
Introduction
While you may not hear about L-cysteine as often as other nutrients, this powerful amino acid is a master key to your body’s defense system. Think of it less as a simple supplement and more as the essential fuel for producing glutathione, your body’s most powerful antioxidant.
In this guide, we’ll unlock the science behind L-cysteine, revealing how it supports everything from liver detoxification to glowing skin and healthy hair. We’ll explore the critical link between L-cysteine, its supplement form NAC, and the all-important glutathione, helping you understand not just what it does, but why it’s so fundamental to your health.
What Exactly is L-Cysteine? Structure and Key Features
L-cysteine is an amino acid. This means it is a basic part of proteins. The structure of L-cysteine has a central carbon atom connected to four different groups. These groups are a carboxyl group (-COOH), an amino group (-NH2), a hydrogen atom (H), and its special side chain.
The side chain is what makes each amino acid different. For L-cysteine, its side chain has a thiol group (-SH). This thiol group contains sulfur and is very reactive. This feature makes L-cysteine special with its own unique traits when compared to other amino acids like threonine.
Cysteine comes in two forms, L-cysteine and D-cysteine. They are mirror images of each other. However, only L-cysteine is active in the body and is used in proteins.
Is L-Cysteine Essential? Understanding Its Semi-Essential Status
Amino acids are classified as essential or nonessential based on whether the body can make them. Essential amino acids cannot be made by the human body and need to come from our diet. In contrast, nonessential amino acids can be produced within the body.
L-cysteine is known as a semi-essential amino acid. The body usually makes enough L-cysteine from the essential amino acid methionine, during which homocysteine is formed. However, during times of illness, stress, or when there isn’t enough methionine in the diet, L-cysteine may become conditionally essential.
In these cases, the body might need more L-cysteine than it can produce. So, it is important to get enough L-cysteine from food or through supplementation. This is crucial for staying healthy, particularly when the body needs more.
How Does L-Cysteine Work in Your Body?
L-cysteine is important for our bodies. It helps keep our cells healthy and takes part in important metabolic processes. This shows how essential it is for our overall well-being.
L-cysteine is not only useful on its own. It also helps make other important molecules. For example, it is a precursor for taurine, which is important for heart health and brain function. It also aids in creating coenzyme A, a key part in many enzyme processes.
L-Cysteine’s Crucial Role in Protein Formation
L-cysteine is an amino acid that is very important for making proteins. During this process, cells use ribosomes to link amino acids together in a certain order based on genetic information. This creates long chains called polypeptides. These chains then fold into unique 3D shapes to form functional proteins.
L-cysteine is special because it can create disulfide bridges through disulfide bonds. These strong bonds happen between the thiol groups of two cysteine residues. This can occur within the same chain or in different chains. Disulfide bonds help keep proteins stable and properly shaped.
These bonds are very important for many proteins, including keratin. Keratin is a protein found in skin, hair, and nails. It depends on disulfide bonds to maintain its strength and resilience.
The Glutathione Pathway: L-Cysteine’s Most Important Job
L-cysteine is important not just for making proteins. It is also a key starter for the synthesis of glutathione, which is a very important antioxidant that our bodies produce. Glutathione is made up of three parts: cysteine, glycine, and glutamic acid. It helps protect our cells from damage caused by free radicals.
Free radicals are active molecules that our bodies create during normal processes and when we come into contact with toxins in the environment. These molecules can harm DNA, proteins, and cell membranes. This damage can contribute to aging and lead to chronic diseases.
Glutathione works as a strong fighter against free radicals. It helps to neutralize them and stop cell damage. Since L-cysteine helps make glutathione, it is important to keep enough of this essential antioxidant in our bodies.
From L-Cysteine to NAC: Creating a More Stable Supplement
While L-cysteine is found in food, for supplementation purposes, it’s often converted into a more stable and better-absorbed form called N-Acetylcysteine (NAC). When you take an NAC supplement, you are essentially providing your body with a highly effective form of cysteine, ready to be used for one primary purpose: boosting glutathione levels. This is why NAC is so widely used in both medical settings and for general wellness.
