K2 can interfere with anticoagulant medications | Consult a doctor before taking K2 supplements |
Individuals With Bleeding Disorders | K2 affects blood clotting, which may pose risks | Monitor Vitamin K intake under medical supervision |
Those With Severe Kidney Disease | Impaired kidney function can affect calcium balance | Focus on dietary sources instead of supplements |
People With Hypercalcemia (High Blood Calcium) | K2 influences calcium metabolism, potentially worsening the condition | Avoid high-dose K2 and consult a healthcare provider |
Pregnant or Breastfeeding Women (Without Doctor Approval) | Limited research on high-dose supplementation safety | Get K2 from natural food sources like eggs and dairy |
Individuals With Certain Autoimmune Conditions | Some conditions may alter Vitamin K metabolism | Work with a doctor to determine appropriate intake |
Vitamin K2 Side Effects & Long-Term Safety

Vitamin K2 is usually safe and easy to handle when taken from food sources or supplements at the right amounts. Still, like any supplement, there can be a few side effects, but these are not common.
It’s important to watch for any strange symptoms after you start taking vitamin K2 and to deal with them quickly. Now, let’s look at possible side effects and discuss worries about using vitamin K2 supplements for a long time.
Possible Side Effects of Vitamin K2 Supplements
Vitamin K2 is usually safe for most people. If side effects happen, they are often mild. You might notice some stomach issues, like bloating or diarrhea. These problems usually go away as your body gets used to the supplement.
In rare cases, some people might have an allergic reaction to vitamin K2 supplements. Symptoms can include skin rashes, itching, swelling, or trouble breathing. If you notice any of these symptoms, stop taking the supplement and get medical help right away.
It’s always a good idea to start with a small dose of vitamin K2. You can slowly increase it as your body tolerates it, especially if you’re new to taking supplements.
Vitamin K2 Overdose: Risks, Symptoms & Safety
Overdosing on vitamin K2 from food is very unlikely. But taking too many vitamin K2 supplements can upset the balance of vitamin K in your body.
Though it is rare, high levels of vitamin K can lead to problems, especially if you take blood thinners. Taking more than the recommended amount for a long time may affect blood clotting.
It is important to follow the dosage on the supplement label or what your doctor says. If you think you might have taken too much vitamin K2, please call your doctor or a poison control center right away.
Scientific Studies: Vitamin K2 Long-Term Use & Safety
Several studies show that vitamin K2 is safe to use and is well-received by the body both in the short and long term when taken as suggested. These studies look at how vitamin K2 affects different areas of health, like bone health, cardiovascular health, and cognitive function.
The results keep showing that taking vitamin K2 has good effects without serious side effects. Still, more long-term studies are welcome to strengthen the case for the safety of vitamin K2.
Always talk to your doctor or healthcare provider before you start taking vitamin K2. This way, you can make sure it fits your needs and takes your medical history into account.
Conclusion
Vitamin K2 has many health benefits. It helps improve bone density and supports brain health. It’s important to know the differences between the MK-4 and MK-7 forms to choose the best supplement for you. Adding foods with vitamin K2 to your meals can boost your health. If needed, think about taking a supplement. Always talk to a healthcare professional before starting any new supplements. Explore more about Vitamin K2 to unlock its full potential for your health journey.
The content on WellwayHub.com is intended for general informational purposes only and should not be taken as medical advice. Please consult your doctor or a qualified health professional before making any changes to your health routine.
Some links on WellwayHub.com may be affiliate links. This means we may earn a small commission if you make a purchase through these links, at no extra cost to you. This helps support our mission to provide trusted wellness content.
Frequently Asked Questions
People with cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, or those using blood thinners should talk to their doctor before taking K2. This will help make sure it does not affect their health condition or their medication.
Vitamin K2 is usually safe to take if you follow the instructions. Clinical studies have not found harmful levels with normal amounts. However, it is important to talk to your doctor, especially if you use blood thinners.
Yes, it is safe to take vitamin K2 every day as long as you follow the recommended dose. This habit can help you gain health benefits for your bones, heart, and overall well-being.
Taking vitamin K2 with vitamin D3 is not necessary, but it can improve your health. They work well together. This combination helps bone metabolism and boosts calcium absorption. You will see better results when you take them together.
Yes, taking daily doses of vitamins D3 and K2 is usually safe and helpful for most people. It supports heart health, bone health, and overall well-being.
Clinical trials show that you may need to take vitamin K2 consistently for a few weeks to several months to see important health benefits. This can vary based on individual factors and the specific health outcome being tracked.
Vitamin K2 may not directly cause weight loss, but it affects how our body uses energy and stores fat. This area needs more research to understand its potential better.