Fighting Oxidative Stress: L-Cysteine’s Antioxidant Benefits
L-cysteine plays an important role in the body’s antioxidant defense system. This system helps fight against the harmful effects of oxidative stress. Oxidative stress happens when there are too many free radicals and not enough antioxidants to neutralize them.
As noted before, L-cysteine helps make glutathione. Glutathione is one of the body’s strongest antioxidants. It goes after free radicals, stopping them from harming cell parts.
Additionally, L-cysteine has its own antioxidant properties. It fights off free radicals like hydroxyl radicals and superoxide radicals. By reducing the harm caused by these harmful substances, L-cysteine helps keep cells safe from oxidative stress.
Top Health Benefits of L-Cysteine
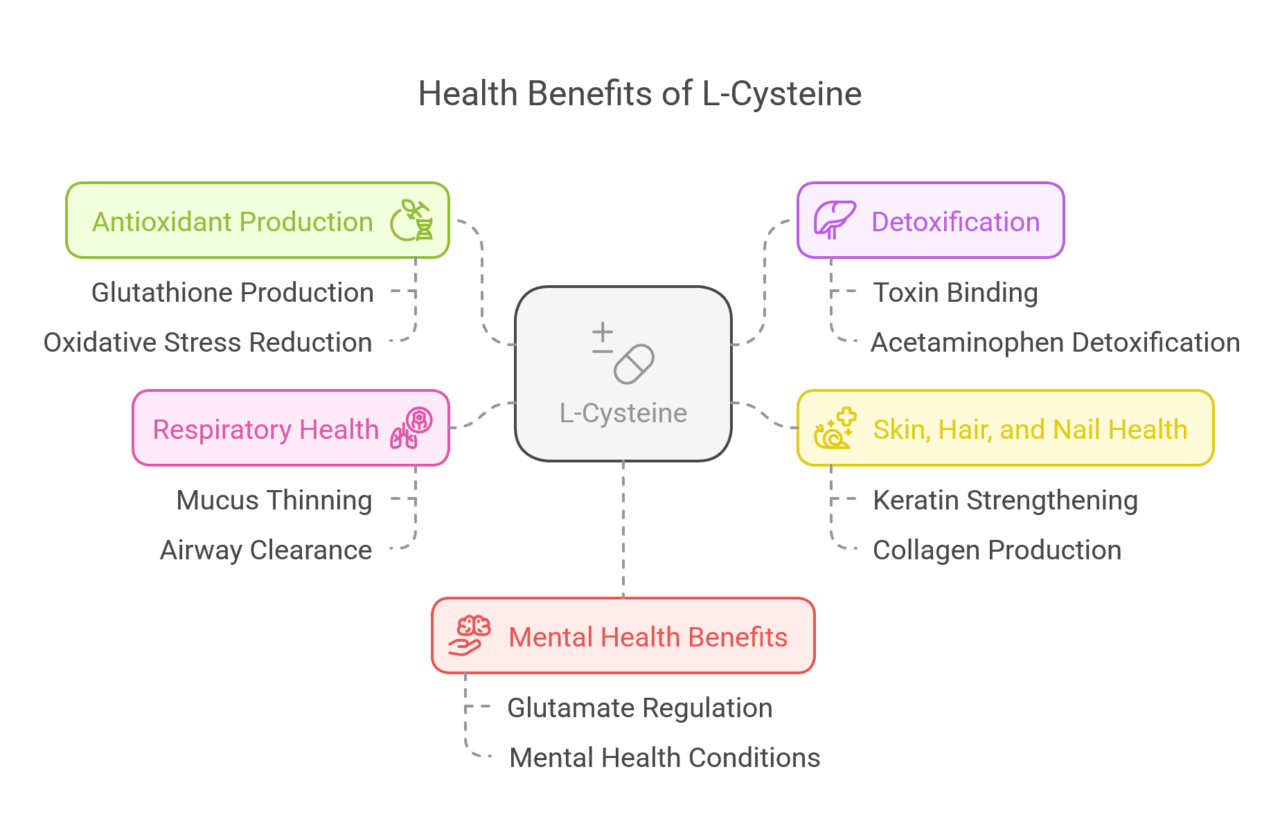
L-cysteine has many health benefits. This is mainly because it helps produce glutathione. It also plays a key part in protecting the body from damage caused by free radicals.
The many positive effects of L-cysteine make it a great nutrient to think about adding to your diet or supplement plans.
Boosts Antioxidant Production
L-cysteine is known for its strong health benefits. It helps boost antioxidant levels in the body. This amino acid is important because it is a key part of making glutathione. A study conducted in Europe highlighted that glutathione is often called the “master antioxidant” because it helps keep our cells balanced.
Glutathione works by neutralizing many free radicals. This protects cells from oxidative stress and the harm it can cause. Oxidative stress can lead to many chronic diseases like heart problems, cancer, brain disorders, and faster aging.
By increasing glutathione levels, L-cysteine helps the body defend against oxidative damage. This may lower the chance of these chronic diseases and support better health and a longer life.
Supports Detoxification
L-cysteine is very important for helping the body remove toxins. It mainly does this in the liver, which is the main organ for detoxification. The liver filters out toxins, drugs, and waste products from the blood. It changes them into less harmful substances that can be removed from the body.
Glutathione, which is made from L-cysteine, plays a key role in detoxifying the liver. It binds to toxins, making them easier to dissolve in water and remove from the body.
N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC) is a form of L-cysteine. It is well-known for restoring glutathione levels in the liver, especially during acetaminophen poisoning. NAC helps the liver detoxify N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine (NAPQI), a harmful substance from acetaminophen, which protects the liver from damage.
Enhances Skin, Hair, and Nail Health
Keratin is the main protein found in skin, hair, and nails. It depends a lot on L-cysteine to stay strong and healthy. L-cysteine can make special bonds, which help connect the keratin fibers. This connection makes a strong and tough protein structure.
This strength is important to keep skin healthy, help hair grow, and make nails stronger. Here are some ways L-cysteine can improve skin, hair, and nail health:
- Promotes Hair Growth: L-cysteine is an important part of hair follicles and helps with hair growth. Taking L-cysteine may boost hair growth and reduce hair loss.
- Supports Skin Elasticity: L-cysteine helps produce collagen, which gives skin its shape and bounce. Having enough L-cysteine is good for keeping skin looking youthful and healthy.
Benefits for Respiratory Health
L-cysteine, especially its form N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC), is known for its ability to help with mucus. This amino acid can thin and clear mucus in the airways. It can be very helpful for people who have respiratory issues that cause a lot of mucus.
NAC works well to promote mucus clearance because it breaks down bonds in mucus proteins. This action makes the mucus less thick and sticky. Because of this, it becomes easier to cough up and clear out of the airways. NAC is often used as a treatment for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), bronchitis, and other problems related to breathing.
Potential Mental Health Benefits
Emerging studies show that L-cysteine could have benefits for mental health. This is especially because of its antioxidant and neuroprotective effects. Still, more research is needed to understand these benefits fully.
One interesting area is how L-cysteine may influence glutamate levels in the brain. Glutamate is a neurotransmitter that helps with learning, memory, and other brain functions. Problems with glutamate signaling can lead to different mental health issues, like schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and addiction, as highlighted in various PMC articles.
Some studies suggest that L-cysteine might help keep glutamate levels in check. This could play a role in managing these conditions. However, it’s crucial to remember that this research is still in its early stages. More clinical trials are needed to support these findings.
Table: Health Benefits vs. Potential Risks of L-Cysteine
| Health Benefits | Potential Risks |
|---|---|
| Boosts Antioxidant Levels – Supports glutathione production to fight oxidative stress | Toxicity at High Doses – Can lead to sulfur buildup and potential liver damage |
| Supports Detoxification – Aids liver in removing harmful substances | Gastrointestinal Issues – May cause nausea, cramps, or diarrhea in some users |
| Enhances Skin, Hair & Nails – Key for keratin structure and collagen production | Contraindicated in Cystinuria – Can increase risk of kidney stones |
| Improves Respiratory Health – NAC form helps thin and clear mucus | Drug Interactions – May affect blood thinners or diabetes medications |
| May Support Mental Health – Investigated for neuroprotection and glutamate balance | Limited Safety Data in Pregnancy/Breastfeeding – Use only with medical advice |
Best Food Sources Rich in L-Cysteine
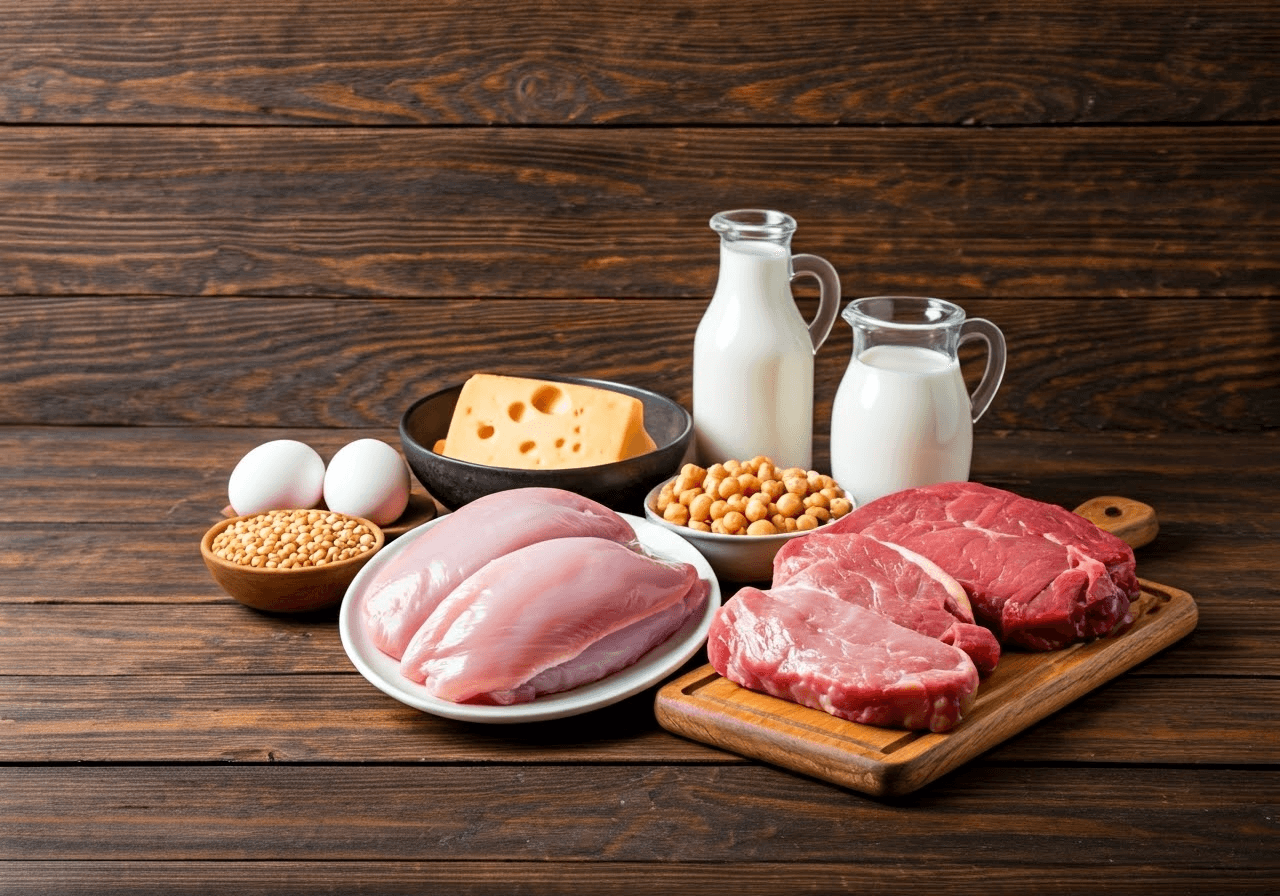

L-cysteine is found in many foods, both from animals and plants. Animal-based foods usually have more L-cysteine. They are also easier for the body to absorb and use.
People who eat vegetarian or vegan diets should be careful about getting enough L-cysteine from plant sources. They might need to think about supplementation to make sure they have enough of this amino acid.
Table: Animal-Based vs Plant-Based Comparison
| Aspect | Animal-Based Sources | Plant-Based Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Examples | Chicken, turkey, beef, pork, eggs, dairy (milk, cheese, yogurt) | Lentils, chickpeas, sunflower seeds, almonds, oats, soybeans |
| Protein Content | High – Complete proteins containing all essential amino acids | Moderate to high – Often incomplete, missing one or more essential amino acids |
| L-Cysteine Content | Rich – Naturally abundant in animal proteins | Moderate – Varies; usually lower than in animal sources |
| Bioavailability | Higher – Easier for the body to digest and absorb L-cysteine | Lower – Plant cell walls may reduce absorption efficiency |
| Best Food Forms | Grilled or roasted meats, boiled eggs, full-fat dairy | Cooked legumes, sprouted seeds, fermented soy (e.g., tempeh) |
| Diet Suitability | Ideal for omnivores and those without dietary restrictions | Essential for vegetarians and vegans; may need to combine multiple sources |
| Supplementation Need | Less likely unless under stress, illness, or restricted diet | More likely to require supplementation, especially in vegan diets |
| Cooking Tips | Avoid overcooking to preserve amino acids | Soak or sprout seeds and legumes to improve bioavailability |
Top Animal-Based Foods High in L-Cysteine
High-protein foods from animals have a lot of L-cysteine. Adding these foods to your meals can help you get enough L-cysteine.
- Poultry: Chicken, turkey, and other poultry are great sources of L-cysteine.
- Meat: Beef, pork, and other red meats also have significant amounts of L-cysteine.
- Eggs: Whole eggs, especially the yolks, are a good source of this amino acid.
- Dairy Products: Milk, cheese, and yogurt help increase your L-cysteine intake.
Eating different types of these protein-rich animal foods in your meals makes sure your body gets a steady supply of L-cysteine.
Best Plant-Based Sources of L-Cysteine for Vegans
While plant-based foods have less L-cysteine than animal foods, they can still help you get enough in your diet:
- Legumes: Lentils, beans, and peas are great sources of L-cysteine. They are helpful for vegetarian and vegan diets.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, sunflower seeds, and pumpkin seeds also provide L-cysteine. Plus, they offer healthy fats and other important nutrients.
By combining these plant-based sources, you can make sure you get enough L-cysteine. This is important for those who live a vegetarian or vegan lifestyle. Besides whole foods, you can also find L-cysteine in dietary supplements. This can help people who find it hard to meet their needs through their diet alone.
Table: Comparison of L-Cysteine Content in Various Foods
| Food Source | Category | Serving Size | L-Cysteine Content (mg) | Absorption Efficiency | Serving Suggestions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chicken Breast | Animal-Based | 100 g (cooked) | 571 mg | High | Grilled, baked, or added to salads and sandwiches. |
| Lentils | Plant-Based | 1 cup (198 g) | 234 mg | Moderate | Soups, stews, salads, or as a meat substitute in various dishes. |
| Sunflower Seeds | Plant-Based | 1 oz (28.35 g) | 109 mg | Moderate | Snacks, toppings for salads and yogurts, or incorporated into baked goods. |
| Almonds | Plant-Based | 1 oz (28.35 g) | 65 mg | Moderate | Snacks, almond butter, or added to cereals and desserts. |
| Soybeans (Edamame) | Plant-Based | 1 cup (155 g) | 482 mg | Moderate | Steamed, added to salads, stir-fries, or as a side dish. |
| Eggs | Animal-Based | 1 large (50 g) | 146 mg | High | Boiled, scrambled, or used in various recipes. |
| Oatmeal | Plant-Based | 1 cup (234 g) | 227 mg | Moderate | Breakfast porridge, smoothies, or used in baking. |
Medical Applications of L-Cysteine & NAC Supplements

L-cysteine is an important nutrient. Its form, N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC), is used in many medical ways. NAC has antioxidant and mucolytic properties. This makes it helpful for different health issues.
Many doctors choose NAC instead of L-cysteine for treatments. This is because NAC is easier for the body to absorb and can treat more conditions effectively.
N-Acetylcysteine (NAC) in Acetaminophen Overdose (Detoxifying Benefits)
N-acetylcysteine (NAC) is very important in cases of acetaminophen poisoning. It helps raise glutathione levels and reduces oxidative stress in the body. In the United States, NAC is approved for drug administration to handle acetaminophen overdoses effectively. Clinical trials show it can prevent liver damage and lower the chances of adverse reactions. NAC acts as a precursor to glutathione, which detoxifies the body and lessens the harmful effects of acetaminophen poisoning.
Medical Use of NAC for Chronic Respiratory Conditions
NAC is often used to treat long-term breathing problems, especially when there is too much mucus. This includes conditions like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and bronchitis.
As a mucolytic agent, NAC makes mucus thinner and easier to clear from the airways. This helps improve airflow and makes breathing easier.
NAC works by breaking down certain bonds in mucus proteins, which makes the mucus less thick. This change helps get rid of the sticky mucus by coughing it out. Additionally, NAC also has antioxidant benefits that may protect lung tissue from damage caused by inflammation in COPD.
Investigational Uses of NAC for Psychiatric Disorders
Emerging research is looking at how NAC might help in treating different mental health issues. Although this is still in the early stage, clinical trials show that NAC could be useful because of its antioxidant and neuroprotective effects. It may help with problems like addiction, depression, and schizophrenia.
NAC might aid in treating addiction by affecting glutamate levels in the brain. Glutamate is a type of neurotransmitter that can influence addiction and the desire for drugs.
By changing the way glutamate works, NAC may lessen cravings and withdrawal symptoms. This could help people recover from addiction. However, more studies, especially larger clinical trials, are needed to support these early results and develop the best treatment plans.
L-Cysteine vs NAC: What’s the Difference and Which is Better?
L-Cysteine and N-Acetylcysteine (NAC) are different in how they work. L-Cysteine is an essential amino acid. It is important for making proteins and helping with antioxidant defense. NAC is a precursor for making glutathione, which is vital for the body. It is often used when someone has acetaminophen poisoning because it helps to quickly boost glutathione levels. NAC can also help in reducing oxidative stress and treating some lung issues. Knowing how L-Cysteine and NAC work can help in using them well in healthcare and supplementation.
| Feature | L-Cysteine | N-Acetylcysteine (NAC) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Form | Naturally occurring amino acid | Acetylated form of L-Cysteine |
| Bioavailability | Moderate; can be affected by digestion | Higher bioavailability; better absorbed in the body |
| Primary Function | Protein synthesis, antioxidant precursor (glutathione), supports skin, hair, and nails | Boosts glutathione levels directly, acts as antioxidant, mucolytic agent |
| Supplement Form | Capsules, powders, tablets | Capsules, powders, IV (in medical use) |
| Medical Uses | General wellness, antioxidant support, skin/hair health | Acetaminophen overdose, COPD, bronchitis, psychiatric conditions (investigational) |
| Onset of Action | Gradual – needs conversion to glutathione | Fast – directly increases glutathione |
| Safety in High Doses | Risk of sulfur buildup and toxicity if overdosed | Generally well-tolerated; used in hospitals under supervision |
| FDA Approval | As dietary supplement | Approved for medical use (e.g., acetaminophen overdose treatment) |
| Best Use Case | General antioxidant support, beauty, mild detox | Acute detox, respiratory issues, clinical antioxidant therapy |
L-Cysteine Side Effects: What You Need to Know Before Supplementing

L-cysteine is usually safe to consume through food or when taken as advised. However, some people might have side effects from L-cysteine supplements. It is important to be careful when using L-cysteine. Always talk to a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement, especially if you have health issues or are on medication.
Common Adverse Effects
Most bad reactions to L-cysteine supplements are mild and go away quickly. They usually get better on their own or with changing the dose. It’s still important to know about these side effects and to see a doctor if they last or become worse.
Some common side effects of L-cysteine supplements are:
- Gastrointestinal Upset: People can feel nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and stomach cramps.
- Headache: Some people might get headaches after taking L-cysteine.
It is a good idea to start with a lower dose and slowly increase it if you can handle it. Taking L-cysteine supplements with food might also help lessen stomach issues.
Toxicity at High Doses
L-cysteine is usually safe when taken in the right amounts. However, taking too much can be harmful. This happens because L-cysteine breaks down in the body into different sulfur-based compounds.
If someone takes a lot of L-cysteine, it can stress the body’s ability to process it. This can cause sulfur-containing substances to build up, which may be toxic.
Signs of L-cysteine toxicity can include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, stomach pain, liver damage, and issues with the nervous system. It’s very important to follow the dosage recommendations and talk to a healthcare professional before taking more.
Contraindications and Precautions
Some people should be careful or avoid taking L-cysteine supplements because of possible risks.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: There is not enough safety information on using L-cysteine during pregnancy and breastfeeding. It is better to skip supplementation unless your healthcare provider says otherwise.
- Cystinuria: Cystinuria is a rare genetic issue where the body struggles to process cysteine and leads to cystine stones in the kidneys. People with cystinuria should stay away from L-cysteine supplements, as they may worsen the problem.
Before starting any new supplement, it is important to talk about possible interactions with your doctor.
How Much L-Cysteine Should You Take Daily? (Dosage & Safety Tips)

Finding the right dose of L-cysteine depends on some factors. These include your health, what you eat, and why you want to take it as a supplement. It is a good idea to talk to a healthcare professional. They can help you find a safe dose that fits your needs.
You should also get L-cysteine from trusted makers. They should follow good manufacturing practices (GMP) to make sure the quality and purity are good.
General Dosage Guidelines
It is important to know that dosage guidelines can change based on personal needs. Always follow the instructions on the product label. It’s a good idea to check with a healthcare professional about the right dosage for you.
Typical doses of L-cysteine supplements are between 500 and 1000 milligrams (mg) each day. This can be split into two or three smaller doses. However, some people might need more or less based on their health needs or advice from their healthcare provider.
L-cysteine supplements come in different forms like capsules, tablets, and powders. This gives you options on how to take them.
Considerations for Specific Populations
When thinking about taking L-cysteine supplements for certain groups of people, like pregnant women, breastfeeding moms, children, older adults, or those with health issues, it is important to be careful.
- Pregnant and Breastfeeding Women: There is not enough safety data, so L-cysteine supplements are usually not recommended for pregnant or breastfeeding women unless a healthcare professional says it is okay.
- Children: Parents should only think about L-cysteine supplements for children if a pediatrician or a qualified healthcare provider gives advice on the right dosage based on the child’s age, weight, and health.
- Older Adults: Although L-cysteine supplements could help older adults, especially with antioxidant support and immune function, it is best to start with a lower dose and watch for any side effects.
Interactions with Other Medications
L-cysteine supplements may interact with some medicines. This is especially true for those processed by the liver or those that influence blood sugar.
If you are taking medications for diabetes, blood pressure, or blood clotting, be careful. It’s important to talk to your healthcare provider before using L-cysteine.
Make sure to tell your healthcare professional about all the medicines, supplements, and herbs you are currently using. They can check for possible interactions and give advice on whether L-cysteine supplementation is a good choice for you.
| Medication Class | Potential Interaction | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Anticoagulants / Antiplatelets | May increase bleeding risk due to mild blood-thinning properties | Monitor for bruising or bleeding; consult a doctor before use |
| Antihypertensives | Could enhance blood pressure-lowering effects | Check blood pressure regularly; dosage adjustments may be necessary |
| Antidiabetic Medications | May affect blood sugar regulation or mask hypoglycemia | Monitor blood glucose closely; consult a healthcare provider |
| Chemotherapy Agents | NAC form may reduce toxicity but potentially lower chemotherapy effectiveness | Use only under oncology supervision |
| Vasodilators (e.g., Nitroglycerin) | May cause excessive vasodilation, leading to low blood pressure and severe headaches | Avoid combination unless medically advised |
| Activated Charcoal | May interfere with L-Cysteine/NAC absorption if taken together | Space doses apart by several hours |
| Aminoglycoside Antibiotics | NAC might protect kidneys, but interactions are not fully understood | Use under medical supervision if needed |
| Immunosuppressants | Theoretical risk of immune system modulation | Monitor immune markers; consult with a specialist |
Important: Always consult with a healthcare professional before beginning L-Cysteine or NAC supplements, particularly if you are on prescription medications or managing chronic health issues.
Conclusion
In conclusion, L-Cysteine is important for many body functions and has many health benefits. It helps increase antioxidant levels, supports detox, and improves the health of skin, hair, and nails. It has possible medical uses and might help with mental health too. However, it is important to be careful about side effects and risks, especially with high doses. It is a good idea to talk to a healthcare provider about how much to take, the use of supplements, and safety. This helps consider personal needs and any interactions with other medications. Knowing both the benefits and risks of L-Cysteine supplementation is essential for using it effectively for better health.
The content on WellwayHub.com is intended for general informational purposes only and should not be taken as medical advice. Please consult your doctor or a qualified health professional before making any changes to your health routine.
Some links on WellwayHub.com may be affiliate links. This means we may earn a small commission if you make a purchase through these links, at no extra cost to you. This helps support our mission to provide trusted wellness content.
Frequently Asked Questions
Taking L-cysteine every day can be safe, but it depends on how much you take and your health. Recommended amounts are usually fine, but it’s best to talk to your doctor. They can help you find the right daily dose for you.
Daily recommendations for L-cysteine can change depending on your health needs and why you are taking the supplement. It’s best to talk to a healthcare professional for advice tailored to you.
To absorb L-cysteine supplements the best, you can take them with or without food. Just follow the directions on the product label or listen to your healthcare professional.
L-cysteine supplementation is usually safe when taken in the recommended amounts. However, there may be some risks. These can include stomach upset, headaches, and interactions with specific medications.
L-Cysteine and NAC are linked but they are different. NAC comes from L-cysteine. It has better absorption in the body and works in more areas, which makes it a better choice for medical applications.
Some people say that L-cysteine helps with alcohol detox. But, there is not much scientific evidence to support this claim.
L-cysteine, especially its form NAC, helps the liver. It does this by being a part of glutathione, which is an important antioxidant needed for detoxifying the liver.